Preview Sample 1
... minerals to deduce attributes common for all minerals and use these observation to build a definition of “mineral.” Along the way, we offer explanations for why minerals exhibit different physical properties and simultaneously introduce important concepts about the composition and bonding character ...
... minerals to deduce attributes common for all minerals and use these observation to build a definition of “mineral.” Along the way, we offer explanations for why minerals exhibit different physical properties and simultaneously introduce important concepts about the composition and bonding character ...
3: Haloalkanes, Alcohols, Ethers, and Amines
... electronegativity differences in Table 3.1 mean that C is positively polarized (δ+) while its attached atom is negatively polarized (δ-). The relative magnitudes of these electronegativity differences reflect the relative magnitudes of the polarity of each bond. The negative (-) electronegativity di ...
... electronegativity differences in Table 3.1 mean that C is positively polarized (δ+) while its attached atom is negatively polarized (δ-). The relative magnitudes of these electronegativity differences reflect the relative magnitudes of the polarity of each bond. The negative (-) electronegativity di ...
Pdf
... diffuse, and rejoin crystals, causing slow kinetic convergence onto a single large crystal. The kinetic driving force is that small crystals have higher solubility than larger crystals of the same substance, causing the latter to grow at the expense of the former. Compared to the amount of substance ...
... diffuse, and rejoin crystals, causing slow kinetic convergence onto a single large crystal. The kinetic driving force is that small crystals have higher solubility than larger crystals of the same substance, causing the latter to grow at the expense of the former. Compared to the amount of substance ...
Organic Chemistry Curriculum Map - Belle Vernon Area School District
... Chemistry is the study of matter and the changes it undergoes. ...
... Chemistry is the study of matter and the changes it undergoes. ...
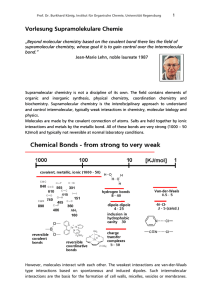
Vorlesung Supramolekulare Chemie
... Supramolecular chemistry is not a discipline of its own. The field contains elements of organic and inorganic synthesis, physical chemistry, coordination chemistry and biochemistry. Supramolecular chemistry is the interdisciplinary approach to understand and control intermolecular, typically weak in ...
... Supramolecular chemistry is not a discipline of its own. The field contains elements of organic and inorganic synthesis, physical chemistry, coordination chemistry and biochemistry. Supramolecular chemistry is the interdisciplinary approach to understand and control intermolecular, typically weak in ...
Net ionic equation
... The forces holding an ionic compound together are the strong electrical attraction that exists between cations and anions. It is therefore somewhat surprising that ionic compounds will dissolve in water. The reason some ionic compounds will dissolve in water is because the water molecules have a par ...
... The forces holding an ionic compound together are the strong electrical attraction that exists between cations and anions. It is therefore somewhat surprising that ionic compounds will dissolve in water. The reason some ionic compounds will dissolve in water is because the water molecules have a par ...
CH4 Student Revision Guides pdf | GCE AS/A
... Although all 11 H atoms are the same, the absorption depends on the environment of the hydrogen atom. The magnetic field at the nucleus is not the same as the applied magnetic field because the charged electrons also interact with the applied magnetic field. The difference between the two is called ...
... Although all 11 H atoms are the same, the absorption depends on the environment of the hydrogen atom. The magnetic field at the nucleus is not the same as the applied magnetic field because the charged electrons also interact with the applied magnetic field. The difference between the two is called ...
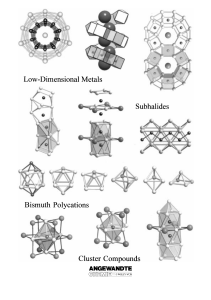
From the Metal to the Molecule
... metals albeit with far fewer examples. For example, recently significant progress has been made especially in research using the elements indium,[6] tin,[7] and bismuth.[8] This research mainly concerns the ternary and quaternary oxides or halides of the aforementioned main group elements which cont ...
... metals albeit with far fewer examples. For example, recently significant progress has been made especially in research using the elements indium,[6] tin,[7] and bismuth.[8] This research mainly concerns the ternary and quaternary oxides or halides of the aforementioned main group elements which cont ...
Organic Chemistry - University of California, Riverside
... electronegativity differences in Table 3.1 mean that C is positively polarized (δ+) while its attached atom is negatively polarized (δ-). The relative magnitudes of these electronegativity differences reflect the relative magnitudes of the polarity of each bond. The negative (-) electronegativity di ...
... electronegativity differences in Table 3.1 mean that C is positively polarized (δ+) while its attached atom is negatively polarized (δ-). The relative magnitudes of these electronegativity differences reflect the relative magnitudes of the polarity of each bond. The negative (-) electronegativity di ...
the Main-Group Metals - McQuarrie General Chemistry
... the group in the periodic table. Boron has a metallic luster but behaves more like the semimetal silicon than like the metal aluminum (Figure I.8). Boron(III) is always covalently bonded; boron forms no simple ionic cations of the type B3+. For example, the boron trihalides, BX3, are trigonal planar ...
... the group in the periodic table. Boron has a metallic luster but behaves more like the semimetal silicon than like the metal aluminum (Figure I.8). Boron(III) is always covalently bonded; boron forms no simple ionic cations of the type B3+. For example, the boron trihalides, BX3, are trigonal planar ...
Neutral ionic liquid [BMIm]BF4 promoted highly selective
... of tert-butanol by acetic anhydride using mesoporous Si-MCM41, clay and alumina supported metal Lewis acid, such as InCl3 and GaCl3 , as catalyst [9–11]. However, these metal species are toxic or expensive. Hence, there is a need to develop an environmentally benign method for the esterification of ...
... of tert-butanol by acetic anhydride using mesoporous Si-MCM41, clay and alumina supported metal Lewis acid, such as InCl3 and GaCl3 , as catalyst [9–11]. However, these metal species are toxic or expensive. Hence, there is a need to develop an environmentally benign method for the esterification of ...
Ultrapure, high mobility organic photoconductors
... program designed to obtain reliable experimental data over wide temperature ranges on charge-cartier transport in organic photoconductors. Naphthalene and perylene were selected, among others, to serve as model substances. Naphthalene is one of the most simple aromatic molecules; very extensive inve ...
... program designed to obtain reliable experimental data over wide temperature ranges on charge-cartier transport in organic photoconductors. Naphthalene and perylene were selected, among others, to serve as model substances. Naphthalene is one of the most simple aromatic molecules; very extensive inve ...
AP Chemistry - Freehold Regional High School District
... Enduring Understandings There are 2 major types of bonding. Valence electrons are involved in bonding. Lewis structures indicate bonding and nonbonding electrons. The strength of a covalent bond depends on the type of the covalent bond. Covalent bonds can polar or non polar based on the electronegat ...
... Enduring Understandings There are 2 major types of bonding. Valence electrons are involved in bonding. Lewis structures indicate bonding and nonbonding electrons. The strength of a covalent bond depends on the type of the covalent bond. Covalent bonds can polar or non polar based on the electronegat ...
Organic Acids and Bases and Some of Their Derivatives
... found in carboxylic acids, esters, and amides. However, in these compounds, the carbonyl group is only part of the functional group. A carboxylic acid1 is an organic compound that has a carboxyl group2. The carboxyl group is a functional group that contains a carbon–oxygen double bond and an OH grou ...
... found in carboxylic acids, esters, and amides. However, in these compounds, the carbonyl group is only part of the functional group. A carboxylic acid1 is an organic compound that has a carboxyl group2. The carboxyl group is a functional group that contains a carbon–oxygen double bond and an OH grou ...
Covalent Bonding and Nomenclature
... to attract electrons when chemically combining with another element. The higher the electronegativity value, the stronger the attraction the atom has for another atom’s electrons. ...
... to attract electrons when chemically combining with another element. The higher the electronegativity value, the stronger the attraction the atom has for another atom’s electrons. ...
Document
... molecule of O2 is 0, since the molecule is produced by species of the same (not different) element(s)] ...
... molecule of O2 is 0, since the molecule is produced by species of the same (not different) element(s)] ...
Chapter 4: Reaction Stoichiometry Reaction Stoichiometry
... 3. Swap the cations to form a new compound - this will be one of your products. 4. Take the remaining cation and convert it to an element this will be the other product. 5. Write the new compounds with balanced formulas. 6. Determine the phases of the new products - are the new compounds soluble or ...
... 3. Swap the cations to form a new compound - this will be one of your products. 4. Take the remaining cation and convert it to an element this will be the other product. 5. Write the new compounds with balanced formulas. 6. Determine the phases of the new products - are the new compounds soluble or ...
Acids ,Bases and Salts
... The more the dissociation the higher the yield of ions and the greater the electrical conductivity of the solution. A compound that conducts electricity in an electrolyte and thus a compound showing high electrical conductivity is a strong electrolyte while a compound showing low electrical conducti ...
... The more the dissociation the higher the yield of ions and the greater the electrical conductivity of the solution. A compound that conducts electricity in an electrolyte and thus a compound showing high electrical conductivity is a strong electrolyte while a compound showing low electrical conducti ...
bicC-DNA manuscript
... they hybridize to the defined target sequences on DNA or RNA. For this purpose, we have been exploring effective modifications (11) and found that incorporation of 7,8-dihydropyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidin-2-one (bicyclic cytosine), a derivative in which a propene is attached to the N4 and C5 atoms of the b ...
... they hybridize to the defined target sequences on DNA or RNA. For this purpose, we have been exploring effective modifications (11) and found that incorporation of 7,8-dihydropyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidin-2-one (bicyclic cytosine), a derivative in which a propene is attached to the N4 and C5 atoms of the b ...
Lecture 2a: Igneous classification, mid-ocean ridges
... – Plutonic rocks crystallize at some depth, and therefore lose heat relatively slowly. Crystals have time to grow after nucleation, and the resulting rocks generally have individual crystals large enough to see unaided. – Rocks of exactly the same composition and mineralogy get different names in th ...
... – Plutonic rocks crystallize at some depth, and therefore lose heat relatively slowly. Crystals have time to grow after nucleation, and the resulting rocks generally have individual crystals large enough to see unaided. – Rocks of exactly the same composition and mineralogy get different names in th ...
Minerals
... How Minerals Form: There are four major processes by which minerals form: 1) crystallization from magma, 2) precipitation, 3) changes in pressure and temperature, 4) formation from hydrothermal solutions. 1. Magma is molten rock that is formed deep within the Earth. As the magma cools the elements ...
... How Minerals Form: There are four major processes by which minerals form: 1) crystallization from magma, 2) precipitation, 3) changes in pressure and temperature, 4) formation from hydrothermal solutions. 1. Magma is molten rock that is formed deep within the Earth. As the magma cools the elements ...
ESO - ENCIGA
... order to be able to predict its behaviour and understand its history. Science is based on systematic experimentation and on observation of natural phenomena to discover facts about them and to formulate laws and principles based on these facts. The organized knowledge that is derived from scientific ...
... order to be able to predict its behaviour and understand its history. Science is based on systematic experimentation and on observation of natural phenomena to discover facts about them and to formulate laws and principles based on these facts. The organized knowledge that is derived from scientific ...
Chemistry - College Catalog
... department. (Students who receive a grade of B+ or higher in CHEM 22000 have the option of moving into honors organic chemistry for Winter/Spring. See following listing for CHEM 23100-23200.) NOTE: Most medical schools require a full academic year of organic chemistry. The fundamental structures of ...
... department. (Students who receive a grade of B+ or higher in CHEM 22000 have the option of moving into honors organic chemistry for Winter/Spring. See following listing for CHEM 23100-23200.) NOTE: Most medical schools require a full academic year of organic chemistry. The fundamental structures of ...
CHOICE BASED CREDIT SYSTEM B. Sc. WITH CHEMISTRY
... Ionic Bonding: General characteristics of ionic bonding. Energy considerations in ionic bonding, lattice energy and solvation energy and their importance in the context of stability and solubility of ionic compounds. Statement of Born-Landé equation for calculation of lattice energy, Born-Haber cycl ...
... Ionic Bonding: General characteristics of ionic bonding. Energy considerations in ionic bonding, lattice energy and solvation energy and their importance in the context of stability and solubility of ionic compounds. Statement of Born-Landé equation for calculation of lattice energy, Born-Haber cycl ...
高雄醫學大學九十二學年度學士後醫學系招生考試試題 科目:化學 考試
... (A) ppm-1 L cm-1 (B) ppm-1 cm-1 (C) cm ppm-1 (D) ppm cm-1 (E) cm ppm 11. The difference between spectrophotometer and photometer is in the (A) source (B) wavelength selector (C) sample container (D) detector ...
... (A) ppm-1 L cm-1 (B) ppm-1 cm-1 (C) cm ppm-1 (D) ppm cm-1 (E) cm ppm 11. The difference between spectrophotometer and photometer is in the (A) source (B) wavelength selector (C) sample container (D) detector ...






![Neutral ionic liquid [BMIm]BF4 promoted highly selective](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/017897985_1-047f9869d5604c115b21339541ccfffe-300x300.png)