Economics of Labor Econ 355
... – Economists test theoretical predictions made by models by appealing to data. – Data are generally gathered from ongoing behaviors not through an experimental approach common to many of the natural sciences.. ...
... – Economists test theoretical predictions made by models by appealing to data. – Data are generally gathered from ongoing behaviors not through an experimental approach common to many of the natural sciences.. ...
Industry Structure I - BYU Marriott School
... Free entry and exit Many, well-informed customers ...
... Free entry and exit Many, well-informed customers ...
Outline of Lecture 1 – Basic Economics Concepts
... Then, after students feel comfortable with this, add average total cost (to teach students how to measure profit or loss). Last, add average variable cost to teach students about the short-run shutdown decision of a firm earning an economic loss. ...
... Then, after students feel comfortable with this, add average total cost (to teach students how to measure profit or loss). Last, add average variable cost to teach students about the short-run shutdown decision of a firm earning an economic loss. ...
Economics
... Define an Indifference Curve What do you mean by utility When is Total Utility Maximum When can Total Utility be negative? In economics what we assume about the marginal utility of money? Explain the relationship between total and marginal utility Why does budget line slope downwards from left to ri ...
... Define an Indifference Curve What do you mean by utility When is Total Utility Maximum When can Total Utility be negative? In economics what we assume about the marginal utility of money? Explain the relationship between total and marginal utility Why does budget line slope downwards from left to ri ...
Price
... price ceilings and floors Prices balance supply and demand and thus coordinate economic activity. If prices are set by laws, they obscure the signals that efficiently allocate scarce resources. Price ceilings and price floors often hurt the people they are intended to help. - Rent controls create a ...
... price ceilings and floors Prices balance supply and demand and thus coordinate economic activity. If prices are set by laws, they obscure the signals that efficiently allocate scarce resources. Price ceilings and price floors often hurt the people they are intended to help. - Rent controls create a ...
Topic 5 – Perfect Competition and Monopoly
... to it from all the other firms, and because the individual firm is so small relative to industry output, to all intents and purposes demand is perfectly elastic. III. There is a distinction between the short run and long run responses to changes in demand or supply conditions. In the short run, ind ...
... to it from all the other firms, and because the individual firm is so small relative to industry output, to all intents and purposes demand is perfectly elastic. III. There is a distinction between the short run and long run responses to changes in demand or supply conditions. In the short run, ind ...
Monopoly and Antitrust Policy
... With one firm in a monopoly market, there is no distinction between the firm and the industry. In a monopoly, the firm is the industry. The market demand curve is the demand curve facing the firm, and the total quantity supplied in the market is what the firm decides to produce. ...
... With one firm in a monopoly market, there is no distinction between the firm and the industry. In a monopoly, the firm is the industry. The market demand curve is the demand curve facing the firm, and the total quantity supplied in the market is what the firm decides to produce. ...
mmaaold
... (Note: The concept of a price ceiling in the wheat market may seem a bit odd relative to the U.S. agriculture policy experience. This is not that strange when one investigates agricultural policy experiences in other countries. A particularly interesting wheat pricing situation occurred in Poland fr ...
... (Note: The concept of a price ceiling in the wheat market may seem a bit odd relative to the U.S. agriculture policy experience. This is not that strange when one investigates agricultural policy experiences in other countries. A particularly interesting wheat pricing situation occurred in Poland fr ...
CHAPTER 3: DEMAND, SUPPLY, AND MARKET EQUILIBRIUM
... Demand Demand is the consumer’s willingness and ability to buy a product at a particular price. Both elements must be present because producers do not respond to wish lists; they produce for customers who are actually able to buy the product. Demand is determined first by developing a schedule indic ...
... Demand Demand is the consumer’s willingness and ability to buy a product at a particular price. Both elements must be present because producers do not respond to wish lists; they produce for customers who are actually able to buy the product. Demand is determined first by developing a schedule indic ...
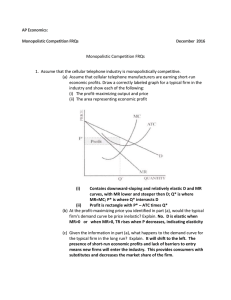
Monopolistic Competition FRQs answers
... (b) At the profit-maximizing price you identified in part (a), would the typical firm's demand curve be price inelastic? Explain. No. D is elastic when MR>0 or when MR>0, TR rises when P decreases, indicating elasticity (c) Given the information in part (a), what happens to the demand curve for the ...
... (b) At the profit-maximizing price you identified in part (a), would the typical firm's demand curve be price inelastic? Explain. No. D is elastic when MR>0 or when MR>0, TR rises when P decreases, indicating elasticity (c) Given the information in part (a), what happens to the demand curve for the ...
Elastic Demand
... • If coefficient is negative (shows inverse relationship) then the good is inferior • If coefficient is positive (shows direct relationship) then the good is normal Ex: If income falls 10% and quantity falls 20%… ...
... • If coefficient is negative (shows inverse relationship) then the good is inferior • If coefficient is positive (shows direct relationship) then the good is normal Ex: If income falls 10% and quantity falls 20%… ...
File
... Microeconomics is generally the study of individuals and business decisions; macroeconomics looks at higher up country and government decisions. Microeconomics Microeconomics is the study of decisions that people and businesses make regarding resources and prices of goods and services. This means al ...
... Microeconomics is generally the study of individuals and business decisions; macroeconomics looks at higher up country and government decisions. Microeconomics Microeconomics is the study of decisions that people and businesses make regarding resources and prices of goods and services. This means al ...
Chapter 5 - Elasticity and its application -class
... very high at low levels of quantity supplied and very low at high levels of quantity supplied. Here an increase in price from $3 to $4 increases the quantity supplied from 100 to 200. Because the 67 percent increase in quantity supplied (computed using the midpoint method) is larger than the 29 perc ...
... very high at low levels of quantity supplied and very low at high levels of quantity supplied. Here an increase in price from $3 to $4 increases the quantity supplied from 100 to 200. Because the 67 percent increase in quantity supplied (computed using the midpoint method) is larger than the 29 perc ...
Supply and demand
In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. It concludes that in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good, or other traded item such as labor or liquid financial assets, will vary until it settles at a point where the quantity demanded (at the current price) will equal the quantity supplied (at the current price), resulting in an economic equilibrium for price and quantity transacted.The four basic laws of supply and demand are: If demand increases (demand curve shifts to the right) and supply remains unchanged, a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price. If demand decreases (demand curve shifts to the left) and supply remains unchanged, a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply increases (supply curve shifts to the right), a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply decreases (supply curve shifts to the left), a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price.↑