Mutations
... • Part breaks off, reattaches to a non-homologous chromosomes – Insertion • Extra DNA is inserted into a non-homologous chromosome ...
... • Part breaks off, reattaches to a non-homologous chromosomes – Insertion • Extra DNA is inserted into a non-homologous chromosome ...
M220 Lecture 13 DNA is replicated by a process known as semi
... concentrations of substrate are present. Repressible enzymes are not manufactured in the presence of increased concentrations of reaction products. Genotypic modifications or changes-these are called mutations. The cell that houses a mutation is called a mutant. The positioning of the nitrogenous ba ...
... concentrations of substrate are present. Repressible enzymes are not manufactured in the presence of increased concentrations of reaction products. Genotypic modifications or changes-these are called mutations. The cell that houses a mutation is called a mutant. The positioning of the nitrogenous ba ...
Mutations
... – Missense mutation- changes one amino acid in polypeptide chain – Nonsense mutation- creates a stop codon in the middle of the polypeptide chain – Splice site mutations- alters the splicing of the pre-mRNA ...
... – Missense mutation- changes one amino acid in polypeptide chain – Nonsense mutation- creates a stop codon in the middle of the polypeptide chain – Splice site mutations- alters the splicing of the pre-mRNA ...
Notes: Mutations
... (sex cells) are really important – Are passed on to the next generation – Affect the gene that the mutation occurred in ...
... (sex cells) are really important – Are passed on to the next generation – Affect the gene that the mutation occurred in ...
Protein Synthesis Questions
... 13. If an mRNA had the following code, what string of amino acids would be formed? Use Figure 12-17 to help you. ...
... 13. If an mRNA had the following code, what string of amino acids would be formed? Use Figure 12-17 to help you. ...
Genetic Mutations and Biotechnology
... laboratory, the result is a genetically modified organism (GMO). It is also sometimes called "transgenic" for transfer of genes. ...
... laboratory, the result is a genetically modified organism (GMO). It is also sometimes called "transgenic" for transfer of genes. ...
Gene Expression and Regulation
... a) Point mutation = substitution of single base pair Changes only one amino acid (if any!) ...
... a) Point mutation = substitution of single base pair Changes only one amino acid (if any!) ...
What causes gene mutations?
... on the X chromosome. X-linked disorders are more common in males because they only have one X chromosome. As a consequence males only need one copy of the altered gene for symptoms to occur. ...
... on the X chromosome. X-linked disorders are more common in males because they only have one X chromosome. As a consequence males only need one copy of the altered gene for symptoms to occur. ...
Mutation and Genetic Change
... Mutations c. Effects of Mutations i.Heritability- Mutations are only able to be inherited by offspring if they affect an individual’s sex cells (gametes). ii. Cancer/tumors- Some mutations cause somatic cells to lose control of their cell division. ...
... Mutations c. Effects of Mutations i.Heritability- Mutations are only able to be inherited by offspring if they affect an individual’s sex cells (gametes). ii. Cancer/tumors- Some mutations cause somatic cells to lose control of their cell division. ...
Fall 2005 Due: 9/9 GENETICS Homework 1 1. (1 point) The
... following table. Give the order of compound A, B, C, and D in a biochemical pathway. Outline a biochemical pathway ...
... following table. Give the order of compound A, B, C, and D in a biochemical pathway. Outline a biochemical pathway ...
Honors Biology
... 5. Describe the process of protein synthesis (both transcription and translation). 6. Explain the steps of mRNA processing and how it can result in different proteins. 7. Describe the relationship between control of gene expression and cell differentiation or specialization. 8. Describe the way that ...
... 5. Describe the process of protein synthesis (both transcription and translation). 6. Explain the steps of mRNA processing and how it can result in different proteins. 7. Describe the relationship between control of gene expression and cell differentiation or specialization. 8. Describe the way that ...
TGFBR2 - Loeys-Dietz syndrome Testing Indication
... and a portion of untranslated regions of the gene are amplified by PCR. Genomic DNA sequences from both forward and reverse directions are obtained by automatic fluorescent detection using an ABI PRISM® 3730 DNA Analyzer. Sequence variants different from the National Center for Biotechnology Informa ...
... and a portion of untranslated regions of the gene are amplified by PCR. Genomic DNA sequences from both forward and reverse directions are obtained by automatic fluorescent detection using an ABI PRISM® 3730 DNA Analyzer. Sequence variants different from the National Center for Biotechnology Informa ...
18.1 Mutations Are Inherited Alterations in the DNA Sequence
... • Loss-of-function mutations-cause complete or partial loss of protein function • Gain-of-function mutations-cause either new function or function expressed at new times or ...
... • Loss-of-function mutations-cause complete or partial loss of protein function • Gain-of-function mutations-cause either new function or function expressed at new times or ...
Sometimes replication, transcription and translation don`t go as
... • a broken piece attaches to a nonhomologous chromosome ...
... • a broken piece attaches to a nonhomologous chromosome ...
Document
... Objective: To know the major steps in protein synthesis and the RNAs and proteins involved in this process. To understand the mechanism by which proteins are targeted to specific cimpartments. I. Genetic code A. Three nucleotides make one codon B. "Universal" C. Degenerate D. Commaless II. Translati ...
... Objective: To know the major steps in protein synthesis and the RNAs and proteins involved in this process. To understand the mechanism by which proteins are targeted to specific cimpartments. I. Genetic code A. Three nucleotides make one codon B. "Universal" C. Degenerate D. Commaless II. Translati ...
GENE MUTATIONS
... E g. sickle cell anemia. Only affects one base pair on the DNA or one codon of mRNA. Can be called a base pair substitution in this ...
... E g. sickle cell anemia. Only affects one base pair on the DNA or one codon of mRNA. Can be called a base pair substitution in this ...
GENE MUTATIONS - mrbemrose / FrontPage
... E g. sickle cell anemia. Only affects one base pair on the DNA or one codon of mRNA. Can be called a base pair substitution in this ...
... E g. sickle cell anemia. Only affects one base pair on the DNA or one codon of mRNA. Can be called a base pair substitution in this ...
Mutation
... Mutations can causes change in the gene sequence that can cause a different amino acid to be made into protein to make it defective (does not work anymore). An example of a mutation (substitution of a nitrogen base) is sickle cell disease (sickle cell anemia). A red blood cell is normally round, but ...
... Mutations can causes change in the gene sequence that can cause a different amino acid to be made into protein to make it defective (does not work anymore). An example of a mutation (substitution of a nitrogen base) is sickle cell disease (sickle cell anemia). A red blood cell is normally round, but ...
4TH 6 WEEKS EXAM REVIEW!
... The 3 bases on the tRNA are known as the _________ and are complimentary to mRNA’s __________ (3 bases) ...
... The 3 bases on the tRNA are known as the _________ and are complimentary to mRNA’s __________ (3 bases) ...
Mutations Notes - Oakman School News
... Read the following notes and complete the concept map – attached - on your own paper Gene Mutations ...
... Read the following notes and complete the concept map – attached - on your own paper Gene Mutations ...
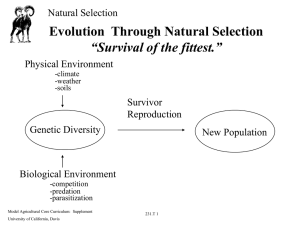
Evolution Through Natural Selection “Survival of the fittest.”
... Evolution Through Natural Selection “Survival of the fittest.” Physical Environment -climate -weather -soils ...
... Evolution Through Natural Selection “Survival of the fittest.” Physical Environment -climate -weather -soils ...
Genetic Mutation - Raymond Williams Foundation
... Dc Tue 22 May at The Blue Mugge pub Based on the BBC IoT broadcast with title Genetic Mutation, in 2007. ...
... Dc Tue 22 May at The Blue Mugge pub Based on the BBC IoT broadcast with title Genetic Mutation, in 2007. ...
Mutations
... Somatic-Cell Mutations ◦ Take place in an organism’s body cells Can affect organism (certain types of cancer) Cannot be inherited ...
... Somatic-Cell Mutations ◦ Take place in an organism’s body cells Can affect organism (certain types of cancer) Cannot be inherited ...
Mutations
... D. Regulation and Development- especially important in shaping the way a complex organism develops from single fertilized cell. 1. Hox genes- controls organs and tissues that develop in various parts of the embryo a. Mutation in one of these “master control genes” can completely change organs that ...
... D. Regulation and Development- especially important in shaping the way a complex organism develops from single fertilized cell. 1. Hox genes- controls organs and tissues that develop in various parts of the embryo a. Mutation in one of these “master control genes” can completely change organs that ...
Frameshift mutation

A frameshift mutation (also called a framing error or a reading frame shift) is a genetic mutation caused by indels (insertions or deletions) of a number of nucleotides in a DNA sequence that is not divisible by three. Due to the triplet nature of gene expression by codons, the insertion or deletion can change the reading frame (the grouping of the codons), resulting in a completely different translation from the original. The earlier in the sequence the deletion or insertion occurs, the more altered the protein. A frameshift mutation is not the same as a single-nucleotide polymorphism in which a nucleotide is replaced, rather than inserted or deleted. A frameshift mutation will in general cause the reading of the codons after the mutation to code for different amino acids. The frameshift mutation will also alter the first stop codon (""UAA"", ""UGA"" or ""UAG"") encountered in the sequence. The polypeptide being created could be abnormally short or abnormally long, and will most likely not be functional.Frameshift mutations are apparent in severe genetic diseases such as Tay-Sachs disease and Cystic Fibrosis; they increase susceptibility to certain cancers and classes of familial hypercholesterolaemia; in 1997, a frameshift mutation was linked to resistance to infection by the HIV retrovirus. Frameshift mutations have been proposed as a source of biological novelty, as with the alleged creation of nylonase, however, this interpretation is controversial. A study by Negoro et al (2006) found that a frameshift mutation was unlikely to have been the cause and that rather a two amino acid substitution in the catalytic cleft of an ancestral esterase amplified Ald-hydrolytic activity.