TB1 - BIOCHEM, Bidichandani, Genetic Diseases
... 5. X linked dilated cardiomyopathy is caused by rare mutations that specifically affect the cardiac expression of the gene. 6. A western blot can be done with a BMD dystrophin protein to see if it is shorter than a normal protein. Histological analysis of DMD/BMD tissue 1. A total lack of dystrophin ...
... 5. X linked dilated cardiomyopathy is caused by rare mutations that specifically affect the cardiac expression of the gene. 6. A western blot can be done with a BMD dystrophin protein to see if it is shorter than a normal protein. Histological analysis of DMD/BMD tissue 1. A total lack of dystrophin ...
Genetic Fine Structure
... coinfection of phage with one of the deletions and phage with each of the site-specific mutations, recombinant phage are observed in the following cases. Assign each site-specific mutation to one of the subdivisions of the deletion map. Deletion Mutants ...
... coinfection of phage with one of the deletions and phage with each of the site-specific mutations, recombinant phage are observed in the following cases. Assign each site-specific mutation to one of the subdivisions of the deletion map. Deletion Mutants ...
10.1 Methods of Recording Variation
... e.g. Down's syndrome, haemophilia. On the basis of this advice parents can choose whether or not to have children. Doctors can diagnose certain genetic defects, e.g. Down's syndrome, in a foetus, by studying samples of cells taken from the amniotic fluid which surrounds the foetus - a process called ...
... e.g. Down's syndrome, haemophilia. On the basis of this advice parents can choose whether or not to have children. Doctors can diagnose certain genetic defects, e.g. Down's syndrome, in a foetus, by studying samples of cells taken from the amniotic fluid which surrounds the foetus - a process called ...
Mutations - GK-12 Program at the University of Houston
... to the proteins that are encoded by the DNA which can lead to a loss of functionality for those proteins. Substitutions, or point mutations, are much more subtle and may have three possible effects. Figure 3 shows how some point mutations may lead to common disorders. 1. Silent – the nucleotide is r ...
... to the proteins that are encoded by the DNA which can lead to a loss of functionality for those proteins. Substitutions, or point mutations, are much more subtle and may have three possible effects. Figure 3 shows how some point mutations may lead to common disorders. 1. Silent – the nucleotide is r ...
Shristi Pandey - X linked Severe Combined Immunodeficiency
... Persistence of infections despite conventional treatment ...
... Persistence of infections despite conventional treatment ...
Genetic Inheritance Teacher Information Sheet
... Genetic Inheritance Teacher Information Sheet There are several ways that a trait, disorder, or disease can be passed down through families. ...
... Genetic Inheritance Teacher Information Sheet There are several ways that a trait, disorder, or disease can be passed down through families. ...
Bio 102 Practice Problems
... 2. The amazing Dr. Johnston, yeast biologist extraordinaire, has discovered a new species of yeast that can grow on high-quality chocolate bars. Dr. Johnston’s new yeast species has three specific enzymes needed to break down lipids found in chocolate. a. Describe a process by which a yeast cell mig ...
... 2. The amazing Dr. Johnston, yeast biologist extraordinaire, has discovered a new species of yeast that can grow on high-quality chocolate bars. Dr. Johnston’s new yeast species has three specific enzymes needed to break down lipids found in chocolate. a. Describe a process by which a yeast cell mig ...
The spectrum of human diseases
... • Start with population genetically isolated for a long time such as Icelanders or Amish • Collect DNA samples from subgroup with disease • Also collect from equal number of people without disease • Genotype each individual in subgroups for haplotypes throughout entire genome • Look for association ...
... • Start with population genetically isolated for a long time such as Icelanders or Amish • Collect DNA samples from subgroup with disease • Also collect from equal number of people without disease • Genotype each individual in subgroups for haplotypes throughout entire genome • Look for association ...
8.7 Mutations - Perry Local Schools
... • Karyotypes can show changes in chromosomes. – deletion of part of a chromosome or loss of a ...
... • Karyotypes can show changes in chromosomes. – deletion of part of a chromosome or loss of a ...
Q on Genetic Control of Protein Structure and function – Chapter 5
... Which enzyme turns DNA nucleotides into a polynucleotide? Explain what is meant by “complementary base pairing”. What type of bond holds the two DNA strands together? What are the 2 essential functions of DNA? What are the 2 main types of RNA and what are their similarities and ...
... Which enzyme turns DNA nucleotides into a polynucleotide? Explain what is meant by “complementary base pairing”. What type of bond holds the two DNA strands together? What are the 2 essential functions of DNA? What are the 2 main types of RNA and what are their similarities and ...
Problem Set 4-key
... In order to figure out the number of possible different mRNAs, you simply multiply these numbers (2x1x2x2x6x6x4), and you get 1152 possible RNA sequences that would code for “AMHERST”... now, just when you are feeling pretty good about your odds of having found a correct RNA sequence to encode AM ...
... In order to figure out the number of possible different mRNAs, you simply multiply these numbers (2x1x2x2x6x6x4), and you get 1152 possible RNA sequences that would code for “AMHERST”... now, just when you are feeling pretty good about your odds of having found a correct RNA sequence to encode AM ...
Back
... Interpreting a Pedigree Chart 2. Determine whether the disorder is dominant or recessive. a. If the disorder is dominant, one of the parents must have the disorder. b. If the disorder is recessive, neither parent has to have the disorder because they can be heterozygous. ...
... Interpreting a Pedigree Chart 2. Determine whether the disorder is dominant or recessive. a. If the disorder is dominant, one of the parents must have the disorder. b. If the disorder is recessive, neither parent has to have the disorder because they can be heterozygous. ...
Genetics 101
... these genes can 'go wrong' when there is a mistake or 'mutation' in the genetic code. In a recessive disease both copies of the gene need to be mutated to see the effects of the disease (as in affected children), in carriers (like all the parents) where one gene is mutated we see no outward sign of ...
... these genes can 'go wrong' when there is a mistake or 'mutation' in the genetic code. In a recessive disease both copies of the gene need to be mutated to see the effects of the disease (as in affected children), in carriers (like all the parents) where one gene is mutated we see no outward sign of ...
Genetic Breast Cancer Testing Article
... BCRA1 mutation have a 55%-65% chance of developing breast cancer by the time they are 70 years old, and those with the BCRA2 mutation have a 45% chance. The BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes occur naturally in the human body, they are responsible for creating protein which helps repair DNA. However, when these ...
... BCRA1 mutation have a 55%-65% chance of developing breast cancer by the time they are 70 years old, and those with the BCRA2 mutation have a 45% chance. The BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes occur naturally in the human body, they are responsible for creating protein which helps repair DNA. However, when these ...
MOLECULAR ANALYSIS OF CYSTIC FIBROSIS PATIENTS IN
... Background: In this study the authors present an update to the CFTR mutation profile in Hungary, utilizing data from a selected cohort of 45 cystic fibrosis (CF) patients from different regions of the country. Methods: Depending on the preceding analysis, four different mutation detection methods we ...
... Background: In this study the authors present an update to the CFTR mutation profile in Hungary, utilizing data from a selected cohort of 45 cystic fibrosis (CF) patients from different regions of the country. Methods: Depending on the preceding analysis, four different mutation detection methods we ...
Spineless Fish and Dark Flies Prove Gene Regulation Crucial
... ful and convincing examples of how [certain] the gene’s coding region is virtually unchanged Three of those mutations are present in regulatory elements can be lost or modified to between fresh- and saltwater fish, suggesting Drosophila with light abdomens, but the reduce [gene] expression, ultimate ...
... ful and convincing examples of how [certain] the gene’s coding region is virtually unchanged Three of those mutations are present in regulatory elements can be lost or modified to between fresh- and saltwater fish, suggesting Drosophila with light abdomens, but the reduce [gene] expression, ultimate ...
幻灯片 1
... There are many different kinds of cancers. Cancer can develop in almost any organ or tissue, such as the lung, colon, breast, skin, bones, or nerve tissue. There are many causes of cancers, including: – Benzene and other chemicals ...
... There are many different kinds of cancers. Cancer can develop in almost any organ or tissue, such as the lung, colon, breast, skin, bones, or nerve tissue. There are many causes of cancers, including: – Benzene and other chemicals ...
ppt
... mutations that change the protein and mutation that do not This provide us with a powerful “internal control” – we are comparing two different types of evolutionary events at the same loci, so all sources of variation in the mutational process are not ...
... mutations that change the protein and mutation that do not This provide us with a powerful “internal control” – we are comparing two different types of evolutionary events at the same loci, so all sources of variation in the mutational process are not ...
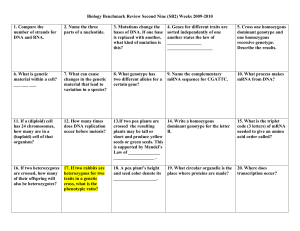
Biology Benchmark Review Second Nine (SB2) Weeks 2009-2010
... show the likelihood a male will be colorblind if his mother is a carrier and his father is not colorblind. ...
... show the likelihood a male will be colorblind if his mother is a carrier and his father is not colorblind. ...
S5. Untangling the central dogma- Extensions on
... 4) What would happen to the primary structure of the protein if one nucleotide were deleted from the protein-coding region of the DNA sequence? What is the name of this type of change? This change is a type of frameshift mutation. It would change the reading frame of the gene, likely changing all th ...
... 4) What would happen to the primary structure of the protein if one nucleotide were deleted from the protein-coding region of the DNA sequence? What is the name of this type of change? This change is a type of frameshift mutation. It would change the reading frame of the gene, likely changing all th ...
Anth. 203 Lab, Exercise #1
... corresponding mRNA codons (on page 2) that would be synthesized during transcription and carry the message to the cytoplasm and the tRNA ant-codons that would bond with each during translation, pulling the appropriate amino acid into position. (see page !!!!!**** 2*****!!!!!!!! for the corresponding ...
... corresponding mRNA codons (on page 2) that would be synthesized during transcription and carry the message to the cytoplasm and the tRNA ant-codons that would bond with each during translation, pulling the appropriate amino acid into position. (see page !!!!!**** 2*****!!!!!!!! for the corresponding ...
Student Name: Teacher
... 18. Abnormal cells (often mutations) that reproduce rapidly eventually overwhelming normal cells and causing death in most organisms are called: A. ...
... 18. Abnormal cells (often mutations) that reproduce rapidly eventually overwhelming normal cells and causing death in most organisms are called: A. ...
Homework 1 / Introduction General questions Programming tasks
... 6. Write a new script (name it sequence_identifier.*) that takes in a random sequence as input (like Rscript myscript.R "ATTTCGGG") and identifies if the sequence represents DNA, RNA or a protein. Depending on the identified sequences in the case of DNA and RNA, calculate the nucleotide composition ...
... 6. Write a new script (name it sequence_identifier.*) that takes in a random sequence as input (like Rscript myscript.R "ATTTCGGG") and identifies if the sequence represents DNA, RNA or a protein. Depending on the identified sequences in the case of DNA and RNA, calculate the nucleotide composition ...
Frameshift mutation

A frameshift mutation (also called a framing error or a reading frame shift) is a genetic mutation caused by indels (insertions or deletions) of a number of nucleotides in a DNA sequence that is not divisible by three. Due to the triplet nature of gene expression by codons, the insertion or deletion can change the reading frame (the grouping of the codons), resulting in a completely different translation from the original. The earlier in the sequence the deletion or insertion occurs, the more altered the protein. A frameshift mutation is not the same as a single-nucleotide polymorphism in which a nucleotide is replaced, rather than inserted or deleted. A frameshift mutation will in general cause the reading of the codons after the mutation to code for different amino acids. The frameshift mutation will also alter the first stop codon (""UAA"", ""UGA"" or ""UAG"") encountered in the sequence. The polypeptide being created could be abnormally short or abnormally long, and will most likely not be functional.Frameshift mutations are apparent in severe genetic diseases such as Tay-Sachs disease and Cystic Fibrosis; they increase susceptibility to certain cancers and classes of familial hypercholesterolaemia; in 1997, a frameshift mutation was linked to resistance to infection by the HIV retrovirus. Frameshift mutations have been proposed as a source of biological novelty, as with the alleged creation of nylonase, however, this interpretation is controversial. A study by Negoro et al (2006) found that a frameshift mutation was unlikely to have been the cause and that rather a two amino acid substitution in the catalytic cleft of an ancestral esterase amplified Ald-hydrolytic activity.