Peking University Industrial Organization, Spring 2013 Guanghua
... (e) What changes if the marginal cost of firm 2 increased to $4 per unit? (f) Compare the perfectly competitive, monopoly and the Cournot outputs, prices, and profits when each firm has a marginal cost of $4 per unit. Question 2: Bertrand Competition If firm 1 has constant marginal cost c1 and firm ...
... (e) What changes if the marginal cost of firm 2 increased to $4 per unit? (f) Compare the perfectly competitive, monopoly and the Cournot outputs, prices, and profits when each firm has a marginal cost of $4 per unit. Question 2: Bertrand Competition If firm 1 has constant marginal cost c1 and firm ...
Geo-point Graphs: An Alternative to Marshallian Cross Diagrams
... 2. Non INTJ Students • “Chalk and Talk”- still dominant among economics Instructors (Watts/Becker surveys) • “If we want to increase learning in economics, then we need to devise ways of presenting course material that are accessible to all students regardless of how they receive and process inform ...
... 2. Non INTJ Students • “Chalk and Talk”- still dominant among economics Instructors (Watts/Becker surveys) • “If we want to increase learning in economics, then we need to devise ways of presenting course material that are accessible to all students regardless of how they receive and process inform ...
Chapter 6
... – Think of prices as a traffic light. A relative high price is a green light that tells producers that a specific good is in demand and that they should use their resources to produce more. A low price is a red light. – For consumers, a low price is a green light to buy more of a good. A high price ...
... – Think of prices as a traffic light. A relative high price is a green light that tells producers that a specific good is in demand and that they should use their resources to produce more. A low price is a red light. – For consumers, a low price is a green light to buy more of a good. A high price ...
Equilibrium
... These pressures are from the needs of consumers for goods and services (demand) and the need of producers to sell their goods and services (supply) These pressures are known as market forces or ‘the invisible hand’. ...
... These pressures are from the needs of consumers for goods and services (demand) and the need of producers to sell their goods and services (supply) These pressures are known as market forces or ‘the invisible hand’. ...
Midterm Exam #1
... This exam consists of three parts. The first part requires you to provide a definition as well as an application for each concept. The second part involves solution of simple economic problems. The third part provides opportunities for students to employ economic analysis to address more complicated ...
... This exam consists of three parts. The first part requires you to provide a definition as well as an application for each concept. The second part involves solution of simple economic problems. The third part provides opportunities for students to employ economic analysis to address more complicated ...
Unit 2 Study Guide
... o Movements along a given curve as opposed to a shift of the curve o Determinants that shift the supply and demand curves o Which way increases and decreases shift the curves o Equilibrium and changes to equilibrium o Shortages and surpluses and how the market will correct o Floors and ceilings and ...
... o Movements along a given curve as opposed to a shift of the curve o Determinants that shift the supply and demand curves o Which way increases and decreases shift the curves o Equilibrium and changes to equilibrium o Shortages and surpluses and how the market will correct o Floors and ceilings and ...
Questions: Show in a diagram the effect on the demand curve, the
... Case 1: People realize how fattening bagels are. Case 2: People have less time to make themselves a cooked breakfast. a. The market for the Krugman and Wells economics textbook Case 1: Your professor makes it required reading for all of his or her students. Case 2: Printing costs for textbooks are l ...
... Case 1: People realize how fattening bagels are. Case 2: People have less time to make themselves a cooked breakfast. a. The market for the Krugman and Wells economics textbook Case 1: Your professor makes it required reading for all of his or her students. Case 2: Printing costs for textbooks are l ...
problem_set_3
... e. In one sentence ONLY, explain what DWL is in this specific case - what is actually lost? f. Calculate the elasticity of demand when the price increases from the equilibrium price found in (a) to $12. Is it elastic or inelastic demand? g. 2. Externalities in Gnomeland a. In Gnomeland, externalitie ...
... e. In one sentence ONLY, explain what DWL is in this specific case - what is actually lost? f. Calculate the elasticity of demand when the price increases from the equilibrium price found in (a) to $12. Is it elastic or inelastic demand? g. 2. Externalities in Gnomeland a. In Gnomeland, externalitie ...
Equilibrium Price - JaminetEconomics
... by the government to prevent prices from going above a certain level. B. Items in short supply might be rationed. C. Shortages can lead to a black market, or illegal places to purchase such products at exorbitant prices. D. Price floors are minimum prices also set by the government to prevent ...
... by the government to prevent prices from going above a certain level. B. Items in short supply might be rationed. C. Shortages can lead to a black market, or illegal places to purchase such products at exorbitant prices. D. Price floors are minimum prices also set by the government to prevent ...
Supply and Demand: Partial Equilibrium and Comparative Statics
... that we can assume that either dD/dp = 0 (the demand curve flat) or dS/dp = 0 (the supply curve is flat), but not both. 2 This assumption is sometimes known as the law of one price. If consumers faced multiple prices for the same good they would only buy at the lowest price. Similarly if producers f ...
... that we can assume that either dD/dp = 0 (the demand curve flat) or dS/dp = 0 (the supply curve is flat), but not both. 2 This assumption is sometimes known as the law of one price. If consumers faced multiple prices for the same good they would only buy at the lowest price. Similarly if producers f ...
Determining and Managing Prices
... product are equal at the same price. QD = QS – The needs of both supplier and consumer are satisfied. – The forces of supply and demand are in balance. – Question: How do producers know if their price is too high or too low? In other words, how do they know if the price they have set is at market eq ...
... product are equal at the same price. QD = QS – The needs of both supplier and consumer are satisfied. – The forces of supply and demand are in balance. – Question: How do producers know if their price is too high or too low? In other words, how do they know if the price they have set is at market eq ...
Supply and Demand Extra Practice Answers
... be demanded at each price) and shift the demand curve to the right. Producers will react as well. Since they also expect prices to be higher in three months, they have an incentive to hold onto their inventories and wait until the prices rise to sell. As a result, the current supply of plywood will ...
... be demanded at each price) and shift the demand curve to the right. Producers will react as well. Since they also expect prices to be higher in three months, they have an incentive to hold onto their inventories and wait until the prices rise to sell. As a result, the current supply of plywood will ...
投影片 1
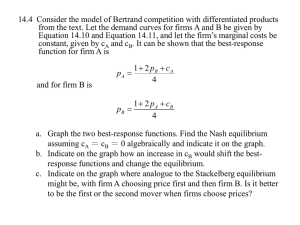
... assuming cA = cB = 0 algebraically and indicate it on the graph. b. Indicate on the graph how an increase in cB would shift the bestresponse functions and change the equilibrium. c. Indicate on the graph where analogue to the Stackelberg equilibrium might be, with firm A choosing price first and the ...
... assuming cA = cB = 0 algebraically and indicate it on the graph. b. Indicate on the graph how an increase in cB would shift the bestresponse functions and change the equilibrium. c. Indicate on the graph where analogue to the Stackelberg equilibrium might be, with firm A choosing price first and the ...
... Economic models are designed to study a particular economic phenomenon. Some of these models are mathematical and some are not. But they almost always contain a set of assumptions which simplifies the ‘real-world’. In this course, we shall focus on mathematical models. Generally, economic models tha ...
Test 1 Review - WordPress.com
... • And the other person a full allocation of food, then… • Trade will occur to a point where both people • Benefit from the interaction • Cannot improve any further without harming the other ...
... • And the other person a full allocation of food, then… • Trade will occur to a point where both people • Benefit from the interaction • Cannot improve any further without harming the other ...
Markets, Equilibrium, and Prices
... 1. What happens at the point where buyers and sellers agree? Use these terms in your answer: market equilibrium, equilibrium price, equilibrium quantity. 2. Why do competitive markets move toward equilibrium? 3. Look at the balance scale in this section, which represents equilibrium. Create your ...
... 1. What happens at the point where buyers and sellers agree? Use these terms in your answer: market equilibrium, equilibrium price, equilibrium quantity. 2. Why do competitive markets move toward equilibrium? 3. Look at the balance scale in this section, which represents equilibrium. Create your ...
Interaction: How Economies Work PowerPoint
... • Interaction of choices—my choices affect your choices, and vice versa— is a feature of most economic situations. • In economics we will quickly see that end results sometimes comes out different from what was intended. ...
... • Interaction of choices—my choices affect your choices, and vice versa— is a feature of most economic situations. • In economics we will quickly see that end results sometimes comes out different from what was intended. ...
Econ 370
... average cost is minimized. Then find the level of average cost at that output. Graphically show the average and marginal cost curves for each floor ...
... average cost is minimized. Then find the level of average cost at that output. Graphically show the average and marginal cost curves for each floor ...
ECON Micro CHAPTER 4 PROBLEMS LO1 – Explain how the law of
... b. The price of cigars increases. c. Wages increase substantially in states that grow tobacco. d. A fertilizer that increases the yield per acre of tobacco is discovered. e. There is a sharp increase in the price of matches, lighters, and lighter fluid. f. More states pass laws restricting smoking i ...
... b. The price of cigars increases. c. Wages increase substantially in states that grow tobacco. d. A fertilizer that increases the yield per acre of tobacco is discovered. e. There is a sharp increase in the price of matches, lighters, and lighter fluid. f. More states pass laws restricting smoking i ...
Basic Economics Baseball Review
... What is the best way to correct a surplus? What is the best way to correct a shortage? Name one factor that determines whether a good is elastic? If the price of butter increases what is the effect of the demand for margarine? Triples: What is a price floor? What is a price ceiling? What is Market S ...
... What is the best way to correct a surplus? What is the best way to correct a shortage? Name one factor that determines whether a good is elastic? If the price of butter increases what is the effect of the demand for margarine? Triples: What is a price floor? What is a price ceiling? What is Market S ...