Supply and demand together!
... SUPPLY and demand TOGETHER • These two laws are directly contrary to each other. If suppliers want high prices, but buyers want low prices, how on earth does anything get traded? • “In the Chips” Activity • You will need a piece of paper and a pencil ...
... SUPPLY and demand TOGETHER • These two laws are directly contrary to each other. If suppliers want high prices, but buyers want low prices, how on earth does anything get traded? • “In the Chips” Activity • You will need a piece of paper and a pencil ...
Final Exam Review Sheet
... The final exam is Tuesday, December 17th, from 8-10am. The final exam will have a portion that is multiple choice, a portion that is short answer, which will involve at least one graph, and a portion that is true, false, explain. Good practice questions can be found on the textbook website. You shou ...
... The final exam is Tuesday, December 17th, from 8-10am. The final exam will have a portion that is multiple choice, a portion that is short answer, which will involve at least one graph, and a portion that is true, false, explain. Good practice questions can be found on the textbook website. You shou ...
Lesson 8 – Business Applications: Break Even Analysis, Equilibrium
... demand function intersect. We can solve problems of this type either algebraically or by using GGB. Example 4: Suppose that a company has determined that the demand equation for its product is 5 x + 3 p − 30 = 0 where p is the price of the product in dollars when x of the product are demanded (x is ...
... demand function intersect. We can solve problems of this type either algebraically or by using GGB. Example 4: Suppose that a company has determined that the demand equation for its product is 5 x + 3 p − 30 = 0 where p is the price of the product in dollars when x of the product are demanded (x is ...
Economics - Hamilton
... Shifts in the demand curve Prices of Factors of Production/resources Consumer Income Price of related goods Consumer Tastes/Expectations Relationship between price and supply Substitutes EQUILIBRIUM PRICE: Complements Who likes equilibrium price? ELASTICITY OF DEMAND: Define Equi ...
... Shifts in the demand curve Prices of Factors of Production/resources Consumer Income Price of related goods Consumer Tastes/Expectations Relationship between price and supply Substitutes EQUILIBRIUM PRICE: Complements Who likes equilibrium price? ELASTICITY OF DEMAND: Define Equi ...
Economics?
... consumption of marketable commodities. In the past 30 years, economists have shown that their ideas can be successfully applied to a much wider variety of problems. The economic approach has been used to study love and marriage, the decision to have children, criminal behavior, legal institutions, a ...
... consumption of marketable commodities. In the past 30 years, economists have shown that their ideas can be successfully applied to a much wider variety of problems. The economic approach has been used to study love and marriage, the decision to have children, criminal behavior, legal institutions, a ...
Example: PPC (Production Possibilities Curve)
... quantity of product exchanged Market equilibrium: a market price is established through competition such that the amount of goods or services sought by buyers is equal to the amount of goods or services produced by sellers. – This price is often called the equilibrium price or market clearing pric ...
... quantity of product exchanged Market equilibrium: a market price is established through competition such that the amount of goods or services sought by buyers is equal to the amount of goods or services produced by sellers. – This price is often called the equilibrium price or market clearing pric ...
Topic 3: Market Equilibrium and Applications
... 2. As P falls, consumers demand more (Qd©) 3. As the P falls the excess supply is eliminated and we reach equilibrium 4. There Qd = Qs (point E) Diagram 2 ...
... 2. As P falls, consumers demand more (Qd©) 3. As the P falls the excess supply is eliminated and we reach equilibrium 4. There Qd = Qs (point E) Diagram 2 ...
The invisible Hand
... Decrease in the price of a related good Increase in productivity Increase in Technology ...
... Decrease in the price of a related good Increase in productivity Increase in Technology ...
1 - Washington College
... DVD rental. Since I am not giving you specific data on prices and quantities, make a “freehand” drawing of the curve or curves you are asked to examine. Focus on the general shape and position of the curve(s) before and after each event occurs. For each scenario, draw a new curve that shows what hap ...
... DVD rental. Since I am not giving you specific data on prices and quantities, make a “freehand” drawing of the curve or curves you are asked to examine. Focus on the general shape and position of the curve(s) before and after each event occurs. For each scenario, draw a new curve that shows what hap ...
Equilibrium - Hicksville Public Schools
... How much is the shortage if the price is $1? Demand P Schedule $5 P Qd ...
... How much is the shortage if the price is $1? Demand P Schedule $5 P Qd ...
Course Outline EE311 Microeconomics Theory
... Course Description: Demand and supply analysis, consumer behavior and demand theory, production and cost of production, different types of product market structures, price determination in factor markets, decision-making over time, general equilibrium analysis, and introductory welfare economics and ...
... Course Description: Demand and supply analysis, consumer behavior and demand theory, production and cost of production, different types of product market structures, price determination in factor markets, decision-making over time, general equilibrium analysis, and introductory welfare economics and ...
Old Midterm - Instructure
... 3. (14 points) Consider the nation-wide market for Washington (WA) apples and Florida (FL) oranges, which are considered substitutes. a) (2 points) Is the cross-price elasticity of demand between apples and oranges positive or negative if they are substitutes? b) (6 points) The graph below represent ...
... 3. (14 points) Consider the nation-wide market for Washington (WA) apples and Florida (FL) oranges, which are considered substitutes. a) (2 points) Is the cross-price elasticity of demand between apples and oranges positive or negative if they are substitutes? b) (6 points) The graph below represent ...
Lecture 5 The Market Equilibrium
... census data. That’s the highest vacancy rate in the region, and a 70 percent increase from a decade ago." The reason? The city's rent control laws make it difficult to raise rents or evict a tenant. "Increasingly, small-time landlords are just giving up, like one who has left two large apartments on ...
... census data. That’s the highest vacancy rate in the region, and a 70 percent increase from a decade ago." The reason? The city's rent control laws make it difficult to raise rents or evict a tenant. "Increasingly, small-time landlords are just giving up, like one who has left two large apartments on ...
Answers to Extra Practice Quiz
... c. (1 point) In the short run we can expect the quantity produced by the market to _____________increase_________. d. (1 point) In the long run if this is a constant cost industry the market price will be (higher, lower, or equal to) the original market price. e. (1 point) In the long run given this ...
... c. (1 point) In the short run we can expect the quantity produced by the market to _____________increase_________. d. (1 point) In the long run if this is a constant cost industry the market price will be (higher, lower, or equal to) the original market price. e. (1 point) In the long run given this ...
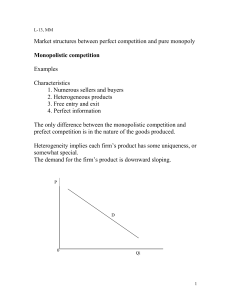
Market structures between perfect competition and pure monopoly
... 2. Inefficiency Not at the point where MU = MC 3. Yet it provides a variety of goods and offer a wide range of choice, which benefits consumers. ...
... 2. Inefficiency Not at the point where MU = MC 3. Yet it provides a variety of goods and offer a wide range of choice, which benefits consumers. ...
Section 2: Changes in Market equilibrium
... When the supply curves shifts to the left, the equilibrium price & quantity sold will change as well As the supply curve shifts to the left, suppliers raise their prices & the ...
... When the supply curves shifts to the left, the equilibrium price & quantity sold will change as well As the supply curve shifts to the left, suppliers raise their prices & the ...
economics paper i
... 1. If the demand and supply function of raw cotton are Qd=250-50P and Qs=25+25P. Find the equilibrium price and the equilibrium quantity demanded and supplied and prove that any price other than equilibrium price leads either to excess supply or excess demand. ...
... 1. If the demand and supply function of raw cotton are Qd=250-50P and Qs=25+25P. Find the equilibrium price and the equilibrium quantity demanded and supplied and prove that any price other than equilibrium price leads either to excess supply or excess demand. ...
ecn5402.ch01
... The Economic Theory of Value • Marshallian Supply-Demand Synthesis – Alfred Marshall showed that supply and demand simultaneously operate to determine price – Prices reflect both the marginal evaluation that consumers place on goods and the marginal costs of producing the goods • Water has a low ma ...
... The Economic Theory of Value • Marshallian Supply-Demand Synthesis – Alfred Marshall showed that supply and demand simultaneously operate to determine price – Prices reflect both the marginal evaluation that consumers place on goods and the marginal costs of producing the goods • Water has a low ma ...
Perfect Competition
... No individual firm or buyer, no matter how large their sales or purchases, can influence market quantity. ...
... No individual firm or buyer, no matter how large their sales or purchases, can influence market quantity. ...