Sponge_and_Cnidarians
... into new individual identical to the parent • can grow back missing parts ...
... into new individual identical to the parent • can grow back missing parts ...
Document
... – From gill capillaries to systemic capillaries and back to the heart • Land vertebrates have double circulation – With separate pulmonary and systemic circuits • Amphibians and reptiles – Have three-chambered hearts • Birds and mammals – Have four-chambered hearts 23.4 The human heart and cardiovas ...
... – From gill capillaries to systemic capillaries and back to the heart • Land vertebrates have double circulation – With separate pulmonary and systemic circuits • Amphibians and reptiles – Have three-chambered hearts • Birds and mammals – Have four-chambered hearts 23.4 The human heart and cardiovas ...
respiratory system cp - Appoquinimink High School
... • Air enters through two openings, THE EXTERNAL NARES or NOSTRILS ...
... • Air enters through two openings, THE EXTERNAL NARES or NOSTRILS ...
Drosophila
... • Under the right conditions, cultured stem cells derived from either source can differentiate into specialized cells. ...
... • Under the right conditions, cultured stem cells derived from either source can differentiate into specialized cells. ...
Glossary of Key Terms and Concepts
... death foci sculpt cusps from the left and right truncoconal septa and from a minor anterior truncus swelling (a cusp of the pulmonary valve) and a minor posterior swelling (a cusp of the aortic valve). Septum intermedium - This structure divides the single AV canal into right and left AV canals as t ...
... death foci sculpt cusps from the left and right truncoconal septa and from a minor anterior truncus swelling (a cusp of the pulmonary valve) and a minor posterior swelling (a cusp of the aortic valve). Septum intermedium - This structure divides the single AV canal into right and left AV canals as t ...
Segmentation
... No cell walls for structure Joined by extracellular proteins and intercellular junctions Most have muscle cells for movement and nerve cells for signal conduction About 35 phyla in kingdom animalia; we examine 9 All but 1 are invertebrates or lack a backbone ...
... No cell walls for structure Joined by extracellular proteins and intercellular junctions Most have muscle cells for movement and nerve cells for signal conduction About 35 phyla in kingdom animalia; we examine 9 All but 1 are invertebrates or lack a backbone ...
Reptile Crossword - Biology Junction
... 2. Reptiles that warm themselves by absorbing heat from the environment 3. Snakes that wrap their bodies around and squeeze their prey to death 5. Leathery egg made by reptiles 8. Muscular wall that divides the ventricle in reptiles 12. Order of lizards 13. Protein covering over the reptile scales t ...
... 2. Reptiles that warm themselves by absorbing heat from the environment 3. Snakes that wrap their bodies around and squeeze their prey to death 5. Leathery egg made by reptiles 8. Muscular wall that divides the ventricle in reptiles 12. Order of lizards 13. Protein covering over the reptile scales t ...
CHAPTER OUTLINE
... Tissues are composed of similarly specialized cells that perform a common function in the body. The tissues of the human body can be categorized into four major types: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscular tissue, and nervous tissue. Epithelial Tissue Epithelial tissue consists of tightly p ...
... Tissues are composed of similarly specialized cells that perform a common function in the body. The tissues of the human body can be categorized into four major types: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscular tissue, and nervous tissue. Epithelial Tissue Epithelial tissue consists of tightly p ...
Animal Top Ten - Explore Biology
... b. structure: neuron, axon, dendrites, synapse c. adaptations / evolutionary trends: ...
... b. structure: neuron, axon, dendrites, synapse c. adaptations / evolutionary trends: ...
Digestive System
... • Layer of dense, irregular connective tissue • Around muscularis mucosae • Contains – Large blood vessels and lymphatic vessels – Exocrine glands buffers and enzymes into lumen – Submucosal plexus contains nerve fibers and neurons ...
... • Layer of dense, irregular connective tissue • Around muscularis mucosae • Contains – Large blood vessels and lymphatic vessels – Exocrine glands buffers and enzymes into lumen – Submucosal plexus contains nerve fibers and neurons ...
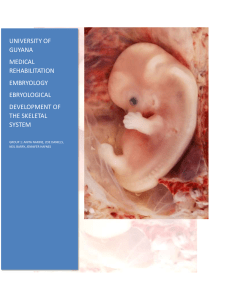
INTRODUCTION TO : The Embryology of the Skeletal System
... INTRODUCTION TO : The Embryology of the Skeletal System The skeletal system develops from paraxial and lateral plate (somatic layer) mesoderm and from neural crest. Paraxial mesoderm forms a segmented series of tissue blocks on each side of the neural tube, known as somitomeres in the head region a ...
... INTRODUCTION TO : The Embryology of the Skeletal System The skeletal system develops from paraxial and lateral plate (somatic layer) mesoderm and from neural crest. Paraxial mesoderm forms a segmented series of tissue blocks on each side of the neural tube, known as somitomeres in the head region a ...
Internal transport
... – Water enters this system through the sieve plate (aka madreporite), passes into a stone canal, then to the ring canal, into radial canal, then into ampullae, and into tube feet; expansion and contraction of tube feet move the sea star along. • Internal transport - fluid in body cavity & water vasc ...
... – Water enters this system through the sieve plate (aka madreporite), passes into a stone canal, then to the ring canal, into radial canal, then into ampullae, and into tube feet; expansion and contraction of tube feet move the sea star along. • Internal transport - fluid in body cavity & water vasc ...
characteristics of life
... d. Explain (and use diagrams to help you) what would happen to a human blood cell if placed in each of the three ...
... d. Explain (and use diagrams to help you) what would happen to a human blood cell if placed in each of the three ...
File
... What is the nerve supply to the medial thigh: obturator The maxillary sinus drains into: middle nasal meatus What muscle abducts the vocal folds: posterior cricoarytenoid What does the major calyces empty into: the renal pelvis Which of the following is the outer lining of the heart: pericardium Wha ...
... What is the nerve supply to the medial thigh: obturator The maxillary sinus drains into: middle nasal meatus What muscle abducts the vocal folds: posterior cricoarytenoid What does the major calyces empty into: the renal pelvis Which of the following is the outer lining of the heart: pericardium Wha ...
Structural Organisation in Animals
... A).Intercellular junctions in epithelial tissues provide both structural and functional links between the individual cells of an epithelium. They are of three types. I) Tight Junctions: They prevent leakages of body fluids. Plasma membrane of adjacent cells are tightly pressed against each other and ...
... A).Intercellular junctions in epithelial tissues provide both structural and functional links between the individual cells of an epithelium. They are of three types. I) Tight Junctions: They prevent leakages of body fluids. Plasma membrane of adjacent cells are tightly pressed against each other and ...
Sydney
... By use of hormones released into bloodstream from glands throughout the body, messages are broadcast throughout the body and stimulate ...
... By use of hormones released into bloodstream from glands throughout the body, messages are broadcast throughout the body and stimulate ...
video slide
... • Important events regulating development occur during fertilization and the three stages that build the animal’s body – Cleavage: cell division creates a hollow ball of cells called a blastula – Gastrulation: cells are rearranged into a threelayered gastrula – Organogenesis: the three layers intera ...
... • Important events regulating development occur during fertilization and the three stages that build the animal’s body – Cleavage: cell division creates a hollow ball of cells called a blastula – Gastrulation: cells are rearranged into a threelayered gastrula – Organogenesis: the three layers intera ...
1 - IT, Sligo
... 23. The building blocks of protein are____ A. amino acids B. monosaccharides C. glycerol D. nucleotides E. fatty acids F. nucleic acids 24. The first phase of glucose metabolism is _____. A. the Krebs cycle B. glycolysis C. the electron transport system D. the transition reaction E. fermentation F. ...
... 23. The building blocks of protein are____ A. amino acids B. monosaccharides C. glycerol D. nucleotides E. fatty acids F. nucleic acids 24. The first phase of glucose metabolism is _____. A. the Krebs cycle B. glycolysis C. the electron transport system D. the transition reaction E. fermentation F. ...
CH 27-1 FOLDABLE CONTENT FOR FOLDABLES
... because they rely on their host’s digestive system. Free-living flatworms have a single opening digestive tract that has a PHARYNX (muscular tube) near the mouth that extends out and pumps food into the digestive cavity; In free-living flatworms a head encloses several groups of nerve cells that con ...
... because they rely on their host’s digestive system. Free-living flatworms have a single opening digestive tract that has a PHARYNX (muscular tube) near the mouth that extends out and pumps food into the digestive cavity; In free-living flatworms a head encloses several groups of nerve cells that con ...
SULIT 4551/2 BIOLOGY/ P KERTAS 2 Sept 2011 2 ½ JAM BIOLOGY
... The couple can use the in-vitro fertilization (IVF) method ...
... The couple can use the in-vitro fertilization (IVF) method ...
Invertebrates
... • Consider the presence of Nervous tissue in lower invertebrates. • Do they have a brain? • Are they able to respond to stimuli? • The sponge has no nervous tissue at all and thus no cephalization • The cnidarians have a neural net but no central processing location. ...
... • Consider the presence of Nervous tissue in lower invertebrates. • Do they have a brain? • Are they able to respond to stimuli? • The sponge has no nervous tissue at all and thus no cephalization • The cnidarians have a neural net but no central processing location. ...
Human embryogenesis
Human embryogenesis is the process of cell division and cellular differentiation of the embryo that occurs during the early stages of development. In biological terms, human development entails growth from a one celled zygote to an adult human being. Fertilisation occurs when the sperm cell successfully enters and fuses with an egg cell (ovum). The genetic material of the sperm and egg then combine to form a single cell called a zygote and the germinal stage of prenatal development commences. Embryogenesis covers the first eight weeks of development and at the beginning of the ninth week the embryo is termed a fetus.Human embryology is the study of this development during the first eight weeks after fertilisation. The normal period of gestation (pregnancy) is nine months or 38 weeks.The germinal stage, refers to the time from fertilization, through the development of the early embryo until implantation is completed in the uterus. The germinal stage takes around 10 days.During this stage, the zygote, which is defined as an embryo because it contains a full complement of genetic material, begins to divide, in a process called cleavage. A blastocyst is then formed and implanted in the uterus. Embryogenesis continues with the next stage of gastrulation when the three germ layers of the embryo form in a process called histogenesis, and the processes of neurulation and organogenesis follow. The embryo is referred to as a fetus in the later stages of prenatal development, usually taken to be at the beginning of the ninth week. In comparison to the embryo, the fetus has more recognizable external features, and a more complete set of developing organs. The entire process of embryogenesis involves coordinated spatial and temporal changes in gene expression, cell growth and cellular differentiation. A nearly identical process occurs in other species, especially among chordates.