De niet-covalente interacties
... pyruvate + NADH + H+ lactate + NAD+; ΔG0pH 7.0 = - 6 kcal/mole. ...
... pyruvate + NADH + H+ lactate + NAD+; ΔG0pH 7.0 = - 6 kcal/mole. ...
Alcoholic fermentation
... …………………….. back to NAD+ so that the energy yielding phase of glycolysis can continue. In yeast, pyruvate is decarboxylated to ETHANAL (…..C), releasing …………….. . The enzyme alcohol dehydrogenase then ……………….. ETHANAL to ETHANOL (…..C), at the same time ………………… NADH back to ……………. . CH3CHO + NADH ...
... …………………….. back to NAD+ so that the energy yielding phase of glycolysis can continue. In yeast, pyruvate is decarboxylated to ETHANAL (…..C), releasing …………….. . The enzyme alcohol dehydrogenase then ……………….. ETHANAL to ETHANOL (…..C), at the same time ………………… NADH back to ……………. . CH3CHO + NADH ...
Here
... In this practical we shall be exploring issues such as differences between the H4 and the M4 isoenzymes in relation to Km, pH-dependence and inhibition by other molecules. It is worth considering whether any differences in behaviour between the isoenzymes represent an adaptation to serve the way tha ...
... In this practical we shall be exploring issues such as differences between the H4 and the M4 isoenzymes in relation to Km, pH-dependence and inhibition by other molecules. It is worth considering whether any differences in behaviour between the isoenzymes represent an adaptation to serve the way tha ...
Key Terms:
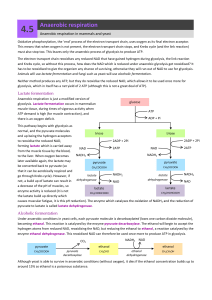
... How is respiration commonly regulated? Why might a cell want to slow down respiration? Lecture Outline: Anaerobic Metabolism recall that in glycolysis no oxygen required 2 ATP generated (net) per glucose but there's an NAD+/NADH problem! continuous running of glycolysis will use up all of your NAD ...
... How is respiration commonly regulated? Why might a cell want to slow down respiration? Lecture Outline: Anaerobic Metabolism recall that in glycolysis no oxygen required 2 ATP generated (net) per glucose but there's an NAD+/NADH problem! continuous running of glycolysis will use up all of your NAD ...
المجلة القطرية للكيمياء-2010 المجلد التاسع والثلاثون39 National
... dehydrogenase are specific cardiac enzymes that are used for evaluation of heart involvement and in patients when there is injury or inflammation(7,8). Creatine kinase, CK(EC 2.7.3.2) is a cytosolic and mitochondrial enzyme with wide tissue distribution, and catalysis the phosphorylation of Creatine ...
... dehydrogenase are specific cardiac enzymes that are used for evaluation of heart involvement and in patients when there is injury or inflammation(7,8). Creatine kinase, CK(EC 2.7.3.2) is a cytosolic and mitochondrial enzyme with wide tissue distribution, and catalysis the phosphorylation of Creatine ...
Lactate dehydrogenase is crucial for tumor associated macrophage
... Multiple myeloma (MM) is a cancer characterized by an accumulation of malignant plasma cells in the bone marrow. Although chemotherapy is the most effective treatment, the majority of patients experience relapse. The major cause of treatment failure is the development of multidrug resistance. Thus, ...
... Multiple myeloma (MM) is a cancer characterized by an accumulation of malignant plasma cells in the bone marrow. Although chemotherapy is the most effective treatment, the majority of patients experience relapse. The major cause of treatment failure is the development of multidrug resistance. Thus, ...
Myocardial infarction - Lectures For UG-5
... Found mostly in the myocardium and erythrocytes Also found in the renal cortex LD3 (HHMM) Found in a number of tissues, predominantly in the white blood cells and brain LD4 and LD5 (HMMM, MMMM) Slow moving and are heat labile Found mostly in the liver and skeletal muscle ...
... Found mostly in the myocardium and erythrocytes Also found in the renal cortex LD3 (HHMM) Found in a number of tissues, predominantly in the white blood cells and brain LD4 and LD5 (HMMM, MMMM) Slow moving and are heat labile Found mostly in the liver and skeletal muscle ...
Pyruvate and Energetics of Glycolysis
... 1. The conversion of pyruvate to ethanol also causes the ________. A) oxidation of NADH B) production of ADP C) consumption of O2 D) generation of an ion gradient across mitochondrial membranes 2. The enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of pyruvate to lactate is ________. A) lactate reductase ...
... 1. The conversion of pyruvate to ethanol also causes the ________. A) oxidation of NADH B) production of ADP C) consumption of O2 D) generation of an ion gradient across mitochondrial membranes 2. The enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of pyruvate to lactate is ________. A) lactate reductase ...
Anaerobic respiration
... has to be reoxidised to give the organism any chance of surviving, otherwise they will run out of NAD to use for glycolysis. Animals will use lactate fermentation and fungi such as yeast will use alcoholic fermentation. Neither method produces any ATP, but they do reoxidise the reduced NAD, which al ...
... has to be reoxidised to give the organism any chance of surviving, otherwise they will run out of NAD to use for glycolysis. Animals will use lactate fermentation and fungi such as yeast will use alcoholic fermentation. Neither method produces any ATP, but they do reoxidise the reduced NAD, which al ...
Week 4 met 2 kin 310
... Kin 310 – Ex Met 2 Fuel Utilization and Neural – Endocrine Control 1. Describe the activation and translocation of free fatty acids into skeletal muscle that is required prior to metabolism as fuel. (do not include the regulation of translocation in your answer). 2. Describe the mobilization, circul ...
... Kin 310 – Ex Met 2 Fuel Utilization and Neural – Endocrine Control 1. Describe the activation and translocation of free fatty acids into skeletal muscle that is required prior to metabolism as fuel. (do not include the regulation of translocation in your answer). 2. Describe the mobilization, circul ...
Anaerobic Respiration
... • Fungi e.g. yeast use ethanol fermentation • Animals use lactate fermentation • Neither of these produce ATP, but two are made during glycolysis ...
... • Fungi e.g. yeast use ethanol fermentation • Animals use lactate fermentation • Neither of these produce ATP, but two are made during glycolysis ...
LACTATE/PYRUVATE RATIO Relevant disorders Related
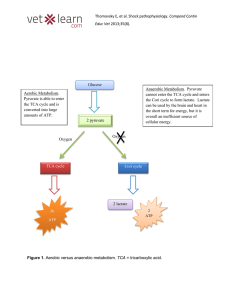
... Pyruvate should only be analysed when lactate is elevated to determine the patients redox state. Pyruvate is an end product of glycolysis. It can either be converted to lactate under anaerobic conditions or transported into mitochondria to feed into the Kreb’s cycle under aerobic conditions. Lactate ...
... Pyruvate should only be analysed when lactate is elevated to determine the patients redox state. Pyruvate is an end product of glycolysis. It can either be converted to lactate under anaerobic conditions or transported into mitochondria to feed into the Kreb’s cycle under aerobic conditions. Lactate ...
Word
... used to produce your team’s poster (as for the Glassbeads experiment), and Word for the abstract - we will be on hand to help with the data analysis; but ensure you bring your data in a spreadsheet! Week 38 : Poster presentation and assessment - The first 15 min will be available to arrange the post ...
... used to produce your team’s poster (as for the Glassbeads experiment), and Word for the abstract - we will be on hand to help with the data analysis; but ensure you bring your data in a spreadsheet! Week 38 : Poster presentation and assessment - The first 15 min will be available to arrange the post ...
... Inborn errors of metabolism (IEM) are defined as inherited diseases, most of which are autosomal recessive, caused by mutations that affect the structure or function of a protein, which causes disruption of a metabolic pathway, with accumulation of metabolites in tissues and biological fluids and th ...
supplementary information
... Sigma-Aldrich) solution (5 mg/ml in PBS) was stored protected from light at -20C until usage. HaCaT keratinocytes, 3000 cells/well, were seeded in 96 well plates and grown in keratinocyte-SFM/BPE-rEGF medium to confluency. Peptides were then added at the concentrations indicated in the figure (in t ...
... Sigma-Aldrich) solution (5 mg/ml in PBS) was stored protected from light at -20C until usage. HaCaT keratinocytes, 3000 cells/well, were seeded in 96 well plates and grown in keratinocyte-SFM/BPE-rEGF medium to confluency. Peptides were then added at the concentrations indicated in the figure (in t ...
3. Related Pathways
... converting the group to ammonia, NH3 (urea is expelled from the body in urine) Lipid Catabolism Glycerol can be converted to glucose through a process called gluconeogenesis Fatty acids undergo beta-oxidation where 2-C acetyl groups are removed Fats can produce 20% more ATP than carbohydrates ...
... converting the group to ammonia, NH3 (urea is expelled from the body in urine) Lipid Catabolism Glycerol can be converted to glucose through a process called gluconeogenesis Fatty acids undergo beta-oxidation where 2-C acetyl groups are removed Fats can produce 20% more ATP than carbohydrates ...
JVB112 gluconeogenesis[1]
... reaction in the direction of pyruvate formation b. In muscle cells and erythrocytes, LDH usually runs this reaction in the direction of lactate formation c. The direction in which the reaction proceeds depends on I ) The ratios of NAD+ to NADH and lactate to pyruvate ii) The isozyme of LDH that is p ...
... reaction in the direction of pyruvate formation b. In muscle cells and erythrocytes, LDH usually runs this reaction in the direction of lactate formation c. The direction in which the reaction proceeds depends on I ) The ratios of NAD+ to NADH and lactate to pyruvate ii) The isozyme of LDH that is p ...
JVB112 gluconeogenesis[1]
... reaction in the direction of pyruvate formation b. In muscle cells and erythrocytes, LDH usually runs this reaction in the direction of lactate formation c. The direction in which the reaction proceeds depends on I ) The ratios of NAD+ to NADH and lactate to pyruvate ii) The isozyme of LDH that is p ...
... reaction in the direction of pyruvate formation b. In muscle cells and erythrocytes, LDH usually runs this reaction in the direction of lactate formation c. The direction in which the reaction proceeds depends on I ) The ratios of NAD+ to NADH and lactate to pyruvate ii) The isozyme of LDH that is p ...
Lecture 8 - People Server at UNCW
... – Located in aortic and carotid bodies, medulla – Sample pO2 and pCO2 in blood ...
... – Located in aortic and carotid bodies, medulla – Sample pO2 and pCO2 in blood ...
24,7 Loctic Fermentotion
... magnitude and courseof diseasein the body. During a heart attack, for example, damaged heart muscle releases LDH, mainly the H4 isoz],.rne. Within 24 hours of the heart attack episode, serum LDH reaches a peak; it then returns to a normal level within 5 or 6 days. A physicianoften can get a good ide ...
... magnitude and courseof diseasein the body. During a heart attack, for example, damaged heart muscle releases LDH, mainly the H4 isoz],.rne. Within 24 hours of the heart attack episode, serum LDH reaches a peak; it then returns to a normal level within 5 or 6 days. A physicianoften can get a good ide ...
Isoenzymes and Other Markers
... • It is relatively specific when skeletal muscle damage is not present • CK-MB resides in the cytosol and facilitates high energy phosphates into and out of mitochondria. It is distributed in a large number of tissues even in the skeletal muscle. Since it has a short duration, it cannot be used for ...
... • It is relatively specific when skeletal muscle damage is not present • CK-MB resides in the cytosol and facilitates high energy phosphates into and out of mitochondria. It is distributed in a large number of tissues even in the skeletal muscle. Since it has a short duration, it cannot be used for ...
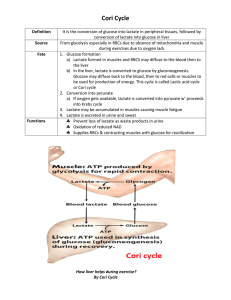
Cori Cycle - COFFEE BREAK CORNER
... or Cori cycle 2. Conversion into pyruvate a) If oxygen gets available, lactate is converted into pyruvate w’ proceeds into Krebs cycle 3. Lactate may be accumulated in muscles causing muscle fatigue ...
... or Cori cycle 2. Conversion into pyruvate a) If oxygen gets available, lactate is converted into pyruvate w’ proceeds into Krebs cycle 3. Lactate may be accumulated in muscles causing muscle fatigue ...
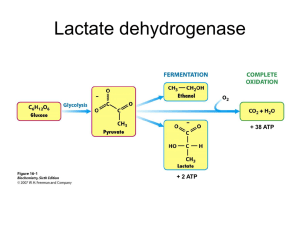
Lactate dehydrogenase

A lactate dehydrogenase (LDH or LD) is an enzyme found in nearly all living cells (animals, plants, and prokaryotes). LDH catalyzes the conversion of pyruvate to lactate and back, as it converts NADH to NAD+ and back. A dehydrogenase is an enzyme that transfers a hydride from one molecule to another.LDH exist in four distinct enzyme classes. This article is about the common NAD(P)-dependent L-lactate dehydrogenase. Other LDHs act on D-lactate and/or are dependent on cytochrome c: D-lactate dehydrogenase (cytochrome)) and L-lactate (L-lactate dehydrogenase (cytochrome)). LDH has been of medical significance because it is found extensively in body tissues, such as blood cells and heart muscle. Because it is released during tissue damage, it is a marker of common injuries and disease such as heart failure.














![JVB112 gluconeogenesis[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000939420_1-ae0fa12f0b4eac306770097ba9ecae40-300x300.png)
![JVB112 gluconeogenesis[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/005255251_1-e457e3f80be2f5d8ecf577d50c416034-300x300.png)