Chapter 6 Notes on Economics
... 1. Price Ceiling – maximum price that can be legally charged for a good. 2. Price Floor – a minimum price for a good or service. a. Price Ceiling – government places price ceiling on goods that are considered “essential” and might be too expensive for some consumers. Ex: Rent Control in NYC. *But, t ...
... 1. Price Ceiling – maximum price that can be legally charged for a good. 2. Price Floor – a minimum price for a good or service. a. Price Ceiling – government places price ceiling on goods that are considered “essential” and might be too expensive for some consumers. Ex: Rent Control in NYC. *But, t ...
Final Exam Review Sheet
... 16. Impact of price floors (minimum wages) and price ceilings (rent control) on market, quantity supplied and quantity demanded. 17. Using equations to calculate market equilibrium. 18. Finding consumer surplus, producer surplus, social surplus, and dead weight loss on a graph. 19. Impact of a unit ...
... 16. Impact of price floors (minimum wages) and price ceilings (rent control) on market, quantity supplied and quantity demanded. 17. Using equations to calculate market equilibrium. 18. Finding consumer surplus, producer surplus, social surplus, and dead weight loss on a graph. 19. Impact of a unit ...
1.3 Choosing to spend
... • When buyers and sellers come together, a market is formed. • For most goods and services, the market price is determined by the amount buyers are willing to pay and the price that businesses need to be paid to cover their costs. • Eventually, the price will settle at a point where supply equals de ...
... • When buyers and sellers come together, a market is formed. • For most goods and services, the market price is determined by the amount buyers are willing to pay and the price that businesses need to be paid to cover their costs. • Eventually, the price will settle at a point where supply equals de ...
Precept03Q.pdf
... outlined in Pindyck-Rubinfeld, pp. 47-57. As in P-R, we will assume that the supply and demand curves are straight lines. (Note – We will discuss this assumption in the precept.) We use estimates of elasticities produced by previous researchers, and current quantity and price information, to find th ...
... outlined in Pindyck-Rubinfeld, pp. 47-57. As in P-R, we will assume that the supply and demand curves are straight lines. (Note – We will discuss this assumption in the precept.) We use estimates of elasticities produced by previous researchers, and current quantity and price information, to find th ...
Eco 101 Principles of Microeconomics
... slopes down, we expect elasticity to have this property. ...
... slopes down, we expect elasticity to have this property. ...
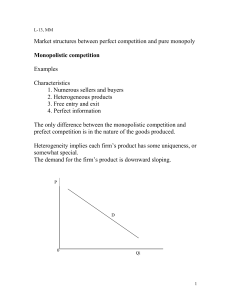
Market structures between perfect competition and pure monopoly
... 4. Perfect information The only difference between the monopolistic competition and prefect competition is in the nature of the goods produced. Heterogeneity implies each firm’s product has some uniqueness, or somewhat special. The demand for the firm’s product is downward sloping. ...
... 4. Perfect information The only difference between the monopolistic competition and prefect competition is in the nature of the goods produced. Heterogeneity implies each firm’s product has some uniqueness, or somewhat special. The demand for the firm’s product is downward sloping. ...
Equilibrium Price - JaminetEconomics
... D. Surpluses occur when the quantity supplied (at equilibrium price) is greater than quantity demanded. E. Market forces can cause the prices to rise or fall to correct shortages and surpluses. ...
... D. Surpluses occur when the quantity supplied (at equilibrium price) is greater than quantity demanded. E. Market forces can cause the prices to rise or fall to correct shortages and surpluses. ...
The invisible Hand
... power. • Producers aim to sell at the highest possible price so they can maximise their revenue. • Market equilibrium occurs at the price where quantity demanded equals quantity supplied. ...
... power. • Producers aim to sell at the highest possible price so they can maximise their revenue. • Market equilibrium occurs at the price where quantity demanded equals quantity supplied. ...
1 - Washington College
... axis of your graph, show the quantity of DVD rentals. On the vertical axis show the price per DVD rental. Since I am not giving you specific data on prices and quantities, make a “freehand” drawing of the curve or curves you are asked to examine. Focus on the general shape and position of the curve( ...
... axis of your graph, show the quantity of DVD rentals. On the vertical axis show the price per DVD rental. Since I am not giving you specific data on prices and quantities, make a “freehand” drawing of the curve or curves you are asked to examine. Focus on the general shape and position of the curve( ...
The Free Enterprise System
... • Profit – the money earned from conducting business after all costs and expenses are paid. – Profit is the motivation for taking a risk. – Profits are high when sales are high and costs are low. ...
... • Profit – the money earned from conducting business after all costs and expenses are paid. – Profit is the motivation for taking a risk. – Profits are high when sales are high and costs are low. ...
Review of Supply and Demand
... market supply curve shows the market quantity supplied (the amount that sellers of the good want to sell) at each price holding all factors other than the price of the good constant (ceteris paribus). In addition to the price of a good, factors that may affect the supply for a good are: P Prices of ...
... market supply curve shows the market quantity supplied (the amount that sellers of the good want to sell) at each price holding all factors other than the price of the good constant (ceteris paribus). In addition to the price of a good, factors that may affect the supply for a good are: P Prices of ...
public_finance_part1_ch1 (2)
... 3- Capability of reducing and increasing quantities of supply according to the changes of prices 4- Prices in the inputs markets continually adjust to the equilibrium of market demand (firms) and market supply (resources) 5- Organization of production is determined by consumers sovereignty 6- The pr ...
... 3- Capability of reducing and increasing quantities of supply according to the changes of prices 4- Prices in the inputs markets continually adjust to the equilibrium of market demand (firms) and market supply (resources) 5- Organization of production is determined by consumers sovereignty 6- The pr ...
Document
... be legally charged for a good or service. The government interferes with market equilibrium when it creates a price floor. Minimum wage is an example of a price ...
... be legally charged for a good or service. The government interferes with market equilibrium when it creates a price floor. Minimum wage is an example of a price ...
Answers to pause for thought questions
... profit. We will explore this relationship in the next chapter.) Even though an increase in production will lead to an increase in revenue for the firm, costs may increase by more than revenue, thereby reducing the firm's profits. The issue, then, is whether revenue increases more than costs (in whic ...
... profit. We will explore this relationship in the next chapter.) Even though an increase in production will lead to an increase in revenue for the firm, costs may increase by more than revenue, thereby reducing the firm's profits. The issue, then, is whether revenue increases more than costs (in whic ...
Perfect Competition
... No individual firm or buyer, no matter how large their sales or purchases, can influence market quantity. ...
... No individual firm or buyer, no matter how large their sales or purchases, can influence market quantity. ...
Honors Economics Unit 2 Study Guide
... 21. Define rent control. (129)What type of price fixing is this?(129) 22. Define minimum wage. (130)What happens if the government sets wages above the equilibrium level?(130) 23. What happens at market equilibrium?(125) 24. What happens to a market in equilibrium when there is an increase in supply ...
... 21. Define rent control. (129)What type of price fixing is this?(129) 22. Define minimum wage. (130)What happens if the government sets wages above the equilibrium level?(130) 23. What happens at market equilibrium?(125) 24. What happens to a market in equilibrium when there is an increase in supply ...
Economic equilibrium

In economics, economic equilibrium is a state where economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external influences the (equilibrium) values of economic variables will not change. For example, in the standard text-book model of perfect competition, equilibrium occurs at the point at which quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal. Market equilibrium in this case refers to a condition where a market price is established through competition such that the amount of goods or services sought by buyers is equal to the amount of goods or services produced by sellers. This price is often called the competitive price or market clearing price and will tend not to change unless demand or supply changes and the quantity is called ""competitive quantity"" or market clearing quantity.