* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download public_finance_part1_ch1 (2)
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
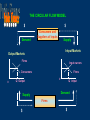
Lectures in By Prof. Dr. Younis El Batrik THE FIELD OF PUBLIC FINANCE Fundamental Economic Facts The Scarcity of Resources The necessity of economizing Choices Private wants/ collective wants Public finance is particularly concerned with the satisfaction of collective wants National resources are divided between the private and the public sector (Gov.) The field of public finance is studying and analysing both sides of the government financial activities (Expenditures/ Revenues) The public and private sectors are complementary The Modern economy is a mixed economy The public sector is complex with numerous activities The classic theory of Adam Smith the government's activities are limited The Economic and social objectives of the modern government include: Provision of public goods and services Full employment of resources A stable value of money Steady economic growth Satisfactory balance of payments Reasonably equitable distribution of income and wealth Minimum standard of individual welfare The Government objectives in the field of public finance Provision of public goods Redistribution of income and wealth Stabilization of level of activity at full employment without inflation Balanced and steady growth of national product The Necessity of Public Sector - Classical theory “ laissez- faire “ Two economic groups: 1- Producers 2- Consumers ( suppliers of inputs) Two Markets: 1- Outputs market 2- Inputs or factors market In outputs markets: The consumer the ratio of marginal utility per price for particular commodity is equal to the ratio of marginal utility per price of other commodities MU1 = P1 MU2 ---------= P2 = MUm Pm In intputs markets: The producer are equal MP1 = P1 marginal product of all inputs relative to its prices MP2 ---------= P2 = MPm Pm This equilibrium reflects the most efficient use of resources -But this requires perfect competition in all markets (inputs & outputs) - What about the social welfare? THE CIRCULAR FLOW MODEL $ Demand $ Consumers and Suppliers of inputs Supply Intput Markets Output Markets Firms Input owners Consumers 0 Firms 0 Q Output Q intput Demand Supply Firms $ $ Based on some assumptions: 1- The market price and quantity are determined by equilibrium of demand and supply 2- The price and quantity of specific resources are determined by equilibrium of firms demand for resources and owners supply 3- Capability of reducing and increasing quantities of supply according to the changes of prices 4- Prices in the inputs markets continually adjust to the equilibrium of market demand (firms) and market supply (resources) 5- Organization of production is determined by consumers sovereignty 6- The price system allows to declare consumers tastes so producers can adjust their productions and achieve maximum profits The Necessary Conditions for perfect Competition Basic Assumptions: -The motive is self interest - Freedom of choice - Private Property - Reliance upon private price mechanism - Limited role of government Pareto Optimum Perfect competition maximizes economic welfare -The consumer preferences outputs are automatically allocated to maximize utility - Any reallocation of inputs or outputs will reduce allocative efficiency - Allocative efficiency optimal welfare situation = Pareto Optimum The pareto optimum accepts whatever distribution of income arises out of free market system first best isolated from social and political justice The value of equity is disregarded THE NEED FOR GOVERNMENT INTERVENTION The Deficiencies of the Price System: 1- Divergence between private and social costs and benefits 2- Diffusion of benefits 3- Loss of consumers sovereignty 4- Inequality of distribution of income and wealth 5- Unemployment 6- Insufficient scale of provision of capital The Economic Intervention of Government - The theory of market failure - J. M. Keynes: The general theory of employment, interest and money (1936) - The periodic booms and slumps of private enterprises (trade cycle) - The need of various actions of government to stabilize the national economy