Suppose you run an ice cream store
... price, and this brings up the question of the elasticity of demand. Elasticity means responsiveness. Suppose you have a piece of elastic. If you stretch it, it responds and changes shape. If it didn’t change shape, that is, if it were unresponsive to your pulling on it, it wouldn’t be elastic, would ...
... price, and this brings up the question of the elasticity of demand. Elasticity means responsiveness. Suppose you have a piece of elastic. If you stretch it, it responds and changes shape. If it didn’t change shape, that is, if it were unresponsive to your pulling on it, it wouldn’t be elastic, would ...
UNIT 6: Economics
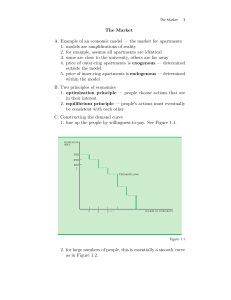
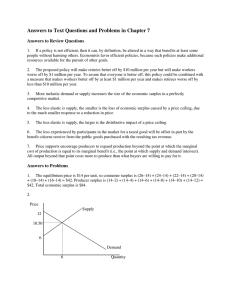
... prices couldn’t be lower. If they were then firms would make losses and leave the industry. Consumers in this market are getting the product at the lowest possible price consistent with a reliable source of supply. A second point is worth making too. Notice that in the middle diagram production is t ...
... prices couldn’t be lower. If they were then firms would make losses and leave the industry. Consumers in this market are getting the product at the lowest possible price consistent with a reliable source of supply. A second point is worth making too. Notice that in the middle diagram production is t ...
Meaning of elasticity of demand
... It is When two goods are not related to each other. FOR EXAMPLE Rise in the price of wheat will have no effect on demand for shoes. Their cross elasticity of demand will be called zero. ...
... It is When two goods are not related to each other. FOR EXAMPLE Rise in the price of wheat will have no effect on demand for shoes. Their cross elasticity of demand will be called zero. ...
monopolist
... Rates then increased sharply and so local governments had to set limits on cable prices. The cost of “basic” service leveled off. Although cable TV is a monopoly, other players have emerged, such as fiber-optic Internet providers, who caused prices to drop. ...
... Rates then increased sharply and so local governments had to set limits on cable prices. The cost of “basic” service leveled off. Although cable TV is a monopoly, other players have emerged, such as fiber-optic Internet providers, who caused prices to drop. ...
Q = 100K 0.5 L 0.5
... We know that L=K, w=10, r=20, so (10)(L) + (20)(L) = 1200, therefore L=40, K=40 ...
... We know that L=K, w=10, r=20, so (10)(L) + (20)(L) = 1200, therefore L=40, K=40 ...
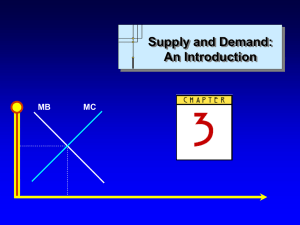
Supply and Demand: An Introduction
... An Increase In Quantity Supplied vs. An Increase In Supplied Price ...
... An Increase In Quantity Supplied vs. An Increase In Supplied Price ...
Week 6 Chapter 5 & 6: Main lecture on Revenue and Production
... the total market and that they do not have much influence over the price charged. • In such a market if they raise price people will go elsewhere… • … and if they reduce price (even if it were profitable) they would not be able to cope with the resultant demand. ...
... the total market and that they do not have much influence over the price charged. • In such a market if they raise price people will go elsewhere… • … and if they reduce price (even if it were profitable) they would not be able to cope with the resultant demand. ...
Document
... 'Price elasticity of demand' ('PED' or 'Ed') is a measure used in economics to show the responsiveness, or elasticity (economics)|elasticity, of the quantity demanded of a good or service to a change in its price. More precisely, it gives the percentage change in quantity demanded in response to a o ...
... 'Price elasticity of demand' ('PED' or 'Ed') is a measure used in economics to show the responsiveness, or elasticity (economics)|elasticity, of the quantity demanded of a good or service to a change in its price. More precisely, it gives the percentage change in quantity demanded in response to a o ...
Supply and demand
In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. It concludes that in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good, or other traded item such as labor or liquid financial assets, will vary until it settles at a point where the quantity demanded (at the current price) will equal the quantity supplied (at the current price), resulting in an economic equilibrium for price and quantity transacted.The four basic laws of supply and demand are: If demand increases (demand curve shifts to the right) and supply remains unchanged, a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price. If demand decreases (demand curve shifts to the left) and supply remains unchanged, a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply increases (supply curve shifts to the right), a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply decreases (supply curve shifts to the left), a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price.↑