Slide 1
... 2) However, only the initial portion of F factor DNA gets copied and transferred, the remaining majority of what is copied and transferred is chromosomal DNA from the donor cell. Only a fragment of the donor chromosome transfers. 3) Recombination between the recipient’s chromosome and the transferre ...
... 2) However, only the initial portion of F factor DNA gets copied and transferred, the remaining majority of what is copied and transferred is chromosomal DNA from the donor cell. Only a fragment of the donor chromosome transfers. 3) Recombination between the recipient’s chromosome and the transferre ...
Sample Questions from Previous Problem Sets in MCB 240 Here
... death pathway that specifically prevent the death in hermaphrodites of the male-specific neurons called CEMs. Initially, both XX and XO embryos have CEMs; these neurons survive and differentiate in XO animals (or XX animals masculinized by tra-1 mutations) but are killed in wild-type XX animals by t ...
... death pathway that specifically prevent the death in hermaphrodites of the male-specific neurons called CEMs. Initially, both XX and XO embryos have CEMs; these neurons survive and differentiate in XO animals (or XX animals masculinized by tra-1 mutations) but are killed in wild-type XX animals by t ...
Study Questions – Chapter 1
... “Human mutation rate revealed: Next-generation sequencing provides the most accurate estimate to date” by Elie Dolgin in Scientific American, August 2009. “The real cause of obesity: It’s not gluttony. It’s genetics. Why our moralizing misses the point” by Jeffrey Friedman, Newsweek Web Exclusive, S ...
... “Human mutation rate revealed: Next-generation sequencing provides the most accurate estimate to date” by Elie Dolgin in Scientific American, August 2009. “The real cause of obesity: It’s not gluttony. It’s genetics. Why our moralizing misses the point” by Jeffrey Friedman, Newsweek Web Exclusive, S ...
View PDF
... does not mean the cancer will occur. Cancer involves a series of mutations. What is inherited is a mutation that is one step in the series. The disease occurs only if other mutations come into play. ...
... does not mean the cancer will occur. Cancer involves a series of mutations. What is inherited is a mutation that is one step in the series. The disease occurs only if other mutations come into play. ...
100 colorectal adenomatous polyps
... I am writing to request coverage for analysis of the APC and MYH genes for __________________________________________________due to a personal history of ________________________________________________________ diagnosed at age(s) ______________________________. The number of adenomatous colorectal ...
... I am writing to request coverage for analysis of the APC and MYH genes for __________________________________________________due to a personal history of ________________________________________________________ diagnosed at age(s) ______________________________. The number of adenomatous colorectal ...
Final
... The autosomal genes cinnabar and brown in Drosophila encode proteins required for eye pigments. When the recessive allele of the sex-linked white gene is homozygous or hemizygous, however, neither pigment is actually visible in the fly's eye. What is this relationship among different ...
... The autosomal genes cinnabar and brown in Drosophila encode proteins required for eye pigments. When the recessive allele of the sex-linked white gene is homozygous or hemizygous, however, neither pigment is actually visible in the fly's eye. What is this relationship among different ...
Genetic Mutations SDK Nov 2, 2012
... change in the beta-globin gene, where a GAG codon is converted to GUG. GAG GUG Nonsense mutations. convert an amino acid into a stop codon. The effect is to shorten the resulting protein. Sometimes this has only a little effect, however, often nonsense mutations result in completely non-functional p ...
... change in the beta-globin gene, where a GAG codon is converted to GUG. GAG GUG Nonsense mutations. convert an amino acid into a stop codon. The effect is to shorten the resulting protein. Sometimes this has only a little effect, however, often nonsense mutations result in completely non-functional p ...
Dana-Farber Cancer Institute | Spring 2002
... Through these studies, Dana-Farber researchers are learning that DIPGs are highly heterogeneous and complex, which can make them challenging to treat (see sidebar). One drug might only knock out the tumor cells driven by one mutation, leaving other cancer cells to survive and continue growing. To ov ...
... Through these studies, Dana-Farber researchers are learning that DIPGs are highly heterogeneous and complex, which can make them challenging to treat (see sidebar). One drug might only knock out the tumor cells driven by one mutation, leaving other cancer cells to survive and continue growing. To ov ...
Milan Manchandia - Werner Syndrome
... Recombinant human insulin-like growth factor for associated osteoporosis ...
... Recombinant human insulin-like growth factor for associated osteoporosis ...
Lecture#31 – Evolution and cis
... a. changes gene product (RNA or protein) - > alters function-> affects phenotype b. doesn’t change gene’s transcription c. natural selection for/against function of product Result: Evolution occurs via random mutation and selection for/against the function of the gene’s product 3) Gene’s regulatory ...
... a. changes gene product (RNA or protein) - > alters function-> affects phenotype b. doesn’t change gene’s transcription c. natural selection for/against function of product Result: Evolution occurs via random mutation and selection for/against the function of the gene’s product 3) Gene’s regulatory ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 03. In E. Coli according to operon theory an operator gene combines with a. regulator protein to “ switch on “ structural gene transcription. b. regulator protein to “ switch off “ structural gene transcription. c. regulator gene to “ switch off “ structural gene transcription. d. regulator gene to ...
... 03. In E. Coli according to operon theory an operator gene combines with a. regulator protein to “ switch on “ structural gene transcription. b. regulator protein to “ switch off “ structural gene transcription. c. regulator gene to “ switch off “ structural gene transcription. d. regulator gene to ...
... Law of Segregation -during fertilization gametes randomly pair to produce four sets of alleles (monohyrid) TT=homozygous dominant, Tt=heterozygous, tt=homozygous recessive Genotype is the combination of alleles, Phenotype is the physical expression of alleles Law of Independent Assortment -g ...
PDF file - the Houpt Lab
... 3. Open reading frames: In the mRNA, there are no spaces to distinguish one codon from the next, so we have to look for the open reading frame = the grouping of stretches of RNA so it makes “sense” to ribosomes as a series of codons. ...
... 3. Open reading frames: In the mRNA, there are no spaces to distinguish one codon from the next, so we have to look for the open reading frame = the grouping of stretches of RNA so it makes “sense” to ribosomes as a series of codons. ...
Protein Synthesis
... i. Gene = a segment of DNA coding for a RNA segment. These RNA segments will be used to produce a polypeptide (structural or enzymatic protein) ii. Each strand of DNA can contain thousands of genes iii. Each gene has a beginning and an end b. DNA is used as the blueprint to direct the production of ...
... i. Gene = a segment of DNA coding for a RNA segment. These RNA segments will be used to produce a polypeptide (structural or enzymatic protein) ii. Each strand of DNA can contain thousands of genes iii. Each gene has a beginning and an end b. DNA is used as the blueprint to direct the production of ...
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... i. Gene = a segment of DNA coding for a RNA segment. These RNA segments will be used to produce a polypeptide (structural or enzymatic protein) ii. Each strand of DNA can contain thousands of genes iii. Each gene has a beginning and an end b. DNA is used as the blueprint to direct the production of ...
... i. Gene = a segment of DNA coding for a RNA segment. These RNA segments will be used to produce a polypeptide (structural or enzymatic protein) ii. Each strand of DNA can contain thousands of genes iii. Each gene has a beginning and an end b. DNA is used as the blueprint to direct the production of ...
Genetic Engineering
... Finding the location of certain genes on chromosomes The arrangement of the nitrogen base pairs (A,T,C and G) determines what an organism looks like Human Genome Project ...
... Finding the location of certain genes on chromosomes The arrangement of the nitrogen base pairs (A,T,C and G) determines what an organism looks like Human Genome Project ...
1. Suppose the nucleotide composition of a DNA virus was found to
... of these mRNA sequences, a stop codon is present either at the end of the sequence or within the interior of the sequence. a. 5’- AUGUUUAAAUUUAAAUUUUGA -3’ ...
... of these mRNA sequences, a stop codon is present either at the end of the sequence or within the interior of the sequence. a. 5’- AUGUUUAAAUUUAAAUUUUGA -3’ ...
Exploring Mutant Organisms Teacher Extended Background
... originated from the same population and had spread out over numerous islands. Some birds developed physical traits, specifically distinct beak shapes, which gave them an advantage in their new habitats and made it easier for them to access food. Darwin suggested that these advantageous traits were p ...
... originated from the same population and had spread out over numerous islands. Some birds developed physical traits, specifically distinct beak shapes, which gave them an advantage in their new habitats and made it easier for them to access food. Darwin suggested that these advantageous traits were p ...
Bis2A 8.2 The Flow of Genetic Information
... be part of the conceptual toolkit for all biologists. Two of these processes are transcription and translation; the coping of parts of the genetic code written in DNA into molecules of the related polymer RNA and the reading and encoding of the RNA code into proteins, respectively. In BIS2A we focus ...
... be part of the conceptual toolkit for all biologists. Two of these processes are transcription and translation; the coping of parts of the genetic code written in DNA into molecules of the related polymer RNA and the reading and encoding of the RNA code into proteins, respectively. In BIS2A we focus ...
doc
... DNA fingerprinting — technique for identifying individuals, generally using repeated sequences in the human genome that produce a pattern of bands that is unique for every individual Double helix — term used to describe the structure of DNA; two strands that are coiled Gamete — specialized reproduct ...
... DNA fingerprinting — technique for identifying individuals, generally using repeated sequences in the human genome that produce a pattern of bands that is unique for every individual Double helix — term used to describe the structure of DNA; two strands that are coiled Gamete — specialized reproduct ...
G T A C A T C T T A A C G C A T A T
... 11. Can mutations lead to genetic variation? Yes, mutations are how species change over time. 12. Name a genetic disorder caused by a gene mutation. Albinism, PKU, Cystic Fibrosis, Tay-Sachs 13. Compare the following codon sequences: (6E) GUG-UGA-CGC-UGU-CCA And GUG-UGA-CCG-CUG-UCC-A Which mutation ...
... 11. Can mutations lead to genetic variation? Yes, mutations are how species change over time. 12. Name a genetic disorder caused by a gene mutation. Albinism, PKU, Cystic Fibrosis, Tay-Sachs 13. Compare the following codon sequences: (6E) GUG-UGA-CGC-UGU-CCA And GUG-UGA-CCG-CUG-UCC-A Which mutation ...
Key- PRE-LAB: Before the lab, please answer the following questions:
... substance and reflects background response induced by the diluent or other ingredients (sometimes these are not necessarily inert or known to be without effect) for which the test substance is not responsible. It commonly would give the spontaneous rate of effect (without any trigger). It is importa ...
... substance and reflects background response induced by the diluent or other ingredients (sometimes these are not necessarily inert or known to be without effect) for which the test substance is not responsible. It commonly would give the spontaneous rate of effect (without any trigger). It is importa ...
Lab/Activity: Prot
... can cause great changes to the gene and therefore greatly alter the protein that is made from that gene. This will likely have great effects on the organism, since the protein will not be able to perform its normal function. This may lead to the inheritance of a genetic disease. 3. POINT MUTATION 1: ...
... can cause great changes to the gene and therefore greatly alter the protein that is made from that gene. This will likely have great effects on the organism, since the protein will not be able to perform its normal function. This may lead to the inheritance of a genetic disease. 3. POINT MUTATION 1: ...
Complete the blank spaces in the following chart:
... Part A: Circle the correct choice within the parenthesis for 1-8. 1. (DNA/RNA) can leave the nucleus. 2. mRNA is made during (transcription/translation). 3. mRNA is made in the (cytoplasm/nucleus). 4. DNA is located in the (nucleus/cytoplasm) 5. (Translation/Transcription) converts DNA into mRNA. 6. ...
... Part A: Circle the correct choice within the parenthesis for 1-8. 1. (DNA/RNA) can leave the nucleus. 2. mRNA is made during (transcription/translation). 3. mRNA is made in the (cytoplasm/nucleus). 4. DNA is located in the (nucleus/cytoplasm) 5. (Translation/Transcription) converts DNA into mRNA. 6. ...
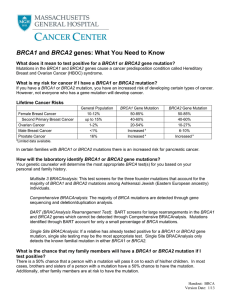
BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes: What You Need to Know
... Comprehensive BRACAnalysis: The majority of BRCA mutations are detected through gene sequencing and deletion/duplication analysis. BART (BRACAnalysis Rearrangement Test): BART screens for large rearrangements in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes which cannot be detected through Comprehensive BRACAnalysis. M ...
... Comprehensive BRACAnalysis: The majority of BRCA mutations are detected through gene sequencing and deletion/duplication analysis. BART (BRACAnalysis Rearrangement Test): BART screens for large rearrangements in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes which cannot be detected through Comprehensive BRACAnalysis. M ...
Frameshift mutation

A frameshift mutation (also called a framing error or a reading frame shift) is a genetic mutation caused by indels (insertions or deletions) of a number of nucleotides in a DNA sequence that is not divisible by three. Due to the triplet nature of gene expression by codons, the insertion or deletion can change the reading frame (the grouping of the codons), resulting in a completely different translation from the original. The earlier in the sequence the deletion or insertion occurs, the more altered the protein. A frameshift mutation is not the same as a single-nucleotide polymorphism in which a nucleotide is replaced, rather than inserted or deleted. A frameshift mutation will in general cause the reading of the codons after the mutation to code for different amino acids. The frameshift mutation will also alter the first stop codon (""UAA"", ""UGA"" or ""UAG"") encountered in the sequence. The polypeptide being created could be abnormally short or abnormally long, and will most likely not be functional.Frameshift mutations are apparent in severe genetic diseases such as Tay-Sachs disease and Cystic Fibrosis; they increase susceptibility to certain cancers and classes of familial hypercholesterolaemia; in 1997, a frameshift mutation was linked to resistance to infection by the HIV retrovirus. Frameshift mutations have been proposed as a source of biological novelty, as with the alleged creation of nylonase, however, this interpretation is controversial. A study by Negoro et al (2006) found that a frameshift mutation was unlikely to have been the cause and that rather a two amino acid substitution in the catalytic cleft of an ancestral esterase amplified Ald-hydrolytic activity.