file
... quantities of life saving drugs are needed no matter what the cost=inelastic. If a resturant can get a better deal on ketchup x vs. y they will buy x (both taste the same and are needed in large ...
... quantities of life saving drugs are needed no matter what the cost=inelastic. If a resturant can get a better deal on ketchup x vs. y they will buy x (both taste the same and are needed in large ...
Microeconomics
... a. List several factors that may change the demand for this product by consumers. ...
... a. List several factors that may change the demand for this product by consumers. ...
AP Macroeconomics - Princeton High School
... test. For the problem, know how to evaluate the effect on equilibrium price and quantity caused by a change in supply and/or demand. Make sure you can identify the non-price determinants of supply and demand. Section 1 Module 1: Macroeconomics vs Microeconomics Scarce economic resources Opport ...
... test. For the problem, know how to evaluate the effect on equilibrium price and quantity caused by a change in supply and/or demand. Make sure you can identify the non-price determinants of supply and demand. Section 1 Module 1: Macroeconomics vs Microeconomics Scarce economic resources Opport ...
Homework C due 8th May51.5 KB
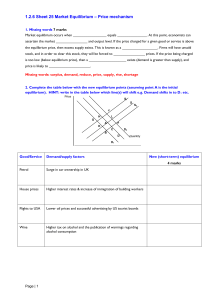
... 1.2.6 Sheet 25 Market Equilibrium – Price mechanism 1. Missing words 7 marks Market equilibrium occurs when _________________ equals _______________. At this point, economists can ascertain the market ________________ and output level. If the price charged for a given good or service is above the eq ...
... 1.2.6 Sheet 25 Market Equilibrium – Price mechanism 1. Missing words 7 marks Market equilibrium occurs when _________________ equals _______________. At this point, economists can ascertain the market ________________ and output level. If the price charged for a given good or service is above the eq ...
Chapter 3 - Mr. Lee GWHS
... Circular Flow Model What things flow from each sector of the economy? From Firms? From Households? ...
... Circular Flow Model What things flow from each sector of the economy? From Firms? From Households? ...
Supply and demand in math form
... Say in general demand is expressed as Qd = A – BP, where A and B are positive numbers. Supply would be expressed as Qs = C + DP where D is positive or zero and C could be any number. To find equilibrium in the market 1) Set Qd = QS to have A – BP = C + DP 2) Collect P terms on the right and non P t ...
... Say in general demand is expressed as Qd = A – BP, where A and B are positive numbers. Supply would be expressed as Qs = C + DP where D is positive or zero and C could be any number. To find equilibrium in the market 1) Set Qd = QS to have A – BP = C + DP 2) Collect P terms on the right and non P t ...
Economics FMA 3_2
... The resources listed above are considered to be the four factors of — A industry B entertainment C government D production ...
... The resources listed above are considered to be the four factors of — A industry B entertainment C government D production ...
File
... Sold slowly at first, and it seemed that stores would have surplus Slowly, the toy became very popular, and a shortage developed Because of this, the price went up to ...
... Sold slowly at first, and it seemed that stores would have surplus Slowly, the toy became very popular, and a shortage developed Because of this, the price went up to ...
Chapter 1 Introduction to Managerial Economics
... where: TRt = the firm’s TR in year t TCt = the firm’s TC in year t i = the interest rate and t goes from 1 (next year) to n (the last year in the planning horizon) ...
... where: TRt = the firm’s TR in year t TCt = the firm’s TC in year t i = the interest rate and t goes from 1 (next year) to n (the last year in the planning horizon) ...
Econ Mid-Term Review Jeopardy
... An increase in consumer’s income will cause the demand curve to do this ...
... An increase in consumer’s income will cause the demand curve to do this ...
ECN 111 PRINCIPLES OF MACROECONOMICS HOMEWORK 1
... PLEASE CIRCLE YOUR SECTION: 10 (111 William Smith Hall; 11:30 – 12:45 PM) 11 (113 William Smith Hall; 1:00 – 2:15 PM) ...
... PLEASE CIRCLE YOUR SECTION: 10 (111 William Smith Hall; 11:30 – 12:45 PM) 11 (113 William Smith Hall; 1:00 – 2:15 PM) ...
Midterm Review Jeopardy
... demanded is to a price change- the percent change in quantity demanded divided by the change in price ...
... demanded is to a price change- the percent change in quantity demanded divided by the change in price ...
Student Number:
... Question 1. [5 marks] Suppose the market demand curve for a product is given by Qd=100-2 P-2U and the market supply curve is given by Qs = -34+5 P +2V. Assume initially that U=15 and V=10. Note that U and V refer to some exogenous variables. a) [2.5 marks] Calculate the equilibrium price and quantit ...
... Question 1. [5 marks] Suppose the market demand curve for a product is given by Qd=100-2 P-2U and the market supply curve is given by Qs = -34+5 P +2V. Assume initially that U=15 and V=10. Note that U and V refer to some exogenous variables. a) [2.5 marks] Calculate the equilibrium price and quantit ...
Unit II: Supply and Demand
... What is demand? More than just want of a good or service. Must have: • Desire to buy • Ability, capacity to buy • Willingness to buy product • It is a mix of what consumers can and will buy ...
... What is demand? More than just want of a good or service. Must have: • Desire to buy • Ability, capacity to buy • Willingness to buy product • It is a mix of what consumers can and will buy ...
The Law of Demand
... the market demands a high quantity of a good or service, the prices for that good will be high When the market demands a low quantity, the price will be low ...
... the market demands a high quantity of a good or service, the prices for that good will be high When the market demands a low quantity, the price will be low ...
Eco 101 Principles of Microeconomics
... This problem occurs with public goods when people attempt to enjoy the benefits of such goods without paying for ...
... This problem occurs with public goods when people attempt to enjoy the benefits of such goods without paying for ...
Economics
... 16. What is the point called where quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal? Where can you find this point on the graph? ...
... 16. What is the point called where quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal? Where can you find this point on the graph? ...
Supply and demand
In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. It concludes that in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good, or other traded item such as labor or liquid financial assets, will vary until it settles at a point where the quantity demanded (at the current price) will equal the quantity supplied (at the current price), resulting in an economic equilibrium for price and quantity transacted.The four basic laws of supply and demand are: If demand increases (demand curve shifts to the right) and supply remains unchanged, a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price. If demand decreases (demand curve shifts to the left) and supply remains unchanged, a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply increases (supply curve shifts to the right), a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply decreases (supply curve shifts to the left), a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price.↑