DNA Webquest - Jackson School District
... 1. When DNA is preparing for replication, what are the bonds that are broken to break it into two strands?__________________________________________________ 2. What enzyme is responsible for splitting the two strands? ____________________________________ 3. The splitting of the DNA starts at a place ...
... 1. When DNA is preparing for replication, what are the bonds that are broken to break it into two strands?__________________________________________________ 2. What enzyme is responsible for splitting the two strands? ____________________________________ 3. The splitting of the DNA starts at a place ...
DNA NOTES
... forming an amino acid chain (protein). (pg. 184) 21. Define Codon: (pg. 184) 22. Define Anticodon: (pg. 185) 23. Use figure 8.4 (pg. 185) to answer the following questions. a. What is the codon sequence labeled in the diagram? ______________ b. On what molecule will you find the codon? _____________ ...
... forming an amino acid chain (protein). (pg. 184) 21. Define Codon: (pg. 184) 22. Define Anticodon: (pg. 185) 23. Use figure 8.4 (pg. 185) to answer the following questions. a. What is the codon sequence labeled in the diagram? ______________ b. On what molecule will you find the codon? _____________ ...
슬라이드 1 - Sogang
... Protein phosphatase 1γ is responsible for dephosphorylation of histone H3 at Thr 11 after DNA damage ...
... Protein phosphatase 1γ is responsible for dephosphorylation of histone H3 at Thr 11 after DNA damage ...
DNA - TeacherWeb
... Messenger RNA carries the code that directs the order in which the amino acids bond b. Ribosomal RNA makes up Ribosomes, where proteins are built c. Transfer RNA brings amino acids to the ribosomes to build the protein. 3. Cells use only the genes that directs the making of proteins needed by that c ...
... Messenger RNA carries the code that directs the order in which the amino acids bond b. Ribosomal RNA makes up Ribosomes, where proteins are built c. Transfer RNA brings amino acids to the ribosomes to build the protein. 3. Cells use only the genes that directs the making of proteins needed by that c ...
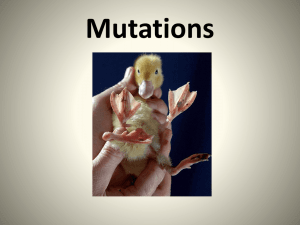
Mutations
... -mutations which occur in the sperm or the egg. If fertilized this mistake would be passed on to the child. Example: Sickle cell anemia ...
... -mutations which occur in the sperm or the egg. If fertilized this mistake would be passed on to the child. Example: Sickle cell anemia ...
Table 3.
... Multiples melting peaks observed for nuclear gene (more than 2) Amplicon melting transitions not visible or are very small ...
... Multiples melting peaks observed for nuclear gene (more than 2) Amplicon melting transitions not visible or are very small ...
DNA and RNA Review
... 10. What does FIGURE 1 (picture on the right) show? 11. How many codons are needed to specify three amino acids? 12. Explain why it is possible for an amino acid to be specified by more than one kind of codon? ...
... 10. What does FIGURE 1 (picture on the right) show? 11. How many codons are needed to specify three amino acids? 12. Explain why it is possible for an amino acid to be specified by more than one kind of codon? ...
Cool Stuff About DNA
... • DNA is the most efficient storage system known to man • It would take 30 gigabytes of hard drive space to save both sides of the sequence • Using the binomial language of modern computers, DNA could store 25 gigabytes of information ...
... • DNA is the most efficient storage system known to man • It would take 30 gigabytes of hard drive space to save both sides of the sequence • Using the binomial language of modern computers, DNA could store 25 gigabytes of information ...
The Code of Life: Topic 3
... • In each pair you get one from your mother and one from your father. • Each chromosome in a pair holds all the same genes as the other. • So what determines which gene is expressed when you develop? • ie how do you get your mother's eyes or your father's nose? ...
... • In each pair you get one from your mother and one from your father. • Each chromosome in a pair holds all the same genes as the other. • So what determines which gene is expressed when you develop? • ie how do you get your mother's eyes or your father's nose? ...
Life Science Vocabulary.xlsx
... an organism that always produces an offspring with the same form of a trait as the purebred parent trait a characteristic that an organism can pass on to its offspring through its genes allele the different forms of a gene Rosalind Franklin famous woman scientist who used x-rays to photograph DNA mo ...
... an organism that always produces an offspring with the same form of a trait as the purebred parent trait a characteristic that an organism can pass on to its offspring through its genes allele the different forms of a gene Rosalind Franklin famous woman scientist who used x-rays to photograph DNA mo ...
Word Definition Synonym 1 DNA replication the
... an organism that always produces an offspring with the same form of a trait as the purebred parent trait a characteristic that an organism can pass on to its offspring through its genes allele the different forms of a gene Rosalind Franklin famous woman scientist who used x-rays to photograph DNA mo ...
... an organism that always produces an offspring with the same form of a trait as the purebred parent trait a characteristic that an organism can pass on to its offspring through its genes allele the different forms of a gene Rosalind Franklin famous woman scientist who used x-rays to photograph DNA mo ...
Science Hand Out 6 - Literacy Action Network
... Students describe structure and function of cells at the intracellular and molecular level including differentiation to form systems, interactions between cells and their environment, and the impact of cellular processes and changes on individuals. a. Describe the similarities and differences in the ...
... Students describe structure and function of cells at the intracellular and molecular level including differentiation to form systems, interactions between cells and their environment, and the impact of cellular processes and changes on individuals. a. Describe the similarities and differences in the ...
Chromosomes Key - Iowa State University
... 3. When relaxed DNA (10.4 bp/turn) becomes either under or over-coiled it is called what? a) mega-coiled b) coiled-coils c) super-coiled d) ultra-coiled The coiling in question 3 is caused by what type of protein? _topoisomerase___ 4. Prokaryotic chromosomes are different than Eukaryotic chromosomes ...
... 3. When relaxed DNA (10.4 bp/turn) becomes either under or over-coiled it is called what? a) mega-coiled b) coiled-coils c) super-coiled d) ultra-coiled The coiling in question 3 is caused by what type of protein? _topoisomerase___ 4. Prokaryotic chromosomes are different than Eukaryotic chromosomes ...
DNA WebQuest - Pearland ISD
... Take the tour of DNA by clicking on “What is DNA?” and answer the questions below: 1. In what organelle (CELL PART) would I find your DNA (YOUR INSTRUCTIONS)? 2. What does DNA stand for? 3. The DNA molecule comes in the form of a ...
... Take the tour of DNA by clicking on “What is DNA?” and answer the questions below: 1. In what organelle (CELL PART) would I find your DNA (YOUR INSTRUCTIONS)? 2. What does DNA stand for? 3. The DNA molecule comes in the form of a ...
LEQ: How do we splice new genes into DNA?
... RESTRICTION FRAGMENT LENGTH POLYMORPHISMS (RFLP’S) (rif′-lips) The differences in homologous DNA ...
... RESTRICTION FRAGMENT LENGTH POLYMORPHISMS (RFLP’S) (rif′-lips) The differences in homologous DNA ...
DNA (isolate
... “If there are cells, there is DNA.” DNA can be obtained from dead cells if they are not too damaged. Forensic pathology techniques are improving so that it is possible to get useable DNA from many types of post-mortem tissues. ...
... “If there are cells, there is DNA.” DNA can be obtained from dead cells if they are not too damaged. Forensic pathology techniques are improving so that it is possible to get useable DNA from many types of post-mortem tissues. ...