NoB1ch02QUICKcheck-ed
... Plant cells without chloroplasts can capture the energy of sunlight. False: The cell organelles that are essential for the capture of the energy of sunlight are the chloroplasts. ...
... Plant cells without chloroplasts can capture the energy of sunlight. False: The cell organelles that are essential for the capture of the energy of sunlight are the chloroplasts. ...
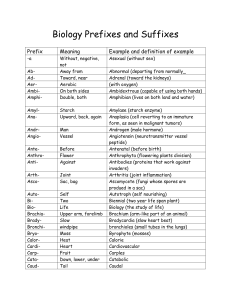
Biology Prefixes and Suffixes
... heterozygous (having two different alleles for a given trait) histoma (tumor derived from mature tissue) holotrophs (organisms that eat other organisms whole or in pieces) homozygous (having two alleles for a given trait that are the same) hydrophilic (having an affinity for water; water loving) hyp ...
... heterozygous (having two different alleles for a given trait) histoma (tumor derived from mature tissue) holotrophs (organisms that eat other organisms whole or in pieces) homozygous (having two alleles for a given trait that are the same) hydrophilic (having an affinity for water; water loving) hyp ...
Slide 1
... • The parts of the circulatory system work together to bring about the transport of substances around the body: – arteries transport blood away from the heart thick muscular and elastic wall – veins transport blood to the heart - large lumen and presence of valves – veins; capillaries are involved ...
... • The parts of the circulatory system work together to bring about the transport of substances around the body: – arteries transport blood away from the heart thick muscular and elastic wall – veins transport blood to the heart - large lumen and presence of valves – veins; capillaries are involved ...
Grade 7 - Humble ISD
... generation from parents to offspring. • Sexual reproduction results in more diverse offspring while asexual reproduction results in more uniform offspring. • Human organ systems have specialized cell and tissue functions that perform work to maintain life. • Compounds that contain carbon are called ...
... generation from parents to offspring. • Sexual reproduction results in more diverse offspring while asexual reproduction results in more uniform offspring. • Human organ systems have specialized cell and tissue functions that perform work to maintain life. • Compounds that contain carbon are called ...
Evolution PPT
... no function. These structures support the theory of evolution because they show structural changes over time. ...
... no function. These structures support the theory of evolution because they show structural changes over time. ...
chapter2 review
... by layers of other cells would not be able to obtain nutrients by diffusion directly from the source or get rid of wastes directly to the outside. It needs some way to have nutrients delivered to it. Specialized cells, tissues, and organs fulfill these special functions. An individual cell in a larg ...
... by layers of other cells would not be able to obtain nutrients by diffusion directly from the source or get rid of wastes directly to the outside. It needs some way to have nutrients delivered to it. Specialized cells, tissues, and organs fulfill these special functions. An individual cell in a larg ...
CANCER COURSE MODULE SIGN
... Submit a separate form for each course you plan to take- you may not take the same module for more than one course. Appropriate modules offered by the Immunology Research Group may be used for electives upon approval by the course and module coordinators- see www.ucalgary.ca/irg/education for a desc ...
... Submit a separate form for each course you plan to take- you may not take the same module for more than one course. Appropriate modules offered by the Immunology Research Group may be used for electives upon approval by the course and module coordinators- see www.ucalgary.ca/irg/education for a desc ...
Ch. 3 Cells
... ► Interphase- is a period of cell growth and new molecules are synthesized ► S phase- DNA of cell is replicated to prepare for cell division ► G1 & G2 phases- cell grows and other structures are duplicated ...
... ► Interphase- is a period of cell growth and new molecules are synthesized ► S phase- DNA of cell is replicated to prepare for cell division ► G1 & G2 phases- cell grows and other structures are duplicated ...
Biology 2nd QTR EQT Review To which group does an organism
... 71. Two organisms in the same order will also have to be in which other taxons? 72. Refer to the illustration below. An analysis of DNA from these organisms would indicate what about their nucleotide sequence? ...
... 71. Two organisms in the same order will also have to be in which other taxons? 72. Refer to the illustration below. An analysis of DNA from these organisms would indicate what about their nucleotide sequence? ...
evolution
... deleterious) mutations can be reduced in frequency in the gene pool by natural selection, while more favorable (beneficial or advantageous) mutations may accumulate and result in adaptive evolutionary changes. ...
... deleterious) mutations can be reduced in frequency in the gene pool by natural selection, while more favorable (beneficial or advantageous) mutations may accumulate and result in adaptive evolutionary changes. ...
Phylum Porifera: Sponges
... Sperm released out of osculum and swim to another sponge (with the help of currents) ◦ Enter another sponge’s pore cell ◦ Picked up by collar cells ◦ Carried to an egg by amoebocytes ◦ Fertilization occurs ◦ Zygote develops into a flagellated larvae which is mobile (can be dispersed) ...
... Sperm released out of osculum and swim to another sponge (with the help of currents) ◦ Enter another sponge’s pore cell ◦ Picked up by collar cells ◦ Carried to an egg by amoebocytes ◦ Fertilization occurs ◦ Zygote develops into a flagellated larvae which is mobile (can be dispersed) ...
biocomp-exam-2009 - National Biology Competition
... b. Chromosomes gradually decrease in length because normal DNA synthesis cannot complete replication at the end of the lagging strand. c. The cell’s ability to repair mistakes made during DNA replication decreases, allowing the number of base substitutions in the genome to increase. d. DNA replicati ...
... b. Chromosomes gradually decrease in length because normal DNA synthesis cannot complete replication at the end of the lagging strand. c. The cell’s ability to repair mistakes made during DNA replication decreases, allowing the number of base substitutions in the genome to increase. d. DNA replicati ...
5 Variation and Natural selection
... to its offspring Over time more individuals will have this variation, and eventually it is so common that it becomes a characteristic of the population ...
... to its offspring Over time more individuals will have this variation, and eventually it is so common that it becomes a characteristic of the population ...
Biology - Gorman Learning Center
... f. at each link in a food web, some energy is stored in newly made structures but much is dissipated into the environment as heat and this can be represented in a food pyramid. g.* how to distinguish between the accommodation of an individual organism to its environment and the gradual adaptation of ...
... f. at each link in a food web, some energy is stored in newly made structures but much is dissipated into the environment as heat and this can be represented in a food pyramid. g.* how to distinguish between the accommodation of an individual organism to its environment and the gradual adaptation of ...
NEO-LAMARCKISM AND NEO
... However, Darwinism also has certain drawbacks. He did not know the mechanism of inheritance. He laid emphasis on individual variation and lack clarity in accounting the sources of variation and ignored the role of recombination. This leads to the formation of a new school of thought in the middle of ...
... However, Darwinism also has certain drawbacks. He did not know the mechanism of inheritance. He laid emphasis on individual variation and lack clarity in accounting the sources of variation and ignored the role of recombination. This leads to the formation of a new school of thought in the middle of ...
Chapter 30: Comparing Invertebrates
... There is a third cell layer in embryos, called the __________________________, which is located between the endoderm and the ectoderm ...
... There is a third cell layer in embryos, called the __________________________, which is located between the endoderm and the ectoderm ...
PDQ1
... 3. Why are certain cellular structures unable to be observed with a light microscope? 4. How does the ratio of a cell’s surface area to volume place upward and downward limits on cell size? 5. How do organelles allow for increased complexity in cells? 6. Provide four examples of cell tasks that are ...
... 3. Why are certain cellular structures unable to be observed with a light microscope? 4. How does the ratio of a cell’s surface area to volume place upward and downward limits on cell size? 5. How do organelles allow for increased complexity in cells? 6. Provide four examples of cell tasks that are ...
Year Long Biology EOC Review PPT
... • Technique used to separate molecules (DNA or proteins) based on their size • Sometimes called a DNA fingerprint • Used to analyze and compare DNA ...
... • Technique used to separate molecules (DNA or proteins) based on their size • Sometimes called a DNA fingerprint • Used to analyze and compare DNA ...
Biology Top 101
... Parasites • Lives on or within a host • Benefits while causing harm to the host • Ex. Plasmodium causes malaria (genetic influencecarriers of sickle cell are resistant to malaria) ...
... Parasites • Lives on or within a host • Benefits while causing harm to the host • Ex. Plasmodium causes malaria (genetic influencecarriers of sickle cell are resistant to malaria) ...
Biology Top 101
... Parasites • Lives on or within a host • Benefits while causing harm to the host • Ex. Plasmodium causes malaria (genetic influencecarriers of sickle cell are resistant to malaria) ...
... Parasites • Lives on or within a host • Benefits while causing harm to the host • Ex. Plasmodium causes malaria (genetic influencecarriers of sickle cell are resistant to malaria) ...
Biology Top 101
... Parasites • Lives on or within a host • Benefits while causing harm to the host • Ex. Plasmodium causes malaria (genetic influencecarriers of sickle cell are resistant to malaria) ...
... Parasites • Lives on or within a host • Benefits while causing harm to the host • Ex. Plasmodium causes malaria (genetic influencecarriers of sickle cell are resistant to malaria) ...
Eoct_review
... Parasites • Lives on or within a host • Benefits while causing harm to the host • Ex. Plasmodium causes malaria (genetic influencecarriers of sickle cell are resistant to malaria) ...
... Parasites • Lives on or within a host • Benefits while causing harm to the host • Ex. Plasmodium causes malaria (genetic influencecarriers of sickle cell are resistant to malaria) ...
EOC Review PPT
... Parasites • Lives on or within a host • Benefits while causing harm to the host • Ex. Plasmodium causes malaria (genetic influencecarriers of sickle cell are resistant to malaria) ...
... Parasites • Lives on or within a host • Benefits while causing harm to the host • Ex. Plasmodium causes malaria (genetic influencecarriers of sickle cell are resistant to malaria) ...
Evolution: The Public`s Problem, and the Scientists`
... the competition between individuals marginally different from one another with respect to the small, inherited, morphological, physiological, or behavioral variations encountered in any natural population, has been sufficient to generate the entire array of biologically distinct types seen on the fa ...
... the competition between individuals marginally different from one another with respect to the small, inherited, morphological, physiological, or behavioral variations encountered in any natural population, has been sufficient to generate the entire array of biologically distinct types seen on the fa ...