COMPARISON OF THREE DNA ISOLATION AND
... pyridinovorans TPIK grown in medium nutrient agar at 370C overnight. The bacteria were suspended in1 ml TE buffer (10mM Tris-HCl, 1 mM EDTA, pH 8).The mixture then centrifugated 1000 rpm for 15 min at 4°C . The pellet was added with 50 µL lysozyme solution and incubated at 370C for 30 min. An amount ...
... pyridinovorans TPIK grown in medium nutrient agar at 370C overnight. The bacteria were suspended in1 ml TE buffer (10mM Tris-HCl, 1 mM EDTA, pH 8).The mixture then centrifugated 1000 rpm for 15 min at 4°C . The pellet was added with 50 µL lysozyme solution and incubated at 370C for 30 min. An amount ...
投影片 1
... • LOD score > 3.0: evidence for linkage. (A score of 3.0 means the likelihood of observing the given pedigree if the two loci are not linked is less than 1 in 1000). • LOD score < -2.0: evidence to exclude linkage ...
... • LOD score > 3.0: evidence for linkage. (A score of 3.0 means the likelihood of observing the given pedigree if the two loci are not linked is less than 1 in 1000). • LOD score < -2.0: evidence to exclude linkage ...
md 2 bbq
... • C. IT NICKS THE dna strands that have formed thymidine dimers • D. it cleaves DNA strands to relax positive supercoils • E. it can remove groups of nucleotides (up to ten) at a time a ...
... • C. IT NICKS THE dna strands that have formed thymidine dimers • D. it cleaves DNA strands to relax positive supercoils • E. it can remove groups of nucleotides (up to ten) at a time a ...
Chapter 12: Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids
... ions in the medium. The result is stronger chargecharge repulsion between the phosphate, which favors strand separation. The unusual bases in tRNA are added by enzymatically modifying specific nucleotide residues in the pre-tRNA molecule. ...
... ions in the medium. The result is stronger chargecharge repulsion between the phosphate, which favors strand separation. The unusual bases in tRNA are added by enzymatically modifying specific nucleotide residues in the pre-tRNA molecule. ...
Document
... 1. The basic subunit of a nucleic acid polymer that consists of a phosphate, pentose sugar and a nitrogenous base is called a ___nucleotide____________. 2. ______continuous____ variation is the condition whereby a seemingly infinite spectrum of phenotypes exist in a population. 3. A mutation of an e ...
... 1. The basic subunit of a nucleic acid polymer that consists of a phosphate, pentose sugar and a nitrogenous base is called a ___nucleotide____________. 2. ______continuous____ variation is the condition whereby a seemingly infinite spectrum of phenotypes exist in a population. 3. A mutation of an e ...
Building with DNA: methods and applications
... Advantages -No restriction enzymes -Very fast and efficient Disadvantages -products likely contain gaps (cannot be used for PCR) -need compatible overhangs missing 1 nucleotide type ...
... Advantages -No restriction enzymes -Very fast and efficient Disadvantages -products likely contain gaps (cannot be used for PCR) -need compatible overhangs missing 1 nucleotide type ...
Polymerase chain reaction
... polymerase, the process they usually describe employs just a single primertemplate complex, and therefore would not lead to the exponential amplification seen in PCR. Also by 1971 Kjell Kleppe, a researcher in Khorana's lab, envisions a process very similar to PCR. At the end of a paper on the earli ...
... polymerase, the process they usually describe employs just a single primertemplate complex, and therefore would not lead to the exponential amplification seen in PCR. Also by 1971 Kjell Kleppe, a researcher in Khorana's lab, envisions a process very similar to PCR. At the end of a paper on the earli ...
Chapter 12: Genetic Engineering
... Genetic engineering could not have come about without the development of a ______________________________ to support the process o A way to carefully _________________________ containing the gene away from the genes surrounding it o Find a way to ________________________________ with a piece of DNA ...
... Genetic engineering could not have come about without the development of a ______________________________ to support the process o A way to carefully _________________________ containing the gene away from the genes surrounding it o Find a way to ________________________________ with a piece of DNA ...
MCD – Genetics 4 - Prenatal diagnosis of genetic diseases Anil
... 4. Describe the use of PCR for mutation detection with examples PCR involves the use of DNA primer to amplify a specific small region of the genome. DNA in this region can then be analysed for mutations. Advantages of PCR: - very little DNA needed – 1 cell - very fast – 1 day - can be automate ...
... 4. Describe the use of PCR for mutation detection with examples PCR involves the use of DNA primer to amplify a specific small region of the genome. DNA in this region can then be analysed for mutations. Advantages of PCR: - very little DNA needed – 1 cell - very fast – 1 day - can be automate ...
Genetic Engineering
... • Gel Electrophoresis uses electricity • Separates based on size! – HA! Again! – Size (and shape) are SOOOOO important! ...
... • Gel Electrophoresis uses electricity • Separates based on size! – HA! Again! – Size (and shape) are SOOOOO important! ...
SNPGray
... First to show how whole-genome sequencing can be used to identify the genetic cause of an individual's disease. "I have hundreds of thousands of differences from all the other genomes that have been sequenced. I expect that to hold true for others. Everyone is truly unique.” ...
... First to show how whole-genome sequencing can be used to identify the genetic cause of an individual's disease. "I have hundreds of thousands of differences from all the other genomes that have been sequenced. I expect that to hold true for others. Everyone is truly unique.” ...
PPT
... used a fuel DNA strands acting as a hybridization catalyst to generate a sequence of motions in another tweezers strand of DNA extended this technique to be DNA sequence dependant the two strands of DNA bind and unbind with the overhangs to alternately open and shut the tweezers. ...
... used a fuel DNA strands acting as a hybridization catalyst to generate a sequence of motions in another tweezers strand of DNA extended this technique to be DNA sequence dependant the two strands of DNA bind and unbind with the overhangs to alternately open and shut the tweezers. ...
Reg Bio DNA tech 2013 ppt
... The sequence of chromosome 1 took an international team of 150 scientists 10 years to complete. ...
... The sequence of chromosome 1 took an international team of 150 scientists 10 years to complete. ...
IRAP (interretroelement amplified polymorphism)
... The plant nuclear genome consists of DNA divided among the chromosomes within the cell nucleus. Plant genomes contain coding and regulatory sequences for the genes and repetitive DNA (see Heslop-Harrison and Schmidt, Plant Nuclear Genomes, Encyclopaedia of Life Sciences 2007). Genomes are evolutiona ...
... The plant nuclear genome consists of DNA divided among the chromosomes within the cell nucleus. Plant genomes contain coding and regulatory sequences for the genes and repetitive DNA (see Heslop-Harrison and Schmidt, Plant Nuclear Genomes, Encyclopaedia of Life Sciences 2007). Genomes are evolutiona ...
BACTERIAL GENETICS CH. 6,7,8
... g. Ribosome separates, released from m-RNA, h. Ribosome attaches to first codon on m-RNA i. ...
... g. Ribosome separates, released from m-RNA, h. Ribosome attaches to first codon on m-RNA i. ...
Chp. 3, Section E: How Does a Genetic Counselor Detect Mutant
... Affected individuals are usually wheelchair-bound before they reach their teens and few survive into their twenties, most frequently dying from lung or heart failure. Fewer than 10% of carrier females exhibit any muscular weakness as a consequence of having one mutant allele, and female homozygotes ...
... Affected individuals are usually wheelchair-bound before they reach their teens and few survive into their twenties, most frequently dying from lung or heart failure. Fewer than 10% of carrier females exhibit any muscular weakness as a consequence of having one mutant allele, and female homozygotes ...
draft key
... 2. [2 POINTS] The map distance between gene A and gene B is 10 map units. The map distance between gene B and gene C is 20 map units. However, in a testcross of an individual heterozygous for genes A and C only 26% of the progeny are recombinant. Briefly explain how can you reconcile the result of t ...
... 2. [2 POINTS] The map distance between gene A and gene B is 10 map units. The map distance between gene B and gene C is 20 map units. However, in a testcross of an individual heterozygous for genes A and C only 26% of the progeny are recombinant. Briefly explain how can you reconcile the result of t ...
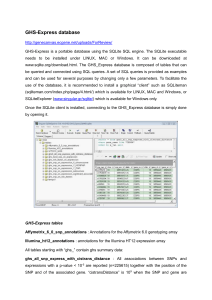
GHS-Express database http://genecanvas.ecgene.net/uploads/Fo
... expressions with a p-value < 10-5 are reported (n=225615) together with the position of the SNP and of the associated gene. “cistransDistance” is 109 when the SNP and gene are ...
... expressions with a p-value < 10-5 are reported (n=225615) together with the position of the SNP and of the associated gene. “cistransDistance” is 109 when the SNP and gene are ...
AP Biology: Evolution
... as the unknown fragments and is then used to create a standard curve. The standard curve, in this case a straight line, is created by graphing the distance each fragment traveled through the gel versus the log10 of its base pair length. Creating the Standard Curve As explained above, base pair (bp) ...
... as the unknown fragments and is then used to create a standard curve. The standard curve, in this case a straight line, is created by graphing the distance each fragment traveled through the gel versus the log10 of its base pair length. Creating the Standard Curve As explained above, base pair (bp) ...
BIOLOGY Cells Unit GUIDE SHEET
... 15. Compare and contrast the two types of mutations in the table below. Then, provide a specific example of each type of mutation as follows: 1. Using the DNA sequence TACCGGGCATTCAAA as a starting point, make a mutation of the indicated type. Write your mutated DNA sequence. 2. Using the Genetic Co ...
... 15. Compare and contrast the two types of mutations in the table below. Then, provide a specific example of each type of mutation as follows: 1. Using the DNA sequence TACCGGGCATTCAAA as a starting point, make a mutation of the indicated type. Write your mutated DNA sequence. 2. Using the Genetic Co ...
SNP genotyping

SNP genotyping is the measurement of genetic variations of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) between members of a species. It is a form of genotyping, which is the measurement of more general genetic variation. SNPs are one of the most common types of genetic variation. An SNP is a single base pair mutation at a specific locus, usually consisting of two alleles (where the rare allele frequency is >1%). SNPs are found to be involved in the etiology of many human diseases and are becoming of particular interest in pharmacogenetics. Because SNPs are conserved during evolution, they have been proposed as markers for use in quantitative trait loci (QTL) analysis and in association studies in place of microsatellites. The use of SNPs is being extended in the HapMap project, which aims to provide the minimal set of SNPs needed to genotype the human genome. SNPs can also provide a genetic fingerprint for use in identity testing. The increase in interest in SNPs has been reflected by the furious development of a diverse range of SNP genotyping methods.