Benefit, Cost, & “Producer Surplus”
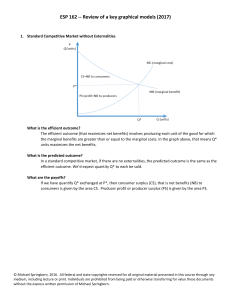
... Resource use efficient when marginal social benefit equals marginal social cost. When the efficient quantity is produced, total surplus (the sum of consumer surplus and producer surplus) is maximized. ...
... Resource use efficient when marginal social benefit equals marginal social cost. When the efficient quantity is produced, total surplus (the sum of consumer surplus and producer surplus) is maximized. ...
Review of key models used
... The efficient outcome is for quantity and price to be such thatis to minimize the sum of the total damage and total abatement cost, i.e. keep reducing emissions until the avoided MD no longer outweighs the MAC. the marginal abatement cost equals the marginal damages. This occurs when pollution is pr ...
... The efficient outcome is for quantity and price to be such thatis to minimize the sum of the total damage and total abatement cost, i.e. keep reducing emissions until the avoided MD no longer outweighs the MAC. the marginal abatement cost equals the marginal damages. This occurs when pollution is pr ...
The Consumer`s Psychology and his Purchasing Power– Milestones
... the present. [...] It seemed unnatural that no plan figures are coming, that nobody is telling the enterprises what to produce and where to deliver the products...”7 In these conditions, from an economy fallen into fiction, but in which the statistical data confirmed however “the prices stability” o ...
... the present. [...] It seemed unnatural that no plan figures are coming, that nobody is telling the enterprises what to produce and where to deliver the products...”7 In these conditions, from an economy fallen into fiction, but in which the statistical data confirmed however “the prices stability” o ...
Section 1.7
... Substitute the expression from step 1 into the other equation to give an equation in one variable. Solve the linear equation for the variable. Substitute this solution into the equation from step 1 or into one of the original equations and solve this equation for the second variable. Check the solut ...
... Substitute the expression from step 1 into the other equation to give an equation in one variable. Solve the linear equation for the variable. Substitute this solution into the equation from step 1 or into one of the original equations and solve this equation for the second variable. Check the solut ...
Varian-Chapter 25
... Then there is no NE at all! Why? The possibilities are: – (i) All 3 sellers locate at the same point. – (ii) 2 sellers locate at the same point. – (iii) Every seller locates at a different ...
... Then there is no NE at all! Why? The possibilities are: – (i) All 3 sellers locate at the same point. – (ii) 2 sellers locate at the same point. – (iii) Every seller locates at a different ...
lecture 5 - WordPress @ VIU Sites
... Monopolistic Competition (market power based on product differentiation) – Large number of relatively small firms acting ...
... Monopolistic Competition (market power based on product differentiation) – Large number of relatively small firms acting ...
EC 101
... caused by the tax. b. bounded by the supply curve, the demand curve, the effective price paid by buyers, and the effective price received by sellers. c. a right triangle. d. a triangle, but not necessarily a right triangle. ANS: A 8. Taxes cause deadweight losses because they a. lead to losses in su ...
... caused by the tax. b. bounded by the supply curve, the demand curve, the effective price paid by buyers, and the effective price received by sellers. c. a right triangle. d. a triangle, but not necessarily a right triangle. ANS: A 8. Taxes cause deadweight losses because they a. lead to losses in su ...
Sample Exam Questions
... 16. Explain the effect on consumers and producers when the government grants a subsidy to the producers of a product that has relatively elastic demand and supply. 17. Using a diagram, explain why cigarette smoking is a cause of market failure. 18. Use a diagram to explain why government interventio ...
... 16. Explain the effect on consumers and producers when the government grants a subsidy to the producers of a product that has relatively elastic demand and supply. 17. Using a diagram, explain why cigarette smoking is a cause of market failure. 18. Use a diagram to explain why government interventio ...
1/23) PP Curve and Terms of Trade
... Quantity demanded--it is the amount that will be purchased at a specific P. Demand--it is a schedule of quantities of goods and services that will be purchased at various prices at a specified time, all other things held constant. ...
... Quantity demanded--it is the amount that will be purchased at a specific P. Demand--it is a schedule of quantities of goods and services that will be purchased at various prices at a specified time, all other things held constant. ...
This PDF is a selection from an out-of-print volume from... Bureau of Economic Research
... where w is its wage rate in the labor market, the labor market, and V is its nonwage income for the period.' Given an appropriately inclusive definition of market goods, the money income is equal to the total money expenditure. The household also has some fixed amount of time at its disposal, t, whi ...
... where w is its wage rate in the labor market, the labor market, and V is its nonwage income for the period.' Given an appropriately inclusive definition of market goods, the money income is equal to the total money expenditure. The household also has some fixed amount of time at its disposal, t, whi ...
Supply and demand
In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. It concludes that in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good, or other traded item such as labor or liquid financial assets, will vary until it settles at a point where the quantity demanded (at the current price) will equal the quantity supplied (at the current price), resulting in an economic equilibrium for price and quantity transacted.The four basic laws of supply and demand are: If demand increases (demand curve shifts to the right) and supply remains unchanged, a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price. If demand decreases (demand curve shifts to the left) and supply remains unchanged, a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply increases (supply curve shifts to the right), a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply decreases (supply curve shifts to the left), a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price.↑