Micro Questions - personal.kent.edu
... wishes. Determine how many plants Acme will operate, the number of widgets it will produce at each plant, the price it will charge for widgets, and its profits. (Acme’s environmental exemption and hence its cost break applies to only one plant) d) Now suppose that widgets are subject to a $1 tax. Wh ...
... wishes. Determine how many plants Acme will operate, the number of widgets it will produce at each plant, the price it will charge for widgets, and its profits. (Acme’s environmental exemption and hence its cost break applies to only one plant) d) Now suppose that widgets are subject to a $1 tax. Wh ...
First Generation Marginalists
... • Price adjustment leading to quantity adjustments (Q is the dependant variable) • But the system will fail if there is any trading at non-equilibrium prices • Analysis of an equilibrium system only ...
... • Price adjustment leading to quantity adjustments (Q is the dependant variable) • But the system will fail if there is any trading at non-equilibrium prices • Analysis of an equilibrium system only ...
Chapter 5 - Elasticity and its application -class
... very high at low levels of quantity supplied and very low at high levels of quantity supplied. Here an increase in price from $3 to $4 increases the quantity supplied from 100 to 200. Because the 67 percent increase in quantity supplied (computed using the midpoint method) is larger than the 29 perc ...
... very high at low levels of quantity supplied and very low at high levels of quantity supplied. Here an increase in price from $3 to $4 increases the quantity supplied from 100 to 200. Because the 67 percent increase in quantity supplied (computed using the midpoint method) is larger than the 29 perc ...
Price elasticity of supply
... The good news about an increase in price is that a higher price will increase the revenue obtained from each unit sold. The bad news is that at a higher price, fewer units are sold. Elasticity of demand tells us whether ...
... The good news about an increase in price is that a higher price will increase the revenue obtained from each unit sold. The bad news is that at a higher price, fewer units are sold. Elasticity of demand tells us whether ...
Micro chapter 25- presentation 1 Derived Demand
... Different Market Structures In the oligopoly, pure monopoly and monopolistic ...
... Different Market Structures In the oligopoly, pure monopoly and monopolistic ...
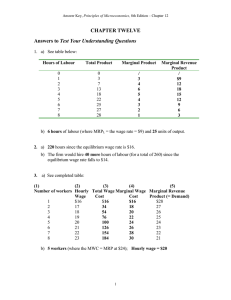
Answer Key
... e) The new quantity, Q2, could be higher, lower or exactly equal to Q1 depending on the magnitudes of the shifts in D2 and S2. f) The demand for labour could increase because labour productivity rises or because total output for the economy increase while the decrease in the supply of labour could b ...
... e) The new quantity, Q2, could be higher, lower or exactly equal to Q1 depending on the magnitudes of the shifts in D2 and S2. f) The demand for labour could increase because labour productivity rises or because total output for the economy increase while the decrease in the supply of labour could b ...
Midterm and Key 04
... greater quantities of one input gained by trading away quantities of the other input now used in smaller portions. But as he thus trades, he retains the same output as he slides along the same isoquant. That would mean that all the gains of trade are going to the other producer. An alternative outco ...
... greater quantities of one input gained by trading away quantities of the other input now used in smaller portions. But as he thus trades, he retains the same output as he slides along the same isoquant. That would mean that all the gains of trade are going to the other producer. An alternative outco ...
ch09, lecture
... Monopoly disadvantages are these: (1) A monopolist charges a higher price and produces less output than a perfectly competitive firm, (2) resource allocation is inefficient because the monopolist produces less than if competition existed, (3) monopoly produces higher long-run profits than if compet ...
... Monopoly disadvantages are these: (1) A monopolist charges a higher price and produces less output than a perfectly competitive firm, (2) resource allocation is inefficient because the monopolist produces less than if competition existed, (3) monopoly produces higher long-run profits than if compet ...
1. a. They currently have together 4 fish and 4 pounds
... b. If the amount of plastic in a toy is fixed, then the revenue to toy makers rises and out of pocket costs go down (though opportunity costs may go up.) c. You can't tell whether they will buy, sell, or keep the 85 percent. At the new equilibrium opportunity cost of plastic, it is likely that a com ...
... b. If the amount of plastic in a toy is fixed, then the revenue to toy makers rises and out of pocket costs go down (though opportunity costs may go up.) c. You can't tell whether they will buy, sell, or keep the 85 percent. At the new equilibrium opportunity cost of plastic, it is likely that a com ...
AP Micro 2-9 Summary
... start to decrease • In other words, the more you buy of ANY GOOD the less satisfaction you get from each new unit. Discussion Questions: 1. What does this have to do with the Law of Demand? 2. How does this effect the pricing of businesses? ...
... start to decrease • In other words, the more you buy of ANY GOOD the less satisfaction you get from each new unit. Discussion Questions: 1. What does this have to do with the Law of Demand? 2. How does this effect the pricing of businesses? ...
EC1110 -Demand and Supply - Paul Tilley`s Resource Wiki
... • Horizontal summation of each individual producer’s supply curve ...
... • Horizontal summation of each individual producer’s supply curve ...
Test #1, ECMC02, Oct 10 2003
... the new supply curve (S=) and show the new equilibrium quantity (Q1*) and the new equilibrium price (P1*). (b) Now suppose that a 50% tariff is placed on shoes. Show the new supply curve (S@) and the new (after-tariff) equilibrium quantity (Q2*) and the new equilibrium price (P2*). (c) Indicate by s ...
... the new supply curve (S=) and show the new equilibrium quantity (Q1*) and the new equilibrium price (P1*). (b) Now suppose that a 50% tariff is placed on shoes. Show the new supply curve (S@) and the new (after-tariff) equilibrium quantity (Q2*) and the new equilibrium price (P2*). (c) Indicate by s ...
Pure Monopoly: Cost and Revenue Data
... AP Microeconomics: Unit on Market Structures Lesson 04: Monopoly– Handout 02 Module 03: Theory of the Firm ...
... AP Microeconomics: Unit on Market Structures Lesson 04: Monopoly– Handout 02 Module 03: Theory of the Firm ...
How a monopolist determines the profit
... quantity effect (the price received from the additional unit) and a price effect (the reduction in the price at which all units are sold). Because of the price effect, a monopolist’s marginal revenue is always less than the market price, and the marginal revenue curve lies below the demand curve. 20 ...
... quantity effect (the price received from the additional unit) and a price effect (the reduction in the price at which all units are sold). Because of the price effect, a monopolist’s marginal revenue is always less than the market price, and the marginal revenue curve lies below the demand curve. 20 ...
3. CONCEPT OF ELASTICITY
... If the economy is already using most of its scarce resources then firms will find it difficult to employ more and so output will not be able to rise. The supply of most goods and services will therefore be price inelastic. If, however, there is much unemployment of resources, for example, labour, fi ...
... If the economy is already using most of its scarce resources then firms will find it difficult to employ more and so output will not be able to rise. The supply of most goods and services will therefore be price inelastic. If, however, there is much unemployment of resources, for example, labour, fi ...
LectE3 - University of Washington
... THE DEMAND FOR LABOR FOR AN INDIVIDUAL FIRM IS GIVEN BY THE DECLINING PORTION OF THE VALUE OF THE MARGINAL PRODUCT THE MARKET WAGE RATE IS DETERMINED BY THE DEMAND BY ALL “EMPLOYERS” AND THE SUPPLY OF LABOR SERVICES BASIC THEORY OF WAGE DETERMINATION SUPPLY AND DEMAND SUPPLY - determined by people’ ...
... THE DEMAND FOR LABOR FOR AN INDIVIDUAL FIRM IS GIVEN BY THE DECLINING PORTION OF THE VALUE OF THE MARGINAL PRODUCT THE MARKET WAGE RATE IS DETERMINED BY THE DEMAND BY ALL “EMPLOYERS” AND THE SUPPLY OF LABOR SERVICES BASIC THEORY OF WAGE DETERMINATION SUPPLY AND DEMAND SUPPLY - determined by people’ ...
Supply and demand
In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. It concludes that in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good, or other traded item such as labor or liquid financial assets, will vary until it settles at a point where the quantity demanded (at the current price) will equal the quantity supplied (at the current price), resulting in an economic equilibrium for price and quantity transacted.The four basic laws of supply and demand are: If demand increases (demand curve shifts to the right) and supply remains unchanged, a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price. If demand decreases (demand curve shifts to the left) and supply remains unchanged, a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply increases (supply curve shifts to the right), a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply decreases (supply curve shifts to the left), a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price.↑