In Class Exercise 3
... The central bank wants to achieve national income of $1500 billion through open market operations. (a) What must investment be for the equilibrium level of national income to be $1500 billion? (b) At what interest rate is this level of investment achieved? (c) If the central bank pursues this level ...
... The central bank wants to achieve national income of $1500 billion through open market operations. (a) What must investment be for the equilibrium level of national income to be $1500 billion? (b) At what interest rate is this level of investment achieved? (c) If the central bank pursues this level ...
Midterm Exam #1
... “Fueling the Frustration” describes gasoline markets after Hurricane Katrina. What is the primary claim in the article? Which economic principles can be used to explain the observed market behavior? c. Why would one expect short run markets to differ markedly from long run markets for gasoline? d. H ...
... “Fueling the Frustration” describes gasoline markets after Hurricane Katrina. What is the primary claim in the article? Which economic principles can be used to explain the observed market behavior? c. Why would one expect short run markets to differ markedly from long run markets for gasoline? d. H ...
MICROECONOMIC THEORY
... The Economic Theory of Value • Marshallian Supply-Demand Synthesis – Alfred Marshall showed that supply and demand simultaneously operate to determine price – prices reflect both the marginal evaluation that consumers place on goods and the marginal costs of producing the goods • water has a low ma ...
... The Economic Theory of Value • Marshallian Supply-Demand Synthesis – Alfred Marshall showed that supply and demand simultaneously operate to determine price – prices reflect both the marginal evaluation that consumers place on goods and the marginal costs of producing the goods • water has a low ma ...
Chapter 6 Notes on Economics
... *But, the problem with that is this can create an increase in demand and a decrease in supply, which will then create excess demand!!! **Also, the “cost” of price ceilings: -destroys incentive to improve condition. -abuse (who is rent control meant for?) -reduce the number of apartments. b. Price Fl ...
... *But, the problem with that is this can create an increase in demand and a decrease in supply, which will then create excess demand!!! **Also, the “cost” of price ceilings: -destroys incentive to improve condition. -abuse (who is rent control meant for?) -reduce the number of apartments. b. Price Fl ...
Honors Economics Unit 2 Study Guide
... 12. What does the law of supply state?(101) 13. What is the difference between a change in quantity supplied and a shift in the supply curve? (117) 14. What is the effect of import restrictions on price?(118) 15. What are fixed costs? Examples?(111) 15. What are variable costs? Examples(111) 16. Wha ...
... 12. What does the law of supply state?(101) 13. What is the difference between a change in quantity supplied and a shift in the supply curve? (117) 14. What is the effect of import restrictions on price?(118) 15. What are fixed costs? Examples?(111) 15. What are variable costs? Examples(111) 16. Wha ...
course syllabus
... one exam. Homework will be handed out periodically. Your grade will be calculated using the method list below. Homework: Exam: ...
... one exam. Homework will be handed out periodically. Your grade will be calculated using the method list below. Homework: Exam: ...
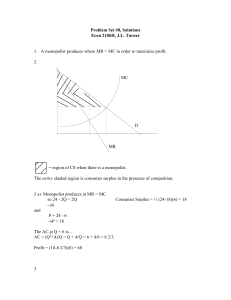
Problem Set #8, Solutions Econ 2106H, J.L. Turner 1. A monopolist
... e. Students will pay at most $30. Executives would get $12 in net consumer surplus. Hence, the Journal can charge at most $38 for the 100-article package if it wants executives to buy it. f. It earns more with a 60-article student package. On average, it gets .5 (30) + .5 (38) = $34 if it does this. ...
... e. Students will pay at most $30. Executives would get $12 in net consumer surplus. Hence, the Journal can charge at most $38 for the 100-article package if it wants executives to buy it. f. It earns more with a 60-article student package. On average, it gets .5 (30) + .5 (38) = $34 if it does this. ...
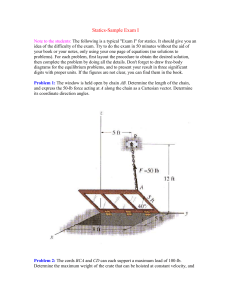
EXAM1
... Note to the students: The following is a typical "Exam I" for statics. It should give you an idea of the difficulty of the exam. Try to do the exam in 50 minutes without the aid of your book or your notes, only using your one page of equations (no solutions to problems). For each problem, first layo ...
... Note to the students: The following is a typical "Exam I" for statics. It should give you an idea of the difficulty of the exam. Try to do the exam in 50 minutes without the aid of your book or your notes, only using your one page of equations (no solutions to problems). For each problem, first layo ...
Supply and Demand
... b. Wages of workers in this industry fall. c. There is an improvement in technology. d. The price of the good falls. e. Producers expect that the price of the good will fall in the future. ...
... b. Wages of workers in this industry fall. c. There is an improvement in technology. d. The price of the good falls. e. Producers expect that the price of the good will fall in the future. ...
Perfect Competition and Monopoly
... Competition • Many independently acting firms. No collusion • Products are close, but not perfect, substitutes • No barriers to entry or exit • Imperfect information, bringing out the possibility of advertising ...
... Competition • Many independently acting firms. No collusion • Products are close, but not perfect, substitutes • No barriers to entry or exit • Imperfect information, bringing out the possibility of advertising ...
An example of competitive equilibrium in production economy: U1
... Lets extend it to a production economy. Suppose a firm exists which can produce (only) good y using good x as input with production function y = αx. Each agent has equal share in the profits. 2 Compute a competitive equilibrium (if any exist) which has no (extra) production of good y i.e. availabili ...
... Lets extend it to a production economy. Suppose a firm exists which can produce (only) good y using good x as input with production function y = αx. Each agent has equal share in the profits. 2 Compute a competitive equilibrium (if any exist) which has no (extra) production of good y i.e. availabili ...
Precept03Q.pdf
... How much crude petroleum would the U.S. government have to release from its strategic petroleum reserve to restore the price to $50? If the reserve holds a total of 700 million barrels, how long will it last? (c) Long run after the hurricanes hit Suppose the damaged U.S. capacity cannot be brought b ...
... How much crude petroleum would the U.S. government have to release from its strategic petroleum reserve to restore the price to $50? If the reserve holds a total of 700 million barrels, how long will it last? (c) Long run after the hurricanes hit Suppose the damaged U.S. capacity cannot be brought b ...
Equilibrium
... -Equilibrium is the point where supply & demand meet. -The market is stable at the equilibrium price. -To graph equilibrium combine the supply and demand graphs where they intersect is the equilibrium price. ...
... -Equilibrium is the point where supply & demand meet. -The market is stable at the equilibrium price. -To graph equilibrium combine the supply and demand graphs where they intersect is the equilibrium price. ...
Lecture 5 The Market Equilibrium
... ■ Demanders compete with each other to get goods. Their efforts push price up, enriching suppliers. ■ Suppliers compete with each other to attract customers. Their efforts push price down, enriching demanders. ■ Demanders do NOT compete with suppliers, even thought it sometimes seems that way! They ...
... ■ Demanders compete with each other to get goods. Their efforts push price up, enriching suppliers. ■ Suppliers compete with each other to attract customers. Their efforts push price down, enriching demanders. ■ Demanders do NOT compete with suppliers, even thought it sometimes seems that way! They ...
From Micro to Macro
... on a large sectors of the economy (say, the market for inputs, such as labor). It deals with the interaction among the different sectors. Under certain assumptions, it shows that disturbances or malfunctions in one sector can infect all other sectors. ...
... on a large sectors of the economy (say, the market for inputs, such as labor). It deals with the interaction among the different sectors. Under certain assumptions, it shows that disturbances or malfunctions in one sector can infect all other sectors. ...
Chapter_6_Section_2
... Surplus—situation in which the quantity supplied is greater than the quantity demanded at a price Shortage—situation in which quantity demanded is greater than the quantity supplied at a price Equilibrium price—the price that “clears the market” by leaving neither a surplus nor a shortage ...
... Surplus—situation in which the quantity supplied is greater than the quantity demanded at a price Shortage—situation in which quantity demanded is greater than the quantity supplied at a price Equilibrium price—the price that “clears the market” by leaving neither a surplus nor a shortage ...
Important Lecture Vocabulary and Concepts
... Vocabulary words from the End of Chapters 1 – 4 Baumol and Blinder Macroeconomics, 11th ed. ...
... Vocabulary words from the End of Chapters 1 – 4 Baumol and Blinder Macroeconomics, 11th ed. ...
Polynomial Time Algorithms For Market Equilibria Vazirani
... Uses Kakutani’s Fixed Point Theorem. ...
... Uses Kakutani’s Fixed Point Theorem. ...
Course Outline-ECO-301-Spring-2017
... This course is an intermediate level study of microeconomics which mainly concentrates on the analysis of individual prices and markets and the allocation of specific resources to particular uses. The theories of individual consumer behavior in a perfectly competitive economy mainly discuss the cons ...
... This course is an intermediate level study of microeconomics which mainly concentrates on the analysis of individual prices and markets and the allocation of specific resources to particular uses. The theories of individual consumer behavior in a perfectly competitive economy mainly discuss the cons ...
Principles of Economics
... supplied. Search cost: The financial and opportunity cost consumers pay when searching for a good ...
... supplied. Search cost: The financial and opportunity cost consumers pay when searching for a good ...