Biology EOC Review
... L. Together we determined the double helix shape of DNA. M. I developed the theory of natural selection and I am known as the father of evolution. N. I hypothesized that life originated in the early oceans. Q. I am the scientist who erroneously came up with the idea that traits are acquired from ani ...
... L. Together we determined the double helix shape of DNA. M. I developed the theory of natural selection and I am known as the father of evolution. N. I hypothesized that life originated in the early oceans. Q. I am the scientist who erroneously came up with the idea that traits are acquired from ani ...
Biomembrane Structure & Function
... Proteins associated with a particular membrane are responsible for its distinctive activities. The kinds and amounts of proteins associated with biomembranes vary depending on cell type and subcellular location. Membrane proteins are defined by their location within or at the surface of a phospholip ...
... Proteins associated with a particular membrane are responsible for its distinctive activities. The kinds and amounts of proteins associated with biomembranes vary depending on cell type and subcellular location. Membrane proteins are defined by their location within or at the surface of a phospholip ...
8TH Grade Fourth Marking Period Test
... d. Mechanical (physical) weathering 7. The wearing away of rock material and moving of rock material by natural forces Is known as____________ a. Deposition b. Horizon c. Erosion d. Watershed 8. A smooth and rounded rock has most likely been shaped by___________ a. Running water b. Freezing and crac ...
... d. Mechanical (physical) weathering 7. The wearing away of rock material and moving of rock material by natural forces Is known as____________ a. Deposition b. Horizon c. Erosion d. Watershed 8. A smooth and rounded rock has most likely been shaped by___________ a. Running water b. Freezing and crac ...
MCAS And Final Review Packet 2014
... Describe how temperature/pH affects Enzyme activity: Extreme temperatures and pH or other environmental factors can change the shape of the enzyme. The change in shape alters the effectiveness of the enzyme by preventing the substrate and the enzyme fitting together. The lock and key no longer fit t ...
... Describe how temperature/pH affects Enzyme activity: Extreme temperatures and pH or other environmental factors can change the shape of the enzyme. The change in shape alters the effectiveness of the enzyme by preventing the substrate and the enzyme fitting together. The lock and key no longer fit t ...
Themes and Concepts of Biology
... to reproduce.) Some organisms consist of a single cell and others are multicellular. Cells are classi ed as prokaryotic or eukaryotic. ...
... to reproduce.) Some organisms consist of a single cell and others are multicellular. Cells are classi ed as prokaryotic or eukaryotic. ...
mutation-story-cystic
... better which is significant for thin flowing mucus. Transporting sodium ions is crucial for normal function of the lungs and pancreas. Unfortunately, there was a fault in me (CFTR gene) which causes my proteins to not work properly. Cystic Fibrosis (CF) occurred in Maddy’s body because 3 DNA nucleot ...
... better which is significant for thin flowing mucus. Transporting sodium ions is crucial for normal function of the lungs and pancreas. Unfortunately, there was a fault in me (CFTR gene) which causes my proteins to not work properly. Cystic Fibrosis (CF) occurred in Maddy’s body because 3 DNA nucleot ...
T3 Scopes Weeks 1-9
... D The water temperature of the sea has increased 8-2 (12A) In a forest community, a shelf fungus and a slug live on the side of a decaying tree trunk. The fungus digests and absorbs materials from the tree, while the slug eats algae growing on the outside of the trunk. These organisms do not compete ...
... D The water temperature of the sea has increased 8-2 (12A) In a forest community, a shelf fungus and a slug live on the side of a decaying tree trunk. The fungus digests and absorbs materials from the tree, while the slug eats algae growing on the outside of the trunk. These organisms do not compete ...
EOC study guide self assessment
... I can describe the similarities and/or differences (i.e., embryology, homology, analogous structures, genetic sequences) of given organisms in terms of biological evolution (e.g., Darwin's finches had different beaks due to food sources on the islands where they evolved). I can describe the evolutio ...
... I can describe the similarities and/or differences (i.e., embryology, homology, analogous structures, genetic sequences) of given organisms in terms of biological evolution (e.g., Darwin's finches had different beaks due to food sources on the islands where they evolved). I can describe the evolutio ...
EP BIOLOGY ANSWERS 1st Quarter - Easy Peasy All-in
... 1. All organisms are composed of cells. 2. Cells are alive and the basic living units of organization in all organisms. 3.All cells come from other cells. 3. According the cell theory, can you create a cell by combining molecules in a laboratory? Why or why not? ...
... 1. All organisms are composed of cells. 2. Cells are alive and the basic living units of organization in all organisms. 3.All cells come from other cells. 3. According the cell theory, can you create a cell by combining molecules in a laboratory? Why or why not? ...
The origin/change of major body plans during the Cambrian
... like the fruit fly's gene. [1] This means that whatever is causing the differences between a fly and a mouse, it is not the HOX genes. Furthermore, HOX genes are turned on in an animal embryo only after the body plan has already become established. [2] Thus HOX genes could not possibly be responsibl ...
... like the fruit fly's gene. [1] This means that whatever is causing the differences between a fly and a mouse, it is not the HOX genes. Furthermore, HOX genes are turned on in an animal embryo only after the body plan has already become established. [2] Thus HOX genes could not possibly be responsibl ...
cells, cellular respiration, and heredity.
... Previous/Future knowledge: In 5th grade (5-2.1), students recalled that the smallest unit of life was the cell and identified its major structures (including cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, and vacuole). In 6th grade (6-2.1), students summarized the characteristics that all organisms share (inclu ...
... Previous/Future knowledge: In 5th grade (5-2.1), students recalled that the smallest unit of life was the cell and identified its major structures (including cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, and vacuole). In 6th grade (6-2.1), students summarized the characteristics that all organisms share (inclu ...
Introduction to Life Sciences
... The course aims at introducing crucial concepts and insights in the origin and evolution of life on earth, the organisation of life, the building blocks of life, the energy conversions in life, inheritance and expression of genes. The course is situated at the interface between molecular biology, ge ...
... The course aims at introducing crucial concepts and insights in the origin and evolution of life on earth, the organisation of life, the building blocks of life, the energy conversions in life, inheritance and expression of genes. The course is situated at the interface between molecular biology, ge ...
Biology Curriculum Map
... conditions shape successional changes in an ecosystem? What adaptations do organisms exhibit in response to stressful environmental conditions? What are the differences between the ecological landscapes (biomes)? ...
... conditions shape successional changes in an ecosystem? What adaptations do organisms exhibit in response to stressful environmental conditions? What are the differences between the ecological landscapes (biomes)? ...
Presentation - science
... The laundries expect to increase the amount of clothes they can clean by using enzymes from thermophilic bacteria instead of using the biological washing powders the laundries use now. 3 (b) (i) The laundries expect to be able to increase the amount of clothes that they can clean each day. ...
... The laundries expect to increase the amount of clothes they can clean by using enzymes from thermophilic bacteria instead of using the biological washing powders the laundries use now. 3 (b) (i) The laundries expect to be able to increase the amount of clothes that they can clean each day. ...
Document
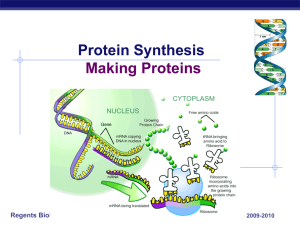
... Passing on DNA information Need to get DNA gene information from nucleus to cytoplasm ...
... Passing on DNA information Need to get DNA gene information from nucleus to cytoplasm ...
7-2 Science Support Document
... Previous/Future knowledge: In 5th grade (5-2.1), students recalled that the smallest unit of life was the cell and identified its major structures (including cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, and vacuole). In 6th grade (6-2.1), students summarized the characteristics that all organisms share (inclu ...
... Previous/Future knowledge: In 5th grade (5-2.1), students recalled that the smallest unit of life was the cell and identified its major structures (including cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, and vacuole). In 6th grade (6-2.1), students summarized the characteristics that all organisms share (inclu ...
Artificial Selection
... continued to be produced, most of them didn't survive, while the dark-colored moths flourished. As a result, over the course of many generations of moths, the allele frequency gradually shifted towards the dominant allele, as more and more dark-bodied moths survived to reproduce. By the mid-19th cen ...
... continued to be produced, most of them didn't survive, while the dark-colored moths flourished. As a result, over the course of many generations of moths, the allele frequency gradually shifted towards the dominant allele, as more and more dark-bodied moths survived to reproduce. By the mid-19th cen ...
The paradox of model organisms
... their offspring. As Grossniklaus pointed out, genomic imprinting must almost certainly have evolved independently in plants and animals, as their last common ancestor was unicellular, thus offering little scope for competition between parents. But both plants and mammals seem to have recruited commo ...
... their offspring. As Grossniklaus pointed out, genomic imprinting must almost certainly have evolved independently in plants and animals, as their last common ancestor was unicellular, thus offering little scope for competition between parents. But both plants and mammals seem to have recruited commo ...
B - Sewanhaka Central High School District
... • Cells are the basic unit of structure for all living things. • Cells are the basic unit of function for all living things. • All cells come from pre-existing cells. ...
... • Cells are the basic unit of structure for all living things. • Cells are the basic unit of function for all living things. • All cells come from pre-existing cells. ...
Kingdom Eubacteria
... Cell membrane – surround the cell and give it its’ __________. Nucleus – control center of the cell. Nuclear membrane – surrounds and protects the _______________. Chromosomes – the DNA of the cell (information) Ribosomes – make protein for the cell. (remember, DNA makes RNA, RNA moves out of the nu ...
... Cell membrane – surround the cell and give it its’ __________. Nucleus – control center of the cell. Nuclear membrane – surrounds and protects the _______________. Chromosomes – the DNA of the cell (information) Ribosomes – make protein for the cell. (remember, DNA makes RNA, RNA moves out of the nu ...
Questions From Old Exams
... (abbreviated by their one-letter designation), draw a double-stranded DNA molecule with five base pairs below. Indicate covalent bonds between the P, S, and/or bases using solid lines and indicate hydrogen bonds with dotted or dashed lines. There should be 10 total nucleotides in your drawing. Examp ...
... (abbreviated by their one-letter designation), draw a double-stranded DNA molecule with five base pairs below. Indicate covalent bonds between the P, S, and/or bases using solid lines and indicate hydrogen bonds with dotted or dashed lines. There should be 10 total nucleotides in your drawing. Examp ...
T-1 Chapter One: Biology- Study of Life
... How do things become different from one time to another? What explains how things are constantly changing? o Evolution is the change in living things over time. This change comes about because species genetic makeup changes do to an ever changing environment. (ie: giraffe’s and their necks) One ...
... How do things become different from one time to another? What explains how things are constantly changing? o Evolution is the change in living things over time. This change comes about because species genetic makeup changes do to an ever changing environment. (ie: giraffe’s and their necks) One ...
Unit 1 – Cell Biology
... Contains cell sap made of a solution of salts and sugars. Regulates water content of cell and when vacuole is swollen, it gives the cell a degree of support. Discus shaped structures that contain chlorophyll to trap light energy for photosynthesis ...
... Contains cell sap made of a solution of salts and sugars. Regulates water content of cell and when vacuole is swollen, it gives the cell a degree of support. Discus shaped structures that contain chlorophyll to trap light energy for photosynthesis ...
evolution - Big Picture
... The idea that all living things arose from a common ancestor has given rise to the analogy of the ‘tree of life’. The trunk represents this ancestor, major branches are the high-level taxonomic groups and the twigs are the individual species themselves. It used to be thought there were two main grou ...
... The idea that all living things arose from a common ancestor has given rise to the analogy of the ‘tree of life’. The trunk represents this ancestor, major branches are the high-level taxonomic groups and the twigs are the individual species themselves. It used to be thought there were two main grou ...
Symbiogenesis

Symbiogenesis, or endosymbiotic theory, is an evolutionary theory that explains the origin of eukaryotic cells from prokaryotes. It states that several key organelles of eukaryotes originated as a symbiosis between separate single-celled organisms. According to this theory, mitochondria, plastids (for example chloroplasts), and possibly other organelles representing formerly free-living bacteria were taken inside another cell as an endosymbiont around 1.5 billion years ago. Molecular and biochemical evidence suggest that mitochondria developed from proteobacteria (in particular, Rickettsiales, the SAR11 clade, or close relatives) and chloroplasts from cyanobacteria (in particular, nitrogen-fixing filamentous cyanobacteria).