Q1 Common Assessment Study Guide
... 13. (12.2.1) What is the relationship between price & quantity, according to the Law of Demand. Pg. 52 14-15. (12.2.1) What three economic concepts help explain the law of Demand, and how does each work? Pg. 52-54 16. (12.2.1) What is the relationship between price & quantity according to the Law of ...
... 13. (12.2.1) What is the relationship between price & quantity, according to the Law of Demand. Pg. 52 14-15. (12.2.1) What three economic concepts help explain the law of Demand, and how does each work? Pg. 52-54 16. (12.2.1) What is the relationship between price & quantity according to the Law of ...
Market Equilibrium - Purdue Agriculture
... Market Equilibrium Perfect Competition • Supply forces (producers) P and demand forces (consumers) seek a balance • Price below perceived Pe value increases demand • Price above ATC provides pure profit, an incentive to increase supply ...
... Market Equilibrium Perfect Competition • Supply forces (producers) P and demand forces (consumers) seek a balance • Price below perceived Pe value increases demand • Price above ATC provides pure profit, an incentive to increase supply ...
Ch 4-6 Econ Study Guide
... * Define the following… - Disequilibrium: - Equilibrium: - Price ceiling: - Price floor: - Shortage: - Surplus: * When is the market in equilibrium? * When is the market in disequilibrium? * Explain a surplus: - What is greater than what? - What happens to price? * What happens to quantity demanded? ...
... * Define the following… - Disequilibrium: - Equilibrium: - Price ceiling: - Price floor: - Shortage: - Surplus: * When is the market in equilibrium? * When is the market in disequilibrium? * Explain a surplus: - What is greater than what? - What happens to price? * What happens to quantity demanded? ...
Ch.7 Review Market Equilibrium
... Cannot increase economic well-being by Changing the allocation of consumption among buyers Changing the allocation of production among sellers ...
... Cannot increase economic well-being by Changing the allocation of consumption among buyers Changing the allocation of production among sellers ...
What is Globalization? - Honorsglobalportfolio
... • Supply • The amt of a certain good or service producers are willing to supply when receiving a certain price • Law of Supply: The higher the price, the higher the quantity produced ...
... • Supply • The amt of a certain good or service producers are willing to supply when receiving a certain price • Law of Supply: The higher the price, the higher the quantity produced ...
Movement Along Curves vs. Shifts in Curves
... income, prices, or availabilities. Prices of goods related as substitutes and compliments. The number of buyers in the market. Increase in Demand Change in a non-price factor that causes more of a product to be demanded at each price. Demand curve shift to the right. ...
... income, prices, or availabilities. Prices of goods related as substitutes and compliments. The number of buyers in the market. Increase in Demand Change in a non-price factor that causes more of a product to be demanded at each price. Demand curve shift to the right. ...
lec20 - People.vcu.edu
... In this example each firm would produce 33 1/3 units. (We will not study how this equilibrium is found.) Do these firms make profits in equilibrium? ...
... In this example each firm would produce 33 1/3 units. (We will not study how this equilibrium is found.) Do these firms make profits in equilibrium? ...
Market Structure Wrap-Up
... • An externality is the uncompensated impact of one person’s actions on another person – Both positive & negative externalities exist ...
... • An externality is the uncompensated impact of one person’s actions on another person – Both positive & negative externalities exist ...
Cumulative elasticity factor derivation Qa Pf Pi Supply Demand New
... Demand and supply curves are plotted on a graph with axes representing the market price for a commodity and the quantity demanded or supplied. They cross at the equilibrium point, whose coordinates represent the quantity that will be sold and the price at which each unit will sell, given an efficien ...
... Demand and supply curves are plotted on a graph with axes representing the market price for a commodity and the quantity demanded or supplied. They cross at the equilibrium point, whose coordinates represent the quantity that will be sold and the price at which each unit will sell, given an efficien ...
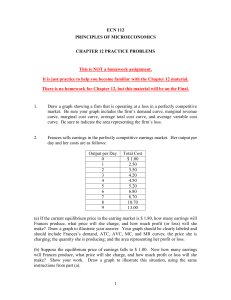
Practice Problems
... (b) Suppose the equilibrium price in the desk lamp market is $ 50. How many table lamps should Edward produce, and how much profit will he make? (c) If next week the equilibrium price of desk lamps drops to $ 30, should Edward shut down? Explain. ...
... (b) Suppose the equilibrium price in the desk lamp market is $ 50. How many table lamps should Edward produce, and how much profit will he make? (c) If next week the equilibrium price of desk lamps drops to $ 30, should Edward shut down? Explain. ...
Warmups 012216
... Tuesday, Jan. 19, 2016 Most countries, including the United States have ______________________ economies If two similar businesses competed against each other, the result would be A. lower prices ...
... Tuesday, Jan. 19, 2016 Most countries, including the United States have ______________________ economies If two similar businesses competed against each other, the result would be A. lower prices ...
Chapter 1
... • Supply Schedule—a table that shows the quantity firms are willing and able to supply at various prices. • Supply Curve—a graph that shows the quantities that sellers are willing and able to supply at different prices. ...
... • Supply Schedule—a table that shows the quantity firms are willing and able to supply at various prices. • Supply Curve—a graph that shows the quantities that sellers are willing and able to supply at different prices. ...
Chapter 6 - Cloudfront.net
... willing to pay this price, were able to buy what they wanted. No one went home empty handed. All sellers, who were offering to sell at this price, were able to sell all that they wanted to sell. They ...
... willing to pay this price, were able to buy what they wanted. No one went home empty handed. All sellers, who were offering to sell at this price, were able to sell all that they wanted to sell. They ...
economics unit #2 study guide
... prices, and profits work to determine production and distribution in a market economy. a. Define the Law of Supply and the Law of Demand. b. Describe the role of buyers and sellers in determining market clearing price. c. Illustrate on a graph how supply and demand determine equilibrium price and qu ...
... prices, and profits work to determine production and distribution in a market economy. a. Define the Law of Supply and the Law of Demand. b. Describe the role of buyers and sellers in determining market clearing price. c. Illustrate on a graph how supply and demand determine equilibrium price and qu ...
Economics 431 Homework 1 Answer key Part II
... This cannot be a long run equilibrium, since the price is above the break-even point. More farmers will enter and supply curve will pivot. Entry will continue until the equilibrium price is back to break-even level of p = 3. Since we know that in the long run price must be back to p = 3, the long-ru ...
... This cannot be a long run equilibrium, since the price is above the break-even point. More farmers will enter and supply curve will pivot. Entry will continue until the equilibrium price is back to break-even level of p = 3. Since we know that in the long run price must be back to p = 3, the long-ru ...
Economic equilibrium

In economics, economic equilibrium is a state where economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external influences the (equilibrium) values of economic variables will not change. For example, in the standard text-book model of perfect competition, equilibrium occurs at the point at which quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal. Market equilibrium in this case refers to a condition where a market price is established through competition such that the amount of goods or services sought by buyers is equal to the amount of goods or services produced by sellers. This price is often called the competitive price or market clearing price and will tend not to change unless demand or supply changes and the quantity is called ""competitive quantity"" or market clearing quantity.