AP Micro Review Powerpoint
... The Basic Determinants of Demand are: 1) consumer tastes and preferences 2) number of consumers in the market 3) consumers’ money incomes 4) prices of related goods 5) consumer expectations about future prices and incomes ...
... The Basic Determinants of Demand are: 1) consumer tastes and preferences 2) number of consumers in the market 3) consumers’ money incomes 4) prices of related goods 5) consumer expectations about future prices and incomes ...
S&D powerpoint
... 6. The teacher will show the question from this PowerPoint presentation on the screen. Once the batters have read the questions, they must turn and face their respective boards to work on the question. There must be NO TALKING from any other team members while the batter is writing the answer on th ...
... 6. The teacher will show the question from this PowerPoint presentation on the screen. Once the batters have read the questions, they must turn and face their respective boards to work on the question. There must be NO TALKING from any other team members while the batter is writing the answer on th ...
Numerical - RN Institute
... per unit respectively. At this point, the marginal rate of substitution will be equal to 6. True or False.Give reason. 41. When elasticity of demand is infinity, slope of demand curve will also be infinity. True or False. Give reason. 42.Find change in expenditure of the commodity when Ed=-0.4 and q ...
... per unit respectively. At this point, the marginal rate of substitution will be equal to 6. True or False.Give reason. 41. When elasticity of demand is infinity, slope of demand curve will also be infinity. True or False. Give reason. 42.Find change in expenditure of the commodity when Ed=-0.4 and q ...
Powerpoint Slides #1
... Price of Service Individual’s Income Price Associated with Doing it at Burger King How much does the person really want to go to China or how big a hassle is it to come ...
... Price of Service Individual’s Income Price Associated with Doing it at Burger King How much does the person really want to go to China or how big a hassle is it to come ...
Ch4
... than the quantity supplied (170 cartons), so there is a surplus of 45 cartons a day. The price begins to fall, and as it does, the quantity demanded increases, the quantity supplied decreases, and the surplus decreases. The price will fall until the surplus is eliminated. The price falls to $1.50 a ...
... than the quantity supplied (170 cartons), so there is a surplus of 45 cartons a day. The price begins to fall, and as it does, the quantity demanded increases, the quantity supplied decreases, and the surplus decreases. The price will fall until the surplus is eliminated. The price falls to $1.50 a ...
Draw a typical firm`s (short-run) marginal cost, average total cost
... The number of firms in the market grows, causing short-run supply curve to shift to right from S1 to S2 . This causes price to fall. Price goes back down to minimum of average total cost. At this point profits are zero so firms stop entering. New long-run equilibrium, at same price as originally, bu ...
... The number of firms in the market grows, causing short-run supply curve to shift to right from S1 to S2 . This causes price to fall. Price goes back down to minimum of average total cost. At this point profits are zero so firms stop entering. New long-run equilibrium, at same price as originally, bu ...
Road opening leads to lifting of price freeze in Zone...
... (PPO) will lift the price freeze, which has been in place since Nov 15, 2004, for Zone 10a (Mary’s Harbour to Cartwright – road connected). The maximum allowable price for all types of gasoline in this zone will increase by 7.8 cents per litre (cpl), diesel by 7.9 cpl, and stove oil by 5.15 cpl. Dav ...
... (PPO) will lift the price freeze, which has been in place since Nov 15, 2004, for Zone 10a (Mary’s Harbour to Cartwright – road connected). The maximum allowable price for all types of gasoline in this zone will increase by 7.8 cents per litre (cpl), diesel by 7.9 cpl, and stove oil by 5.15 cpl. Dav ...
Supply - YLMASS
... Quantity demanded, Quantity supplied and Quantity transacted • Quantity demanded refers to the quantity of a good a consumer plans to buy at each price. • Quantity supplied refers to the quantity of a good a consumer plans to sell at each price. • Quantity transacted/exchanged = quantity bought and ...
... Quantity demanded, Quantity supplied and Quantity transacted • Quantity demanded refers to the quantity of a good a consumer plans to buy at each price. • Quantity supplied refers to the quantity of a good a consumer plans to sell at each price. • Quantity transacted/exchanged = quantity bought and ...
Practice Midterm 1
... a) If the government imposes a 50 cent tax per pack, what effect will this have on the quantity sold? (5 Points) b) Compute the deadweight loss caused by the imposition of the tax (assume that the demand curve is linear (i.e., not curved)). (5 Points) c) Suppose the cross‐price elasticity of d ...
... a) If the government imposes a 50 cent tax per pack, what effect will this have on the quantity sold? (5 Points) b) Compute the deadweight loss caused by the imposition of the tax (assume that the demand curve is linear (i.e., not curved)). (5 Points) c) Suppose the cross‐price elasticity of d ...
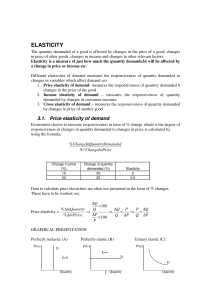
ELASTICITY
... 1. Income inelastic → EY < 1 (Dd rises by a smaller proportion as Y) 2. Unit income elasticity → EY = 1 (Dd rises by exactly the same proportion as Y) 3. Income elastic → EY > 1 (Dd rises by a greater proportion than Y) In the short run, people often save increases in income, so most goods except im ...
... 1. Income inelastic → EY < 1 (Dd rises by a smaller proportion as Y) 2. Unit income elasticity → EY = 1 (Dd rises by exactly the same proportion as Y) 3. Income elastic → EY > 1 (Dd rises by a greater proportion than Y) In the short run, people often save increases in income, so most goods except im ...
The Market for the Factors of Production
... markets for the factors of production. The three most important factors of production are labor, land, and capital. The demand for a factor, such as labor, is a derived demand that comes from firms that use the factors to produce goods and services. ...
... markets for the factors of production. The three most important factors of production are labor, land, and capital. The demand for a factor, such as labor, is a derived demand that comes from firms that use the factors to produce goods and services. ...
Carbon Taxes Vs tradable Permits - Victoria University of Wellington
... Tax Vs Tradable Permit: Perfect Knowledge • Distributional effects (of effectively an additional and new indirect tax) – Government gains area ‘h + i’ – Distribution between producers and consumers depends on relative demand and supply elasticities • Supply perfectly elastic: all passed on to consu ...
... Tax Vs Tradable Permit: Perfect Knowledge • Distributional effects (of effectively an additional and new indirect tax) – Government gains area ‘h + i’ – Distribution between producers and consumers depends on relative demand and supply elasticities • Supply perfectly elastic: all passed on to consu ...
Managerial economics
... of the prices at which the transaction takes place. Under such conditions the price of the commodity will tend to be equal everywhere. Eg-A stock exchange approximates a perfect competition, as do street food markets in developing countries, fish markets and vegetable vendors operating in the same a ...
... of the prices at which the transaction takes place. Under such conditions the price of the commodity will tend to be equal everywhere. Eg-A stock exchange approximates a perfect competition, as do street food markets in developing countries, fish markets and vegetable vendors operating in the same a ...
Week - apgreenecon
... have a direct bearing on one of the markets we are studying in class. For example, you might hear that the frost in California is killing the citrus. Homogonous product? Easy entry (well, not exactly), price taker (yes, for our purposes). So, even though the story is not an exact match for perfect c ...
... have a direct bearing on one of the markets we are studying in class. For example, you might hear that the frost in California is killing the citrus. Homogonous product? Easy entry (well, not exactly), price taker (yes, for our purposes). So, even though the story is not an exact match for perfect c ...
Supply and demand
In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. It concludes that in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good, or other traded item such as labor or liquid financial assets, will vary until it settles at a point where the quantity demanded (at the current price) will equal the quantity supplied (at the current price), resulting in an economic equilibrium for price and quantity transacted.The four basic laws of supply and demand are: If demand increases (demand curve shifts to the right) and supply remains unchanged, a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price. If demand decreases (demand curve shifts to the left) and supply remains unchanged, a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply increases (supply curve shifts to the right), a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply decreases (supply curve shifts to the left), a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price.↑