DNA extraction from cheek cells protocol I mailed to you
... DNA strand by adding the matching nucleotides one at a time and joining each new nucleotide to the previous nucleotide in the growing DNA strand. DNA replication results in two new DNA molecules that are identical to the original DNA molecule. Thus, each of the new DNA molecules carries the same gen ...
... DNA strand by adding the matching nucleotides one at a time and joining each new nucleotide to the previous nucleotide in the growing DNA strand. DNA replication results in two new DNA molecules that are identical to the original DNA molecule. Thus, each of the new DNA molecules carries the same gen ...
Exam 2
... mutations in part but not all of the chromosome. However, I did accept deletions or duplications for the reasons listed below. c) Considering your answer to b): There are different reasons for the reduction in fertility for the two types of mutations. Briefly, explain the differences in 3 sentences ...
... mutations in part but not all of the chromosome. However, I did accept deletions or duplications for the reasons listed below. c) Considering your answer to b): There are different reasons for the reduction in fertility for the two types of mutations. Briefly, explain the differences in 3 sentences ...
Fill-in Handout - Liberty Union High School District
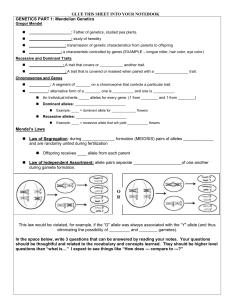
... Law of Segregation: during ______________ formation (MEIOSIS) pairs of alleles _____________ and are randomly united during fertilization Offspring receives ____ allele from each parent Law of Independent Assortment: allele pairs separate _____________________of one another during gamete forma ...
... Law of Segregation: during ______________ formation (MEIOSIS) pairs of alleles _____________ and are randomly united during fertilization Offspring receives ____ allele from each parent Law of Independent Assortment: allele pairs separate _____________________of one another during gamete forma ...
Nucleic Acids - saddleback.edu
... wrong residue slightly less than once every 10,000 times. • The enzyme proof-reads its work to see if the correct deoxyribonucleotide residue has been added; if a mistake has been made, DNA polymerase clips the residue and tries again. • If proofreading does not catch the error, then other DNA rep ...
... wrong residue slightly less than once every 10,000 times. • The enzyme proof-reads its work to see if the correct deoxyribonucleotide residue has been added; if a mistake has been made, DNA polymerase clips the residue and tries again. • If proofreading does not catch the error, then other DNA rep ...
Lab Section_____________ Prelab questions for Lab 8 1. For each
... impaired. The effect on families can be devastating because no cure has been developed and it cannot be treated effectively. Because the onset is typically late in life, individuals bear offspring and pass this gene on before they realize they carry it. Consequently this disease is easily transmitte ...
... impaired. The effect on families can be devastating because no cure has been developed and it cannot be treated effectively. Because the onset is typically late in life, individuals bear offspring and pass this gene on before they realize they carry it. Consequently this disease is easily transmitte ...
DustinHancks_proposal
... Once the sites of polymorphism are found, one of two approaches will be taken in order to develop diagnostic tests to identify each species and hybrid individuals. The first method utilizes restriction enzyme digests. A restriction enzyme can be used to distinguish specific sequences of DNA if sites ...
... Once the sites of polymorphism are found, one of two approaches will be taken in order to develop diagnostic tests to identify each species and hybrid individuals. The first method utilizes restriction enzyme digests. A restriction enzyme can be used to distinguish specific sequences of DNA if sites ...
Ch - TeacherWeb
... semidiscontinuous as well as semiconservative. 3. joining: when DNA polymerase comes to an RNA primer on the DNA, it removes the primer and fills in the place with free DNA nucleotides, then DNA ligase links the two sections. ...
... semidiscontinuous as well as semiconservative. 3. joining: when DNA polymerase comes to an RNA primer on the DNA, it removes the primer and fills in the place with free DNA nucleotides, then DNA ligase links the two sections. ...
Selective propagation of the clones
... (double stranded), a short 12 nucleotide stretch, in which DNA is single stranded. ...
... (double stranded), a short 12 nucleotide stretch, in which DNA is single stranded. ...
DNA
... 2. RNA polymerase unwinds and separates the two strands of DNA 3. RNA polymerase adds and links complementary RNA bases as it ‘reads” the gene, it moves along the bases on the DNA strand similar to how a train moves on a track and a strand of RNA grows. Behind the RNA polymerase, the two strands of ...
... 2. RNA polymerase unwinds and separates the two strands of DNA 3. RNA polymerase adds and links complementary RNA bases as it ‘reads” the gene, it moves along the bases on the DNA strand similar to how a train moves on a track and a strand of RNA grows. Behind the RNA polymerase, the two strands of ...
1) For a couple of decades, biologists knew the
... D) post-translational control that activates certain proteins. E) a eukaryotic equivalent of prokaryotic promoter functioning. 42) Steroid hormones produce their effects in cells by A) activating key enzymes in metabolic pathways. B) activating translation of certain mRNAs. C) promoting the degradat ...
... D) post-translational control that activates certain proteins. E) a eukaryotic equivalent of prokaryotic promoter functioning. 42) Steroid hormones produce their effects in cells by A) activating key enzymes in metabolic pathways. B) activating translation of certain mRNAs. C) promoting the degradat ...
sample exam 2010
... 88. Briefly define or describe the technique of population sampling known as "quadrat sampling." (2 marks) 89. Energy calculations suggest that raising animals for food is not an efficient use of land, and that more people can be fed on a plant-based diet. Describe situations in which an animal-base ...
... 88. Briefly define or describe the technique of population sampling known as "quadrat sampling." (2 marks) 89. Energy calculations suggest that raising animals for food is not an efficient use of land, and that more people can be fed on a plant-based diet. Describe situations in which an animal-base ...
Cover Page In-silico study of Neural Tube Defect in relation to
... in the structure because of this SNP. The ...
... in the structure because of this SNP. The ...
Disease name
... identity to the Victoria/AUS/2007 AbHVscaffold_3172-3200 fragment. The TC02 (NCBI accession no. JF967012) and TC08 fragments (NCBI accession no. HQ890941) of the Taiwanese isolate corresponded to the Victoria/AUS/2007 AbHVscaffold_3197-3033 isolate, and had 66.7% (26,884/40,281) and 61.2% (14,529/23 ...
... identity to the Victoria/AUS/2007 AbHVscaffold_3172-3200 fragment. The TC02 (NCBI accession no. JF967012) and TC08 fragments (NCBI accession no. HQ890941) of the Taiwanese isolate corresponded to the Victoria/AUS/2007 AbHVscaffold_3197-3033 isolate, and had 66.7% (26,884/40,281) and 61.2% (14,529/23 ...
Cloning in Escherichia coli
... replicated in cells to high copy number, a selectable marker (“Ampr”) that confers antibiotic resistance, and a “multiple cloning site” – a sequence that carries cleavage sites for many different restriction enzymes (shown vertically on plasmid map above). pGEM-T® has some unique properties that mak ...
... replicated in cells to high copy number, a selectable marker (“Ampr”) that confers antibiotic resistance, and a “multiple cloning site” – a sequence that carries cleavage sites for many different restriction enzymes (shown vertically on plasmid map above). pGEM-T® has some unique properties that mak ...
DNA and Forensic Science
... five to ten times greater mutation rate than nuclear DNA, so the variation arises through mutation. Usually there is 1-2% variance of mtDNA sequence between unrelated individuals, or 1-2 in 100 bases. Mutations are random and preserved through maternal inheritance, so there is only a remote chance t ...
... five to ten times greater mutation rate than nuclear DNA, so the variation arises through mutation. Usually there is 1-2% variance of mtDNA sequence between unrelated individuals, or 1-2 in 100 bases. Mutations are random and preserved through maternal inheritance, so there is only a remote chance t ...
Detection of Viral, Bacterial and Human Genomic DNA
... stool poses a logistical problem in the form of nucleic acid degradation that occurs during sample collection and transport5. Current techniques which do not make use of preservative require that stool be collected into vials, transported on ice and then frozen at -20°C when received by the diagnost ...
... stool poses a logistical problem in the form of nucleic acid degradation that occurs during sample collection and transport5. Current techniques which do not make use of preservative require that stool be collected into vials, transported on ice and then frozen at -20°C when received by the diagnost ...
L26_ABPG2014
... ectopic site in double-stranded DNA. Inefficient nicking of the antisense strand forms the primer for full-length cDNA synthesis by the RT with completion of intron insertion by DNA repair. The mechanism on the right begins with reverse splicing into the ectopic site at a replication fork. cDNA synt ...
... ectopic site in double-stranded DNA. Inefficient nicking of the antisense strand forms the primer for full-length cDNA synthesis by the RT with completion of intron insertion by DNA repair. The mechanism on the right begins with reverse splicing into the ectopic site at a replication fork. cDNA synt ...
BAC vectors (Bacterial Artificial Chromosome)
... (here BamH I) remove a length of DNA between two telomere sequences leaving the telomeres at the ends of the linearized DNA. Cleavage at another internal site (EcoRI) divides the vector into two DNA segments, referred to as vector arms, each with a different selectable marker. The genomic DNA is pre ...
... (here BamH I) remove a length of DNA between two telomere sequences leaving the telomeres at the ends of the linearized DNA. Cleavage at another internal site (EcoRI) divides the vector into two DNA segments, referred to as vector arms, each with a different selectable marker. The genomic DNA is pre ...
Scientific Advisory Board
... Each spiraling strand, comprised of a sugar-phosphate backbone and attached bases, is connected to a complementary strand by non-covalent hydrogen bonding between paired bases. The bases are adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C) and guanine (G). ...
... Each spiraling strand, comprised of a sugar-phosphate backbone and attached bases, is connected to a complementary strand by non-covalent hydrogen bonding between paired bases. The bases are adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C) and guanine (G). ...
Low-Level Analysis of Affymetrix Data
... • NB: High affinity is not the same as specificity – Probe can give high signal to intended target and also to other transcripts ...
... • NB: High affinity is not the same as specificity – Probe can give high signal to intended target and also to other transcripts ...
Ch. 13 Bioengineering
... – Most DNA molecules are too large to be analyzed, so biologists cut them into smaller fragments using restriction enzymes. • Enzymes found in bacteria used to destroy phage DNA ...
... – Most DNA molecules are too large to be analyzed, so biologists cut them into smaller fragments using restriction enzymes. • Enzymes found in bacteria used to destroy phage DNA ...
SNP genotyping

SNP genotyping is the measurement of genetic variations of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) between members of a species. It is a form of genotyping, which is the measurement of more general genetic variation. SNPs are one of the most common types of genetic variation. An SNP is a single base pair mutation at a specific locus, usually consisting of two alleles (where the rare allele frequency is >1%). SNPs are found to be involved in the etiology of many human diseases and are becoming of particular interest in pharmacogenetics. Because SNPs are conserved during evolution, they have been proposed as markers for use in quantitative trait loci (QTL) analysis and in association studies in place of microsatellites. The use of SNPs is being extended in the HapMap project, which aims to provide the minimal set of SNPs needed to genotype the human genome. SNPs can also provide a genetic fingerprint for use in identity testing. The increase in interest in SNPs has been reflected by the furious development of a diverse range of SNP genotyping methods.