An Introduction to DNA and Genetics Directions: As you watch the
... ________________________. Mutation causes different versions (alleles) of the same ____________. Parent ______________ are shuffled – or recombined – when sex cells created in the body. Because of _______________________, sexual reproduction produces more ...
... ________________________. Mutation causes different versions (alleles) of the same ____________. Parent ______________ are shuffled – or recombined – when sex cells created in the body. Because of _______________________, sexual reproduction produces more ...
BICH/GENE 431 KNOWLEDGE OBJECTIVES Chapter 9 – Mutations
... - alkylating agents (DMS, nitrosamines, MNNG); common product is O6methylguanine - reactive oxygen species (hydrogen peroxide, hydroxide radicals); common product is oxoG UV light causes pyrimidine dimers, such as thymine dimers Ionizing radiation (x rays, gamma rays) cause ds DNA breaks Bleomycin ( ...
... - alkylating agents (DMS, nitrosamines, MNNG); common product is O6methylguanine - reactive oxygen species (hydrogen peroxide, hydroxide radicals); common product is oxoG UV light causes pyrimidine dimers, such as thymine dimers Ionizing radiation (x rays, gamma rays) cause ds DNA breaks Bleomycin ( ...
Chromosome variation
... 1.Quick review of conjugation: F-, F+, Hfr 2. Transformation: a different process of recombination, can be used to map genes 3. Bacteriophages are viruses that use bacteria as hosts; they can mediate bacterial DNA transfer - transduction 4. Extrachromosomal inheritance: Phenotype of maternal parent ...
... 1.Quick review of conjugation: F-, F+, Hfr 2. Transformation: a different process of recombination, can be used to map genes 3. Bacteriophages are viruses that use bacteria as hosts; they can mediate bacterial DNA transfer - transduction 4. Extrachromosomal inheritance: Phenotype of maternal parent ...
Changes in DNA
... DNA sometimes breaks due to mechanical stress, ionizing radiation, or chemical attack. Most organisms contain enzymes that reassemble broken DNA molecules, called non-homologous end joining. If there is more than one break, ends are joined randomly, which can lead to a rearranged genome. – This brea ...
... DNA sometimes breaks due to mechanical stress, ionizing radiation, or chemical attack. Most organisms contain enzymes that reassemble broken DNA molecules, called non-homologous end joining. If there is more than one break, ends are joined randomly, which can lead to a rearranged genome. – This brea ...
Chapter 25: Molecular Basis of Inheritance
... a tumor, an abnormal mass of cells. Carcinogenesis, the development of cancer, is a gradual process. Cancer cells lack differentiation, form tumors, undergo angiogenesis and ...
... a tumor, an abnormal mass of cells. Carcinogenesis, the development of cancer, is a gradual process. Cancer cells lack differentiation, form tumors, undergo angiogenesis and ...
Biology 303 EXAM II 3/14/00 NAME
... 1. base analogues and frameshift. 2. error prone and spontaneous. 3. transversions and transitions. 4. euchromatic and heterochromatic. ...
... 1. base analogues and frameshift. 2. error prone and spontaneous. 3. transversions and transitions. 4. euchromatic and heterochromatic. ...
DNA, Genes, and Chromosomes Guided Notes
... ____________________________ chromosomes have the same general size and appearance, and contain the same _________________. You inherit one homologous chromosome from your __________________________ and one from your _______________________. There are two types of chromosomes: ______________________ ...
... ____________________________ chromosomes have the same general size and appearance, and contain the same _________________. You inherit one homologous chromosome from your __________________________ and one from your _______________________. There are two types of chromosomes: ______________________ ...
Determinants of Gene Duplicability
... expression of mouse Pax 6 Halder, G., Callaerts, P. and Gehring, W.J. (1995). Induction of ectopic eyes by targeted expression of the eyeless gene in Drosophila. Science 267, 17881792. ...
... expression of mouse Pax 6 Halder, G., Callaerts, P. and Gehring, W.J. (1995). Induction of ectopic eyes by targeted expression of the eyeless gene in Drosophila. Science 267, 17881792. ...
BIOLOGY 210 FALL 2004
... Special needs: A student with a verified disability may be entitled to appropriate academic accommodations. Please contact me ASAP and/or the Disabled Student Services office in Craven Hall 5205, ext. 4905, for further assistance. Course goals and requirements: This course is designed for students t ...
... Special needs: A student with a verified disability may be entitled to appropriate academic accommodations. Please contact me ASAP and/or the Disabled Student Services office in Craven Hall 5205, ext. 4905, for further assistance. Course goals and requirements: This course is designed for students t ...
Unit 4: Genetic Engineering and Gene Expression
... 13. HOW does the sugar allow the glowing protein to be made? (Underline the terms inducer, repressor & RNA polymerase in your answer) Sugar is the inducer. When a gene is turned off, the repressor sits on a regulatory segment of DNA, preventing RNA polymerase from reading/ transcribing the gene bein ...
... 13. HOW does the sugar allow the glowing protein to be made? (Underline the terms inducer, repressor & RNA polymerase in your answer) Sugar is the inducer. When a gene is turned off, the repressor sits on a regulatory segment of DNA, preventing RNA polymerase from reading/ transcribing the gene bein ...
Lecture # 5 Mutations
... chromosomes or proteins may be analyzed in order to make the diagnosis. Testing may be done for a variety of reasons, such as in order to determine if an individual carries a defective gene that runs in their family. Many genetic disorders can also be diagnosed in early pregnancy. ...
... chromosomes or proteins may be analyzed in order to make the diagnosis. Testing may be done for a variety of reasons, such as in order to determine if an individual carries a defective gene that runs in their family. Many genetic disorders can also be diagnosed in early pregnancy. ...
genome433
... two homologous chromosomes (for example, the homologous chromosome 1 copies that you received, one from your mother and one from your father). Most human haploid genomes differ by about 1-3 million SNPs from each other. There are a variety of mechanisms used to identify SNPs. The disadvantage of SNP ...
... two homologous chromosomes (for example, the homologous chromosome 1 copies that you received, one from your mother and one from your father). Most human haploid genomes differ by about 1-3 million SNPs from each other. There are a variety of mechanisms used to identify SNPs. The disadvantage of SNP ...
Epigenetics ppt
... The study of the mechanisms by which genes bring about their phenotypic effects ...
... The study of the mechanisms by which genes bring about their phenotypic effects ...
Gene Section LGI1 (leucine-rich, glioma inactivated protein 1 precursor)
... Complete loss of LGI1 expression is associated with malignant brain tumors. Rearrangement or deletion of the region 10q23-q26, following the complete loss of one copy of chromosome 10, frequently occurs in highgrade gliomas. Genetic abnormalities in this region, comprising tumor suppressor genes suc ...
... Complete loss of LGI1 expression is associated with malignant brain tumors. Rearrangement or deletion of the region 10q23-q26, following the complete loss of one copy of chromosome 10, frequently occurs in highgrade gliomas. Genetic abnormalities in this region, comprising tumor suppressor genes suc ...
Criteria for gene mutations to be used in genetic testing of Malignant
... in microsomal SR preparations from muscle biopsies (Richter et al. 1997), and in lymphoblasts (Girard et al. 2001, Tilgen et al. 2001). Read-out parameters were Ca2+ flux and resting [Ca2+] or ryanodine binding to SRRYR1 preparations. Myotubes and lymphoblasts were derived from individual patients a ...
... in microsomal SR preparations from muscle biopsies (Richter et al. 1997), and in lymphoblasts (Girard et al. 2001, Tilgen et al. 2001). Read-out parameters were Ca2+ flux and resting [Ca2+] or ryanodine binding to SRRYR1 preparations. Myotubes and lymphoblasts were derived from individual patients a ...
Genomics and Bioinformatics KEY CONCEPT Entire genomes are
... – Study of entire genomes – can include the sequencing of the genome – Compare genomes within & across species to find similarities & differences among different organisms ...
... – Study of entire genomes – can include the sequencing of the genome – Compare genomes within & across species to find similarities & differences among different organisms ...
CH 9 - Mitosis Regualtion only - Liberty Union High School District
... tumor-suppressor genes genes inhibit cell division if switched “OFF” can cause cancer cell division is not inhibited like it should be ...
... tumor-suppressor genes genes inhibit cell division if switched “OFF” can cause cancer cell division is not inhibited like it should be ...
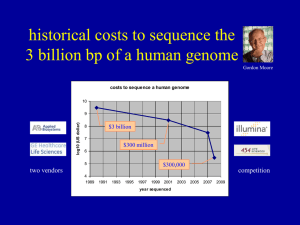
lecture28_Sequencing.. - University of Alberta
... There are 96 plant species with more than 20,000 expressed sequence tags (ESTs), but most are crop plants. If we count only medicinal plants, generously defined to include makers of secondary metabolites with purported health benefits, such as lycopene for tomatoes and resveratrol for grapes, there ...
... There are 96 plant species with more than 20,000 expressed sequence tags (ESTs), but most are crop plants. If we count only medicinal plants, generously defined to include makers of secondary metabolites with purported health benefits, such as lycopene for tomatoes and resveratrol for grapes, there ...
Exome sequencing to define a genetic signature of plasma cells in
... Exome data to determine the cytogenetic groups of AL samples identified 42% hyperdiploid and 21% with t(11;14). The AL samples with t(11;14) did not contain any other copy number abnormalities. We performed exome sequencing on samples from patients with MGUS and myeloma to compare the genetic makeu ...
... Exome data to determine the cytogenetic groups of AL samples identified 42% hyperdiploid and 21% with t(11;14). The AL samples with t(11;14) did not contain any other copy number abnormalities. We performed exome sequencing on samples from patients with MGUS and myeloma to compare the genetic makeu ...
speciation (formation of new species)
... alteration in the resulting protein. Altered proteins are often non-functioning e.g. an enzyme that will no longer fit its product. Two main classes of gene mutation: POINT MUTATION: a change in one of the base pairs in the DNA sequence of a single gene or regulatory DNA sequence. SPLICE-SITE MUTATI ...
... alteration in the resulting protein. Altered proteins are often non-functioning e.g. an enzyme that will no longer fit its product. Two main classes of gene mutation: POINT MUTATION: a change in one of the base pairs in the DNA sequence of a single gene or regulatory DNA sequence. SPLICE-SITE MUTATI ...
FACULTY SPONSOR`S NAME AND DEGREE:
... that is, they are "immortal". Hence replicative senescence is a mechanism of protection against cancer. We have been studying human diploid fibroblasts (HF) to understand the mechanism of multi-step carcinogenesis ("transformation") of such cells in culture and its effect on cellular aging. We have ...
... that is, they are "immortal". Hence replicative senescence is a mechanism of protection against cancer. We have been studying human diploid fibroblasts (HF) to understand the mechanism of multi-step carcinogenesis ("transformation") of such cells in culture and its effect on cellular aging. We have ...
BRCA2 gene - MyriadPro
... relatives of patients in whom clinically significant mutations are identified. Healthcare providers have an important role in making sure that patients with clinically significant mutations are informed about the risks to relatives, and ways in which genetic testing can guide lifesaving intervention ...
... relatives of patients in whom clinically significant mutations are identified. Healthcare providers have an important role in making sure that patients with clinically significant mutations are informed about the risks to relatives, and ways in which genetic testing can guide lifesaving intervention ...
Oncogenomics
Oncogenomics is a relatively new sub-field of genomics that applies high throughput technologies to characterize genes associated with cancer. Oncogenomics is synonymous with ""cancer genomics"". Cancer is a genetic disease caused by accumulation of mutations to DNA leading to unrestrained cell proliferation and neoplasm formation. The goal of oncogenomics is to identify new oncogenes or tumor suppressor genes that may provide new insights into cancer diagnosis, predicting clinical outcome of cancers, and new targets for cancer therapies. The success of targeted cancer therapies such as Gleevec, Herceptin, and Avastin raised the hope for oncogenomics to elucidate new targets for cancer treatment.Besides understanding the underlying genetic mechanisms that initiates or drives cancer progression, one of the main goals of oncogenomics is to allow for the development of personalized cancer treatment. Cancer develops due to an accumulation of mutations in DNA. These mutations accumulate randomly, and thus, different DNA mutations and mutation combinations exist between different individuals with the same type of cancer. Thus, identifying and targeting specific mutations which have occurred in an individual patient may lead to increased efficacy of cancer therapy.The completion of the Human Genome Project has greatly facilitated the field of oncogenomics and has increased the abilities of researchers to find cancer causing genes. In addition, the sequencing technologies now available for sequence generation and data analysis have been applied to the study of oncogenomics. With the amount of research conducted on cancer genomes and the accumulation of databases documenting the mutational changes, it has been predicted that the most important cancer-causing mutations, rearrangements, and altered expression levels will be cataloged and well characterized within the next decade.Cancer research may look either on the genomic level at DNA mutations, the epigenetic level at methylation or histone modification changes, the transcription level at altered levels of gene expression, or the protein level at altered levels of protein abundance and function in cancer cells. Oncogenomics focuses on the genomic, epigenomic, and transcript level alterations in cancer.