TRUE FALSE 1. It is important to make the right choice between
... 3. This is TRUE. Crossover, which is a very efficient operator, is only carried out with a certain probability (the crossover probability), to avoid premature convergence; see p. 53 and pp. 68-69. In cases where crossover is not carried out, the two selected individuals are subjected only to mutatio ...
... 3. This is TRUE. Crossover, which is a very efficient operator, is only carried out with a certain probability (the crossover probability), to avoid premature convergence; see p. 53 and pp. 68-69. In cases where crossover is not carried out, the two selected individuals are subjected only to mutatio ...
Homework: Mutations
... A part of one chromosome attached to another (translocation) B some of the genes on a chromosome were reversed (inversion) C a duplicated chromosome failed to separate (nondisjunction) D a part of a chromosome was lost (deletion) 8. Which of the following is a change that could be passed on to an or ...
... A part of one chromosome attached to another (translocation) B some of the genes on a chromosome were reversed (inversion) C a duplicated chromosome failed to separate (nondisjunction) D a part of a chromosome was lost (deletion) 8. Which of the following is a change that could be passed on to an or ...
Chapter 10
... Review the history of the discovery of this structure. 2. "One geneone polypeptide" Discuss how the structure of DNA allows genes to contain instructions for polypeptide synthesis. List some exceptions to this rule. 3. DNA synthesis is a very precise process by which both strands are reproduc ...
... Review the history of the discovery of this structure. 2. "One geneone polypeptide" Discuss how the structure of DNA allows genes to contain instructions for polypeptide synthesis. List some exceptions to this rule. 3. DNA synthesis is a very precise process by which both strands are reproduc ...
Mutation: The Source of Genetic Variation
... • Missense mutation – replaces one amino acid with another • Nonsense mutations – an amino acid codon is changed to a stop codon • Sense mutation – a termination codon is changed into a one that codes for an amino acid, producing elongated proteins • Silent mutation – no effect on phenotype Frames ...
... • Missense mutation – replaces one amino acid with another • Nonsense mutations – an amino acid codon is changed to a stop codon • Sense mutation – a termination codon is changed into a one that codes for an amino acid, producing elongated proteins • Silent mutation – no effect on phenotype Frames ...
Dark Blue with Orange
... Classified as a global search heuristic Inspired by Evolutionary Biology ...
... Classified as a global search heuristic Inspired by Evolutionary Biology ...
DNA Structure and Function
... C. translation D. transcription 2. What is DNA? P148 A. a type of molecule composed mostly of ...
... C. translation D. transcription 2. What is DNA? P148 A. a type of molecule composed mostly of ...
Genetic Mutations
... • What would happen if a single base were lost from a DNA strand? • This new sequence with the deleted base would be transcribed into mRNA. But then, the mRNA would be out of position by one base. • As a result, every codon after the deleted base would be different. ...
... • What would happen if a single base were lost from a DNA strand? • This new sequence with the deleted base would be transcribed into mRNA. But then, the mRNA would be out of position by one base. • As a result, every codon after the deleted base would be different. ...
Genetic Mutations
... • What would happen if a single base were lost from a DNA strand? • This new sequence with the deleted base would be transcribed into mRNA. But then, the mRNA would be out of position by one base. • As a result, every codon after the deleted base would be different. ...
... • What would happen if a single base were lost from a DNA strand? • This new sequence with the deleted base would be transcribed into mRNA. But then, the mRNA would be out of position by one base. • As a result, every codon after the deleted base would be different. ...
Mathematical Tools for Understanding Genome Rearrangements
... Wednesday September 19, 2012 12:10 - 12:50 p.m. *CETL (OL 1142)* The diversity of life is a direct result of inaccuracy in DNA replication. At some point in the past, humans and mice had a common ancestor, and many "mistakes" later, we have two apparently very different species. At the level of DNA, ...
... Wednesday September 19, 2012 12:10 - 12:50 p.m. *CETL (OL 1142)* The diversity of life is a direct result of inaccuracy in DNA replication. At some point in the past, humans and mice had a common ancestor, and many "mistakes" later, we have two apparently very different species. At the level of DNA, ...
Lecture 9 - Bacterial Genetics Chpt. 8
... Repair of Damaged DNA • Repair of modified bases – Enzyme cuts DNA backbone and removes base – DNA polymerase incorporates new base ...
... Repair of Damaged DNA • Repair of modified bases – Enzyme cuts DNA backbone and removes base – DNA polymerase incorporates new base ...
Gene mutations
... Involves changes in one or a few nucleotides (they occur at a single point in the DNA sequence) They can be: Substitutions Insertions Deletions ...
... Involves changes in one or a few nucleotides (they occur at a single point in the DNA sequence) They can be: Substitutions Insertions Deletions ...
Mutations
... Insertions (duplications) occur after DNA is replicated when part of one chromosome breaks off and rejoins onto another part of the same chromosome so that part of the ...
... Insertions (duplications) occur after DNA is replicated when part of one chromosome breaks off and rejoins onto another part of the same chromosome so that part of the ...
Complete the following chart using your genetic code chart worksheet:
... 8. An agent that can cause a change in DNA is called a(n) a. Zygote b. Inversion c. Mutagen ...
... 8. An agent that can cause a change in DNA is called a(n) a. Zygote b. Inversion c. Mutagen ...
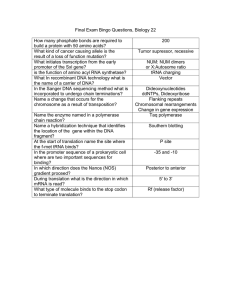
How many phosphate bonds are required to build a protein with 50
... What kind of cancer causing allele is the result of a loss of function mutation? What initiates transcription from the early promoter of the Sxl gene? is the function of amino acyl RNA synthetase? What In recombinant DNA technology what is the name of a carrier of DNA? In the Sanger DNA sequencing m ...
... What kind of cancer causing allele is the result of a loss of function mutation? What initiates transcription from the early promoter of the Sxl gene? is the function of amino acyl RNA synthetase? What In recombinant DNA technology what is the name of a carrier of DNA? In the Sanger DNA sequencing m ...
Evolution: An Introduction
... advantage (i.e. organism is favoured in terms of survival and reproduction) • Other mutations are neutral – no effect on organism’s fitness (ability to reproduce), but may become critical for survival later if the ...
... advantage (i.e. organism is favoured in terms of survival and reproduction) • Other mutations are neutral – no effect on organism’s fitness (ability to reproduce), but may become critical for survival later if the ...
Biology Molecular Genetic Review
... IF you are asked to translate a sequence of DNA, what would you do? ...
... IF you are asked to translate a sequence of DNA, what would you do? ...
Changes in DNA can produce variation
... No effect – Some amino acids have more than one code and may not change resulting protein – May have enough protein being produced ...
... No effect – Some amino acids have more than one code and may not change resulting protein – May have enough protein being produced ...
Mutation Notes
... 1. Mutations can happen during Mitosis (making of body cells) 2. The mutation only affects the person, not the offspring 2. affects the function of the cell a) ...
... 1. Mutations can happen during Mitosis (making of body cells) 2. The mutation only affects the person, not the offspring 2. affects the function of the cell a) ...
Chapter 4 The role of mutation in evolution
... 1. 3rd position – about 2/3 of changes are synonymous 2. 2nd position – no synonymous changes 3. 1st position – a few synonymous changes c. Different base substitutions will have different effects 1. synonymous – invisible or nearly invisible to natural selection, so evolve at neutral rate 2. nonsyn ...
... 1. 3rd position – about 2/3 of changes are synonymous 2. 2nd position – no synonymous changes 3. 1st position – a few synonymous changes c. Different base substitutions will have different effects 1. synonymous – invisible or nearly invisible to natural selection, so evolve at neutral rate 2. nonsyn ...
Notes Unit 4 Part 8
... ___________ gene occur most often during ______ replication so affect _____________ cells more often phenotype may or may ______ be altered depending on type of mutation Types of Gene Mutations: 1. point mutation = a gene mutation involving changes in ____ or few nucleotides usually only _____ ...
... ___________ gene occur most often during ______ replication so affect _____________ cells more often phenotype may or may ______ be altered depending on type of mutation Types of Gene Mutations: 1. point mutation = a gene mutation involving changes in ____ or few nucleotides usually only _____ ...
Frameshift mutation

A frameshift mutation (also called a framing error or a reading frame shift) is a genetic mutation caused by indels (insertions or deletions) of a number of nucleotides in a DNA sequence that is not divisible by three. Due to the triplet nature of gene expression by codons, the insertion or deletion can change the reading frame (the grouping of the codons), resulting in a completely different translation from the original. The earlier in the sequence the deletion or insertion occurs, the more altered the protein. A frameshift mutation is not the same as a single-nucleotide polymorphism in which a nucleotide is replaced, rather than inserted or deleted. A frameshift mutation will in general cause the reading of the codons after the mutation to code for different amino acids. The frameshift mutation will also alter the first stop codon (""UAA"", ""UGA"" or ""UAG"") encountered in the sequence. The polypeptide being created could be abnormally short or abnormally long, and will most likely not be functional.Frameshift mutations are apparent in severe genetic diseases such as Tay-Sachs disease and Cystic Fibrosis; they increase susceptibility to certain cancers and classes of familial hypercholesterolaemia; in 1997, a frameshift mutation was linked to resistance to infection by the HIV retrovirus. Frameshift mutations have been proposed as a source of biological novelty, as with the alleged creation of nylonase, however, this interpretation is controversial. A study by Negoro et al (2006) found that a frameshift mutation was unlikely to have been the cause and that rather a two amino acid substitution in the catalytic cleft of an ancestral esterase amplified Ald-hydrolytic activity.