How Do Natural Selection and Random Drift
... would make fitness causal (in the sense that dispositions are causal). Since fitness is a central concept of evolutionary theory, and natural selection can be defined partly in terms of fitness differences, the PIF would place one of the causes of evolution within evolutionary theory. In this paper ...
... would make fitness causal (in the sense that dispositions are causal). Since fitness is a central concept of evolutionary theory, and natural selection can be defined partly in terms of fitness differences, the PIF would place one of the causes of evolution within evolutionary theory. In this paper ...
Apomictic Parthenogenesis and the Pattern of the
... practically any other sexual organism studied; cf., Powell, 1975) is due to crossings between differentiated populations, though it is not clear whether historically remote phenomena are valid explanations for the presently high heterozygosity. We do appreciate the potential twofold reproductive cap ...
... practically any other sexual organism studied; cf., Powell, 1975) is due to crossings between differentiated populations, though it is not clear whether historically remote phenomena are valid explanations for the presently high heterozygosity. We do appreciate the potential twofold reproductive cap ...
Respiratory System
... nuclei do have characteristic locations within the epithelium. Thus the nuclei located closest to the epithelial surface usually belong to supporting cells, while basal cell nuclei are closest to the basement membrane, and the nuclei in an intermediate position belong mainly to olfactory receptor ce ...
... nuclei do have characteristic locations within the epithelium. Thus the nuclei located closest to the epithelial surface usually belong to supporting cells, while basal cell nuclei are closest to the basement membrane, and the nuclei in an intermediate position belong mainly to olfactory receptor ce ...
explanation - mbhsbiologystaar
... discussed the lac and trp operons in your Biology class and remembered that the genes that code for the breakdown of lactose or the synthesis of tryptophan can be turned on and off as the cell needs those things to be done. • If not, here are some other things you might have known: – Genes are on li ...
... discussed the lac and trp operons in your Biology class and remembered that the genes that code for the breakdown of lactose or the synthesis of tryptophan can be turned on and off as the cell needs those things to be done. • If not, here are some other things you might have known: – Genes are on li ...
the lymphatic system and immunity
... from drying out. Since mucus is slightly viscous, it traps many microbes that enter the respiratory and digestive tracts. The mucous membrane of the nose has mucus-coated hairs that trap and filter air containing microbes, dust, and pollutants. The mucous membrane of the upper respiratory tract cont ...
... from drying out. Since mucus is slightly viscous, it traps many microbes that enter the respiratory and digestive tracts. The mucous membrane of the nose has mucus-coated hairs that trap and filter air containing microbes, dust, and pollutants. The mucous membrane of the upper respiratory tract cont ...
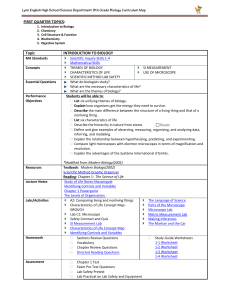
FIRST QUARTER TOPICS
... Compare and contrast, at the cellular level, prokaryotes and eukaryotes (general structures and degrees of complexity). Cells have specific structures and functions that make them distinctive. Processes in a cell can be classified broadly as growth, maintenance, and reproduction Why are cells consid ...
... Compare and contrast, at the cellular level, prokaryotes and eukaryotes (general structures and degrees of complexity). Cells have specific structures and functions that make them distinctive. Processes in a cell can be classified broadly as growth, maintenance, and reproduction Why are cells consid ...
Microsoft Word 97 - 2003 Document
... nutrients into a body cavity, like a stomach. Though such nutrients are within a body space, they are still outside of cells. ...
... nutrients into a body cavity, like a stomach. Though such nutrients are within a body space, they are still outside of cells. ...
DOC
... common in a population as a function of differential reproduction of their bearers. It is a key mechanism of evolution. The genetic variation within a population of organisms may cause some individuals to survive and reproduce more successfully than others. Factors which affect reproductive success ...
... common in a population as a function of differential reproduction of their bearers. It is a key mechanism of evolution. The genetic variation within a population of organisms may cause some individuals to survive and reproduce more successfully than others. Factors which affect reproductive success ...
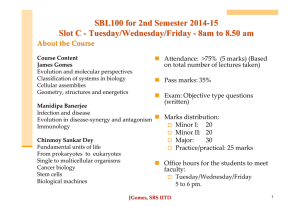
SBL100 for 2nd Semester 2014-1515 Slot C -
... a) In a liquid layer, molecules are agitated by thermal motion. b) The molecules in the liquid layer are heated from below (red zone) and self‐organize into rolls (drawn in cross‐section) when the temperature reaches a critical value (tc). At this value, the molecules start to move collectively ...
... a) In a liquid layer, molecules are agitated by thermal motion. b) The molecules in the liquid layer are heated from below (red zone) and self‐organize into rolls (drawn in cross‐section) when the temperature reaches a critical value (tc). At this value, the molecules start to move collectively ...
body systems1
... • Blood also contains red blood cells, which carry oxygen, and platelets, which help the body heal when a vessel is cut. • White blood cells help the body defend itself from toxins and diseases. ...
... • Blood also contains red blood cells, which carry oxygen, and platelets, which help the body heal when a vessel is cut. • White blood cells help the body defend itself from toxins and diseases. ...
FUNGI
... Homothallic - Refers to species in which individuals can mate with themselves Hyphae - Thin filaments of a fungus that form its body or mycelium Isogamous - Iso implies the same and gamous refers to gametes. In isogamous species the gametes are the same size and shape, thus individuals are not male ...
... Homothallic - Refers to species in which individuals can mate with themselves Hyphae - Thin filaments of a fungus that form its body or mycelium Isogamous - Iso implies the same and gamous refers to gametes. In isogamous species the gametes are the same size and shape, thus individuals are not male ...
Human behavioral ecology and its evil twin
... good for our genes. Culture may sometimes lead us astray from fitness maximization. The most obvious explanation for maladaptive behavior is a rapid change of environment. If some aspect of society, or indeed any part of a person’s environment, has recently changed in ways that would not have occurr ...
... good for our genes. Culture may sometimes lead us astray from fitness maximization. The most obvious explanation for maladaptive behavior is a rapid change of environment. If some aspect of society, or indeed any part of a person’s environment, has recently changed in ways that would not have occurr ...
How do Natural Selection and Random Drift Interact?
... Biologists (e.g. Gillespie 1998; Roughgarden 1979) often say that evolution is the result of the interaction of what they call evolutionary “forces” such as natural selection, mutation, random drift, migration, and mating preferences. Sober (1984b) argued for a realist interpretation of such talk, c ...
... Biologists (e.g. Gillespie 1998; Roughgarden 1979) often say that evolution is the result of the interaction of what they call evolutionary “forces” such as natural selection, mutation, random drift, migration, and mating preferences. Sober (1984b) argued for a realist interpretation of such talk, c ...
TOPIC 5 Energy for biological processes 5.1 Cellular respiration
... protons there are different hydrogen ion concentrations on the two sides of the inner membrane. The membrane space has a higher concentration of hydrogen ions than the matrix, so there is a concentration gradient across the membrane. As a result of the different hydrogen ion concentrations there is ...
... protons there are different hydrogen ion concentrations on the two sides of the inner membrane. The membrane space has a higher concentration of hydrogen ions than the matrix, so there is a concentration gradient across the membrane. As a result of the different hydrogen ion concentrations there is ...
Chapter 8 - Macmillan Learning
... upon the effects of too many genes. d) can produce populations in which the average time to death from starvation is more than 160 hours. e) has little effect because constant mutation reduces starvation resistance, counteracting any benefits from selection. 4. To demonstrate evolution by natural se ...
... upon the effects of too many genes. d) can produce populations in which the average time to death from starvation is more than 160 hours. e) has little effect because constant mutation reduces starvation resistance, counteracting any benefits from selection. 4. To demonstrate evolution by natural se ...
Natural selection-the Making of the Fittest
... • Those individuals whose inherited characteristics best fit them to their environment are likely to leave more offspring than less fit individuals. ...
... • Those individuals whose inherited characteristics best fit them to their environment are likely to leave more offspring than less fit individuals. ...
Science as a way of learning
... This book is designed to help you improve your note-taking skills and help you to focus your studying. The notes are divided into each testing section or unit. Each section begins with outlines for each lecture topic which also provides a great way to review the material before your test. If you can ...
... This book is designed to help you improve your note-taking skills and help you to focus your studying. The notes are divided into each testing section or unit. Each section begins with outlines for each lecture topic which also provides a great way to review the material before your test. If you can ...
Animal Phylum Summary Chart
... gastrodermis secrete digestive enzymes = extracellular digest. & nutitive-muscular cells phagocytose food (intracellular) ...
... gastrodermis secrete digestive enzymes = extracellular digest. & nutitive-muscular cells phagocytose food (intracellular) ...
EOC Biology Study Document
... purposes of photosynthesis and cellular respiration. They should be able to explain the interrelated nature of photosynthesis and cellular respiration in the cells of photosynthetic organisms. Students should be able to identify where cellular respiration and photosynthesis occur at the sub-cellular ...
... purposes of photosynthesis and cellular respiration. They should be able to explain the interrelated nature of photosynthesis and cellular respiration in the cells of photosynthetic organisms. Students should be able to identify where cellular respiration and photosynthesis occur at the sub-cellular ...
EOC Biology Study Document
... purposes of photosynthesis and cellular respiration. They should be able to explain the interrelated nature of photosynthesis and cellular respiration in the cells of photosynthetic organisms. Students should be able to identify where cellular respiration and photosynthesis occur at the sub-cellular ...
... purposes of photosynthesis and cellular respiration. They should be able to explain the interrelated nature of photosynthesis and cellular respiration in the cells of photosynthetic organisms. Students should be able to identify where cellular respiration and photosynthesis occur at the sub-cellular ...
Introduction to Genetic Algorithms
... that is based on the Schema Theorem. • John Holland introduced the notation of schema, which came from the Greek word meaning ‘form’. • A schema is a set of bit strings of 1’s, 0’s and * (asterisks), where each * can be 1 or 0. • 1’s and 0’s represent the fixed positions of a schema, while * represe ...
... that is based on the Schema Theorem. • John Holland introduced the notation of schema, which came from the Greek word meaning ‘form’. • A schema is a set of bit strings of 1’s, 0’s and * (asterisks), where each * can be 1 or 0. • 1’s and 0’s represent the fixed positions of a schema, while * represe ...
Chapter 1 honors review questions
... New variations within certain members of a species allow them to capture fewer A)resources. Members of a population with advantageous variations tend to survive and have B)more offspring. Each successive generation will include more members with the new advantageous C)variations. In the end, most me ...
... New variations within certain members of a species allow them to capture fewer A)resources. Members of a population with advantageous variations tend to survive and have B)more offspring. Each successive generation will include more members with the new advantageous C)variations. In the end, most me ...
File
... 3. The new five-kingdom arrangement of organisms was proposed by Whittakar in 1969 to replace the old two-kingdom classification. These include monera, protista, fungi, plantae and animalia. The criteria for making five kingdoms of life were: complexity of cell structure, complexity of the organism’ ...
... 3. The new five-kingdom arrangement of organisms was proposed by Whittakar in 1969 to replace the old two-kingdom classification. These include monera, protista, fungi, plantae and animalia. The criteria for making five kingdoms of life were: complexity of cell structure, complexity of the organism’ ...
Darwin Finches : Explaining coexistence with adaptive
... optimal point, followed, in case of coexistence, by a character displacement. This scenario is studied here with two methods : First, we make theoretical predictions from the analysis of a deterministic model and second, we test those predictions with a stochastic, individual-based models of seconda ...
... optimal point, followed, in case of coexistence, by a character displacement. This scenario is studied here with two methods : First, we make theoretical predictions from the analysis of a deterministic model and second, we test those predictions with a stochastic, individual-based models of seconda ...