Slides (pdf format)
... • New individuals (vermiform larvae) produced asexually from w/in axial cell of adults. These larvae exactly resemble their parents; break out through the body wall (initially free-swimming, but become reattached to the host kidney). • When the cephalopod host attains sexual maturity, nematogens tra ...
... • New individuals (vermiform larvae) produced asexually from w/in axial cell of adults. These larvae exactly resemble their parents; break out through the body wall (initially free-swimming, but become reattached to the host kidney). • When the cephalopod host attains sexual maturity, nematogens tra ...
ANSWERS on Inheritance File
... 1. breed / “Peaches and Cream” / eq; 2. named good feature of other variety / larger seeds / more seeds / more yellow / more white / sweeter / eq; 3. collect seeds / seeds produced / eq; 4. grow seeds / eq; 5. test new sweet corn / eq; 6. continue process / repeat / further selective breeding / eq ; ...
... 1. breed / “Peaches and Cream” / eq; 2. named good feature of other variety / larger seeds / more seeds / more yellow / more white / sweeter / eq; 3. collect seeds / seeds produced / eq; 4. grow seeds / eq; 5. test new sweet corn / eq; 6. continue process / repeat / further selective breeding / eq ; ...
Q15 Briefly outline the production and fate of Red Blood Cells (RBC
... Erythrocytes (red blood cells) play a vital role in oxygen and carbon dioxide transport through the body. ...
... Erythrocytes (red blood cells) play a vital role in oxygen and carbon dioxide transport through the body. ...
Honors Biology Botany Lab Practical Review
... Monocot leaf: id as monocot, id vascular bundle, bulliform cells, guard cells, cuticle Dicot leaf: id as dicot, id cuticle, palisade mesophyll, epidermis, stomata, guard cells, spongy mesophyll Be able to id the following leaf environments: mesophytic, xerophytic, hydrophytic Monocot stem: id as mon ...
... Monocot leaf: id as monocot, id vascular bundle, bulliform cells, guard cells, cuticle Dicot leaf: id as dicot, id cuticle, palisade mesophyll, epidermis, stomata, guard cells, spongy mesophyll Be able to id the following leaf environments: mesophytic, xerophytic, hydrophytic Monocot stem: id as mon ...
Animal Reproduction
... Spermatogenesis – each primary spermatocyte divides to form 4 sperm. Oogenesis – each primary oocyte divides to form 1 ovum and 2-3 polar bodies. In oogenesis, cytokinesis is unequal, most of the cytoplasm goes to one daughter cell which becomes the ovum. The other cells, polar bodies, degener ...
... Spermatogenesis – each primary spermatocyte divides to form 4 sperm. Oogenesis – each primary oocyte divides to form 1 ovum and 2-3 polar bodies. In oogenesis, cytokinesis is unequal, most of the cytoplasm goes to one daughter cell which becomes the ovum. The other cells, polar bodies, degener ...
File
... beings with a swelling on the side of the polyp. Polyps also bud off tiny polyp . Mature medusae reproduce sexually by releasing gametes into the water. Depending on the species, fertilization occurs either in open water or inside egg-carrying medusa zygote grows into a swimming, ciliated la ...
... beings with a swelling on the side of the polyp. Polyps also bud off tiny polyp . Mature medusae reproduce sexually by releasing gametes into the water. Depending on the species, fertilization occurs either in open water or inside egg-carrying medusa zygote grows into a swimming, ciliated la ...
Chapters 48-49 - SJDAHomework
... specify which ions move and in what order when the fiber is stimulated, and explain what is meant by voltage-sensitive channels. Using a diagram, Explain how the nerve impulse is propagated along the neuron. 5. Explain how diffusion, electrostatic attraction, and the sodium-potassium pump act to ree ...
... specify which ions move and in what order when the fiber is stimulated, and explain what is meant by voltage-sensitive channels. Using a diagram, Explain how the nerve impulse is propagated along the neuron. 5. Explain how diffusion, electrostatic attraction, and the sodium-potassium pump act to ree ...
Kingdom Animalia
... Embryonic Germ Layers • Fundamental tissue types found in the embryo – ________________ • Skin & coverings, nervous system ...
... Embryonic Germ Layers • Fundamental tissue types found in the embryo – ________________ • Skin & coverings, nervous system ...
Tissues and membranes - Mrs. Hud`s Wacky World of Biology
... New epithelial cells push themselves toward the surface of the skin Wound is quickly restored to normal If damage is over a large area connective tissue cells and fibroblasts are involved ...
... New epithelial cells push themselves toward the surface of the skin Wound is quickly restored to normal If damage is over a large area connective tissue cells and fibroblasts are involved ...
Central Nervous System
... basal plates (ventral horns) of the spinal cord. These fibers collect into bundles known as ventral nerve roots. Dorsal nerve roots form as collections of fibers originating from cells in dorsal root ganglia (spinal ganglia). Central processes from these ganglia form bundles that grow into the spina ...
... basal plates (ventral horns) of the spinal cord. These fibers collect into bundles known as ventral nerve roots. Dorsal nerve roots form as collections of fibers originating from cells in dorsal root ganglia (spinal ganglia). Central processes from these ganglia form bundles that grow into the spina ...
Enumerate the organs of female reproductive system. Discuss the
... releases its ovum into the peritoneal cavity. This is called ovulation • Ovulation occurs each menstrual cycle ...
... releases its ovum into the peritoneal cavity. This is called ovulation • Ovulation occurs each menstrual cycle ...
Biology\Worm Unit
... - humans are infected by eating undercooked beef (Taenia saginatta) or pork (Taenia solium) containing tapeworm cysts. ...
... - humans are infected by eating undercooked beef (Taenia saginatta) or pork (Taenia solium) containing tapeworm cysts. ...
File
... 1. What is the name of the muscle responsible for your breathing? • A. lungs • B. diaphragm ...
... 1. What is the name of the muscle responsible for your breathing? • A. lungs • B. diaphragm ...
Scott Foresman Science
... organisms are made of many, many cells. There might be trillions of cells in a complex living creature! Most cells are too small to see with just your eyes. One drop of blood holds millions of red blood cells. Look at the picture to see just one red blood cell. The picture was taken through a powerf ...
... organisms are made of many, many cells. There might be trillions of cells in a complex living creature! Most cells are too small to see with just your eyes. One drop of blood holds millions of red blood cells. Look at the picture to see just one red blood cell. The picture was taken through a powerf ...
Types of Tissues
... 2. Have an apical surface exposed to a body cavity, lining of an internal organ or the exterior of the body; lateral surface facing adjacent cells on either side, basal surface which are the deepest layers of the cell 3. Lack blood vessels get nutrients by diffusion. 4. They have a nerve supply. 5 ...
... 2. Have an apical surface exposed to a body cavity, lining of an internal organ or the exterior of the body; lateral surface facing adjacent cells on either side, basal surface which are the deepest layers of the cell 3. Lack blood vessels get nutrients by diffusion. 4. They have a nerve supply. 5 ...
Female Reproductive System
... Ovarian medulla: deep to the ovarian cortex containing loosely arranged connective tissue, blood vessels, lymphatic vessels and nerves. Ovarian follicles: contains oocytes and cells surrounding them. They are located in the ovarian cortex of the ovary. When the surrounding cells form a single layer ...
... Ovarian medulla: deep to the ovarian cortex containing loosely arranged connective tissue, blood vessels, lymphatic vessels and nerves. Ovarian follicles: contains oocytes and cells surrounding them. They are located in the ovarian cortex of the ovary. When the surrounding cells form a single layer ...
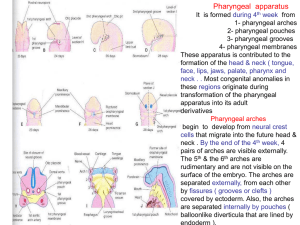
02-pharyngeal arches ,pouchs
... is covered externally by ectoderm & internally by endoderm. The original mesenchyme is derived from mesoderm in the third week. During the 4th week most of the mesenchyme is derived from neural crest cells which are the major source of the arches connective tissue ( bone, cartilage and ligaments) . ...
... is covered externally by ectoderm & internally by endoderm. The original mesenchyme is derived from mesoderm in the third week. During the 4th week most of the mesenchyme is derived from neural crest cells which are the major source of the arches connective tissue ( bone, cartilage and ligaments) . ...
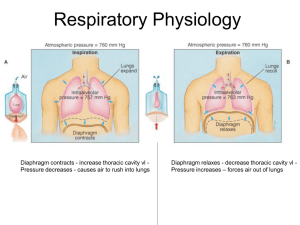
Respiratory Physiology
... Lung cancer –most common cancer and most common cause of cancer deaths in U.S. males. There are several forms of lung cancer, but the most common (and most rapidly increasing) types are those involving the epithelial cells lining the bronchi and bronchioles. Ordinarily, the lining of these airways c ...
... Lung cancer –most common cancer and most common cause of cancer deaths in U.S. males. There are several forms of lung cancer, but the most common (and most rapidly increasing) types are those involving the epithelial cells lining the bronchi and bronchioles. Ordinarily, the lining of these airways c ...
Animilia - Paxon Biology
... They are organisms that store carbohydrates as glycogen. They lack cell walls. Have nervous and muscle tissue. They reproduce sexually, with fertilization resulting in a blastula. The blastula undergoes gastrulation. Organisms may have complicated life stages, such as a larval stage. ...
... They are organisms that store carbohydrates as glycogen. They lack cell walls. Have nervous and muscle tissue. They reproduce sexually, with fertilization resulting in a blastula. The blastula undergoes gastrulation. Organisms may have complicated life stages, such as a larval stage. ...
foreign antigen
... release perforin protein forms pore allowing fluid to flow in & out of cell cell ruptures (lysis) ...
... release perforin protein forms pore allowing fluid to flow in & out of cell cell ruptures (lysis) ...
Mock Exam III
... 18. Which of the following is involved in speeding up breathing? a. Nervous and chemical signals. b. Medulla breathing center impulses. c. A drop in the pH of cerebrospinal fluid. d. Severe deficiencies of oxygen. e. All of the above. 19. Which of the following are similarities between open and clos ...
... 18. Which of the following is involved in speeding up breathing? a. Nervous and chemical signals. b. Medulla breathing center impulses. c. A drop in the pH of cerebrospinal fluid. d. Severe deficiencies of oxygen. e. All of the above. 19. Which of the following are similarities between open and clos ...
Chapter 35. - Cloudfront.net
... “typical” plant cells = least specialized photosynthetic cells, storage cells tissue of leaves, stem, fruit, storage roots ...
... “typical” plant cells = least specialized photosynthetic cells, storage cells tissue of leaves, stem, fruit, storage roots ...
Human embryogenesis
Human embryogenesis is the process of cell division and cellular differentiation of the embryo that occurs during the early stages of development. In biological terms, human development entails growth from a one celled zygote to an adult human being. Fertilisation occurs when the sperm cell successfully enters and fuses with an egg cell (ovum). The genetic material of the sperm and egg then combine to form a single cell called a zygote and the germinal stage of prenatal development commences. Embryogenesis covers the first eight weeks of development and at the beginning of the ninth week the embryo is termed a fetus.Human embryology is the study of this development during the first eight weeks after fertilisation. The normal period of gestation (pregnancy) is nine months or 38 weeks.The germinal stage, refers to the time from fertilization, through the development of the early embryo until implantation is completed in the uterus. The germinal stage takes around 10 days.During this stage, the zygote, which is defined as an embryo because it contains a full complement of genetic material, begins to divide, in a process called cleavage. A blastocyst is then formed and implanted in the uterus. Embryogenesis continues with the next stage of gastrulation when the three germ layers of the embryo form in a process called histogenesis, and the processes of neurulation and organogenesis follow. The embryo is referred to as a fetus in the later stages of prenatal development, usually taken to be at the beginning of the ninth week. In comparison to the embryo, the fetus has more recognizable external features, and a more complete set of developing organs. The entire process of embryogenesis involves coordinated spatial and temporal changes in gene expression, cell growth and cellular differentiation. A nearly identical process occurs in other species, especially among chordates.