feature articles
... Crystal models were constructed by adding extra phenylene rings and the corresponding substituent groups that were introduced to enhance the solubility of the linkers. Rietveld refinements were performed with most of the members of the series using diffraction collected with a synchrotron source. Ho ...
... Crystal models were constructed by adding extra phenylene rings and the corresponding substituent groups that were introduced to enhance the solubility of the linkers. Rietveld refinements were performed with most of the members of the series using diffraction collected with a synchrotron source. Ho ...
Document
... Closer inspection shows another type of motion, shown in figure 1. The sole effect here is to switch two bonds. If we label the two relevant atoms of the five-membered ring L and M, and if U and V are the two key atoms that are not part of the ring, the sole effect is that bonds LU and MV switch to ...
... Closer inspection shows another type of motion, shown in figure 1. The sole effect here is to switch two bonds. If we label the two relevant atoms of the five-membered ring L and M, and if U and V are the two key atoms that are not part of the ring, the sole effect is that bonds LU and MV switch to ...
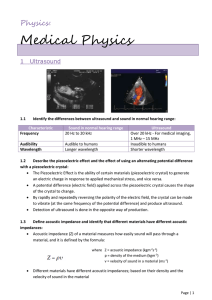
Medical Physics
... An incident electron will be slowed down by interacting with the nucleus of a target atom tungsten (1) The electron’s kinetic energy is converted to a photon of X-radiation (2) Some incident electrons knock inner atomic shell electrons from their orbitals. Other target atom electrons change orbitals ...
... An incident electron will be slowed down by interacting with the nucleus of a target atom tungsten (1) The electron’s kinetic energy is converted to a photon of X-radiation (2) Some incident electrons knock inner atomic shell electrons from their orbitals. Other target atom electrons change orbitals ...
as a PDF
... mentally observed one. The details of the numerical implementation of the method were reported in [7]. For studying features of formation of chemical bond the sublattice method [8] was applied. In the sublattice method, the difference density Δρ(r) is calculated, which is defined as the difference b ...
... mentally observed one. The details of the numerical implementation of the method were reported in [7]. For studying features of formation of chemical bond the sublattice method [8] was applied. In the sublattice method, the difference density Δρ(r) is calculated, which is defined as the difference b ...
References
... The possibility of the simultaneous existence of different forms of nickel (II) complex in the presence of - diimine ligands with different structure can determine some of their physico-chemical properties . Thus, the non-equivalence of the two bromide ions in the complex I and different Ni-Br bond ...
... The possibility of the simultaneous existence of different forms of nickel (II) complex in the presence of - diimine ligands with different structure can determine some of their physico-chemical properties . Thus, the non-equivalence of the two bromide ions in the complex I and different Ni-Br bond ...
Birefringence for facetors I : what is birefringence? First published in
... shows the same symmetry. There is no reason why light should travel more rapidly along this direction when it has one particular polarization plane rather than another. The refractive index, in other words, is polarization-independent, because there is no net direction perpendicular to this axis in ...
... shows the same symmetry. There is no reason why light should travel more rapidly along this direction when it has one particular polarization plane rather than another. The refractive index, in other words, is polarization-independent, because there is no net direction perpendicular to this axis in ...
Chapter 4 Minerals
... 1. Describe why sugar is not a mineral. 2. List the two main ways that minerals can form. 3. What is the name of the atomic structure of the silicates and what is the composition of quartz? 4. Why is color the least useful property for identifying minerals? ...
... 1. Describe why sugar is not a mineral. 2. List the two main ways that minerals can form. 3. What is the name of the atomic structure of the silicates and what is the composition of quartz? 4. Why is color the least useful property for identifying minerals? ...
- Alagappa University
... Explain the methods of measurement of directive constant for low loss and high loss liquids. Give the necessary theory. ...
... Explain the methods of measurement of directive constant for low loss and high loss liquids. Give the necessary theory. ...
Slide 1
... The X-ray structure of the antibody HyHEL-63 (cyan) uncomplexed and complexed with Hen Egg White Lysozyme (yellow) has shown that there are small but significant, local conformational changes in the antibody paratope on binding. The structure also reveals that most of the charged epitope residues fa ...
... The X-ray structure of the antibody HyHEL-63 (cyan) uncomplexed and complexed with Hen Egg White Lysozyme (yellow) has shown that there are small but significant, local conformational changes in the antibody paratope on binding. The structure also reveals that most of the charged epitope residues fa ...
Document
... external electric and magnetic fields. Expressions obtained will be useful when considering real conductors (i) FREE ELECTRONS: The valance electrons are not affected by the electron-ion interaction. That is their dynamical behaviour is as if they are not acted on by any forces internal to the condu ...
... external electric and magnetic fields. Expressions obtained will be useful when considering real conductors (i) FREE ELECTRONS: The valance electrons are not affected by the electron-ion interaction. That is their dynamical behaviour is as if they are not acted on by any forces internal to the condu ...
Theoretical prediction of the nondiffractive propagation of sonic
... media, initiated hundreds of year ago, ever and ever leads to surprisingly new results and insights. One of such “surprises” was the discovery of band gaps in the propagation of light in materials with the refraction index periodically modulated on the scale of the optical wavelength, the socalled p ...
... media, initiated hundreds of year ago, ever and ever leads to surprisingly new results and insights. One of such “surprises” was the discovery of band gaps in the propagation of light in materials with the refraction index periodically modulated on the scale of the optical wavelength, the socalled p ...
Neutrons and new materials - Institut Laue
... spacing between atomic planes, and by measuring these angles and intensities the atomic structure of the material can be deduced. If instead of a crystalline powder an amorphous or liquid sample is used, there are only broad peaks at specific angles corresponding to average interatomic distances. To ...
... spacing between atomic planes, and by measuring these angles and intensities the atomic structure of the material can be deduced. If instead of a crystalline powder an amorphous or liquid sample is used, there are only broad peaks at specific angles corresponding to average interatomic distances. To ...
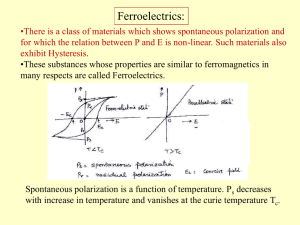
Dielectric loss
... •A stress applied to the crystal will change the electric polarization. Similarly, an electric field E applied to the crystal will cause the crystal to become strained (electrostriction). •All crystals in a ferroelectric state are also Piezoelectric. But vice verse is not true. E.g Quartz. • Crystal ...
... •A stress applied to the crystal will change the electric polarization. Similarly, an electric field E applied to the crystal will cause the crystal to become strained (electrostriction). •All crystals in a ferroelectric state are also Piezoelectric. But vice verse is not true. E.g Quartz. • Crystal ...
Precision Electron Diffraction Structure Analysis and Its Use in
... excitation and the interband transitions [15, 25]. For rather thick crystals, e.g., in convergent-beam electron diffraction [16], one should also take into account absorption. This is done by the introduction of the complex potential. The major contribution to the imaginary part of the structure fac ...
... excitation and the interband transitions [15, 25]. For rather thick crystals, e.g., in convergent-beam electron diffraction [16], one should also take into account absorption. This is done by the introduction of the complex potential. The major contribution to the imaginary part of the structure fac ...
CHAP2
... • Diagenesis is all the chemical, physical, and biologic changes undergone by a sediment after its initial deposition, and during and after its lithification, exclusive of superficial alteration (weathering) and metamorphism. • Lithification is the conversion of a newly deposited sediment into a con ...
... • Diagenesis is all the chemical, physical, and biologic changes undergone by a sediment after its initial deposition, and during and after its lithification, exclusive of superficial alteration (weathering) and metamorphism. • Lithification is the conversion of a newly deposited sediment into a con ...
CC 5 402-403..8121g ose chapter .. Page402
... To further examine the role of water in framework formation, we have applied the hydrothermal method, used previously in our work on CMCR based supramolecular complexes,3 to the CMCR–H2O system, without the addition of potential guest molecules. A new phase, CMCR·H2O 1, in which the CMCR adopts a no ...
... To further examine the role of water in framework formation, we have applied the hydrothermal method, used previously in our work on CMCR based supramolecular complexes,3 to the CMCR–H2O system, without the addition of potential guest molecules. A new phase, CMCR·H2O 1, in which the CMCR adopts a no ...
Topic/Objective: Full Name: Class: Period: _____ Date: Tutor Use
... An element is matter that is made up of the atoms that have the same number of _protons _ in their nucleus. But not all atoms of the same element are the same. Some elements have the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons in the nucleus, these are called ___isotopes__. Most su ...
... An element is matter that is made up of the atoms that have the same number of _protons _ in their nucleus. But not all atoms of the same element are the same. Some elements have the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons in the nucleus, these are called ___isotopes__. Most su ...
Structures and Properties of Ceramics
... Structures and Properties of Ceramics Ch. 12 Nitride Ceramics Nitrides combine the superior hardness of ceramics with high thermal and mechanical stability, making them suitable for applications as cutting tools, wear-resistant parts and structural components at high temperatures. TiN has a cubic s ...
... Structures and Properties of Ceramics Ch. 12 Nitride Ceramics Nitrides combine the superior hardness of ceramics with high thermal and mechanical stability, making them suitable for applications as cutting tools, wear-resistant parts and structural components at high temperatures. TiN has a cubic s ...
- Surrey Research Insight Open Access
... intensity. The system was highly sensitive to vibrations, and changes in observed photodiode output were seen without applied bias or X-ray irradiation. These correlate with minute changes in alignment due to the changes in optical path lengths and, potentially, light guide effects caused by the CZT ...
... intensity. The system was highly sensitive to vibrations, and changes in observed photodiode output were seen without applied bias or X-ray irradiation. These correlate with minute changes in alignment due to the changes in optical path lengths and, potentially, light guide effects caused by the CZT ...
Communicating Research to the General Public
... the opposite of organic chemistry, as the name implies, and then describe organic chemistry. However, this does an injustice to the field of inorganic chemistry, which we interact with on a daily basis and may not even realize we do. Inorganic chemistry, in simplest terms, may be defined as the stud ...
... the opposite of organic chemistry, as the name implies, and then describe organic chemistry. However, this does an injustice to the field of inorganic chemistry, which we interact with on a daily basis and may not even realize we do. Inorganic chemistry, in simplest terms, may be defined as the stud ...
Advanced Characterization methods lectures
... transitions are much narrower than typical ones in UV-VIS spectroscopy, and so are much more useful for identification of the constituents of a sample. The basic physics underlying these bands is easily understood at a simple level using the mass and spring model. The response of a system of masses ...
... transitions are much narrower than typical ones in UV-VIS spectroscopy, and so are much more useful for identification of the constituents of a sample. The basic physics underlying these bands is easily understood at a simple level using the mass and spring model. The response of a system of masses ...
Density Functional Calculation - Gazi University Journal of Science
... In present work, we have made a detailed investigation of the electronic structure and frequency-dependent linear optical properties of the BiOCl crystal using the density functional methods. The task of this work was to apply the density-functional methods to a complex crystal like the BiOCl. It is ...
... In present work, we have made a detailed investigation of the electronic structure and frequency-dependent linear optical properties of the BiOCl crystal using the density functional methods. The task of this work was to apply the density-functional methods to a complex crystal like the BiOCl. It is ...
MINERALS AND THEIR PROPERTIES
... ○ Can the LifeGem diamonds be considered true minerals? Explain your answer. ○ How are these diamonds different than diamonds mined out of the ground? ○ Would you want to use this company for yourself or for a relative? ...
... ○ Can the LifeGem diamonds be considered true minerals? Explain your answer. ○ How are these diamonds different than diamonds mined out of the ground? ○ Would you want to use this company for yourself or for a relative? ...
Structural Studies of DsbA and its Putative Partner, VKOR, in
... secreted proteins. In Mycobacterium tuberculosis, DsbA is proposed to be a disulfide isomerase and is believed to be re-oxidized by its putative partner, vitamin K epoxide reductase (VKOR). The intent of this study is to further investigate the molecular determinants of the interactions between DsbA ...
... secreted proteins. In Mycobacterium tuberculosis, DsbA is proposed to be a disulfide isomerase and is believed to be re-oxidized by its putative partner, vitamin K epoxide reductase (VKOR). The intent of this study is to further investigate the molecular determinants of the interactions between DsbA ...
Structural Investigation of the Antibiotic and ATP
... +This research was supported in part by a grant from the NIH (DK47814). X-ray coordinates have been deposited with the Brookhaven Protein Data Bank under the filename 1KNY. * To whom correspondence should be addressed. Abstract published in Advance ACS Abstracts, October 1, 1995. ...
... +This research was supported in part by a grant from the NIH (DK47814). X-ray coordinates have been deposited with the Brookhaven Protein Data Bank under the filename 1KNY. * To whom correspondence should be addressed. Abstract published in Advance ACS Abstracts, October 1, 1995. ...
X-ray crystallography

X-ray crystallography is a tool used for identifying the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline atoms cause a beam of incident X-rays to diffract into many specific directions. By measuring the angles and intensities of these diffracted beams, a crystallographer can produce a three-dimensional picture of the density of electrons within the crystal. From this electron density, the mean positions of the atoms in the crystal can be determined, as well as their chemical bonds, their disorder and various other information.Since many materials can form crystals—such as salts, metals, minerals, semiconductors, as well as various inorganic, organic and biological molecules—X-ray crystallography has been fundamental in the development of many scientific fields. In its first decades of use, this method determined the size of atoms, the lengths and types of chemical bonds, and the atomic-scale differences among various materials, especially minerals and alloys. The method also revealed the structure and function of many biological molecules, including vitamins, drugs, proteins and nucleic acids such as DNA. X-ray crystallography is still the chief method for characterizing the atomic structure of new materials and in discerning materials that appear similar by other experiments. X-ray crystal structures can also account for unusual electronic or elastic properties of a material, shed light on chemical interactions and processes, or serve as the basis for designing pharmaceuticals against diseases.In a single-crystal X-ray diffraction measurement, a crystal is mounted on a goniometer. The goniometer is used to position the crystal at selected orientations. The crystal is bombarded with a finely focused monochromatic beam of X-rays, producing a diffraction pattern of regularly spaced spots known as reflections. The two-dimensional images taken at different rotations are converted into a three-dimensional model of the density of electrons within the crystal using the mathematical method of Fourier transforms, combined with chemical data known for the sample. Poor resolution (fuzziness) or even errors may result if the crystals are too small, or not uniform enough in their internal makeup.X-ray crystallography is related to several other methods for determining atomic structures. Similar diffraction patterns can be produced by scattering electrons or neutrons, which are likewise interpreted by Fourier transformation. If single crystals of sufficient size cannot be obtained, various other X-ray methods can be applied to obtain less detailed information; such methods include fiber diffraction, powder diffraction and (if the sample is not crystallized) small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS).If the material under investigation is only available in the form of nanocrystalline powders or suffers from poor crystallinity, the methods of electron crystallography can be applied for determining the atomic structure.For all above mentioned X-ray diffraction methods, the scattering is elastic; the scattered X-rays have the same wavelength as the incoming X-ray. By contrast, inelastic X-ray scattering methods are useful in studying excitations of the sample, rather than the distribution of its atoms.