1 Handout #11 ME 262A Summary on Quantum States We showed
... Note that increasing n corresponds to tan increasing electron orbital radius (in the Bohr model). As n approaches ∞ (r approaches ∞) , the energy approaches the ionization energy of hydrogen. We see that for n = 1, we have l =0, m=0, s=±1/2, so that there are two (2) possible combinations of quantum ...
... Note that increasing n corresponds to tan increasing electron orbital radius (in the Bohr model). As n approaches ∞ (r approaches ∞) , the energy approaches the ionization energy of hydrogen. We see that for n = 1, we have l =0, m=0, s=±1/2, so that there are two (2) possible combinations of quantum ...
Seminario Tunable electronic properties of self
... In novel organic optoelectronics applications, the device efficiency depends crucially on the energy barrier that controls charge carrier injection at molecule/electrode interfaces. These processes are determined by the chemical interaction between the deposited species and the inorganic surface, as ...
... In novel organic optoelectronics applications, the device efficiency depends crucially on the energy barrier that controls charge carrier injection at molecule/electrode interfaces. These processes are determined by the chemical interaction between the deposited species and the inorganic surface, as ...
Chapter 3: Electronic Spectroscopy I
... probable positions steadily approach the extremities until, for high v, the quantum and classical pictures merge (see figure below) where we plot the probability distribution in each vibrational state against internuclear distance. If a diatomic molecule undergoes a transition into an upper electron ...
... probable positions steadily approach the extremities until, for high v, the quantum and classical pictures merge (see figure below) where we plot the probability distribution in each vibrational state against internuclear distance. If a diatomic molecule undergoes a transition into an upper electron ...
Some Calculations on the Lithium Atom Ground State
... E Li ( α ) := 2⋅ T1s ( α ) + 2⋅ VN1s ( α ) + V1s1s ( α ) + T2s ( α ) + VN2s ( α ) + 2⋅ V1s2s ( α ) Minimization of the energy with respect to the variational parameter, α, yields the following result: α := ...
... E Li ( α ) := 2⋅ T1s ( α ) + 2⋅ VN1s ( α ) + V1s1s ( α ) + T2s ( α ) + VN2s ( α ) + 2⋅ V1s2s ( α ) Minimization of the energy with respect to the variational parameter, α, yields the following result: α := ...
Additional Notes on Electronic Spectroscopy
... π g * for antibonding MO’s. These labels give the bonding/antibonding nature of the orbital, its symmetry, and its electron density distribution. The ground state and first excited states of molecular nitrogen are given by N2 (ground state): (1σ g ) 2 (1σ u *) 2 (2σ g ) 2 (2σ u *) 2 (1π u ) 4 (3σ g ...
... π g * for antibonding MO’s. These labels give the bonding/antibonding nature of the orbital, its symmetry, and its electron density distribution. The ground state and first excited states of molecular nitrogen are given by N2 (ground state): (1σ g ) 2 (1σ u *) 2 (2σ g ) 2 (2σ u *) 2 (1π u ) 4 (3σ g ...
Atomic Emission Spectra and Quantum mechanical Model
... • Example: Sodium outer electron going to the s orbital to p (p orbital is higher energy than s) ...
... • Example: Sodium outer electron going to the s orbital to p (p orbital is higher energy than s) ...
Ground State
... What is useful and key to a good model? • The complex system can be simplified to – Base structure Clear – Interactions among particles Clear Key 1: What kind of models are employed to simplify the systems? ...
... What is useful and key to a good model? • The complex system can be simplified to – Base structure Clear – Interactions among particles Clear Key 1: What kind of models are employed to simplify the systems? ...
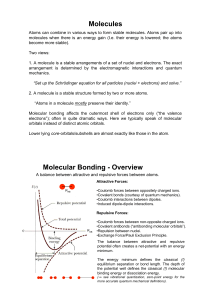
Molecules Molecular Bonding
... •Exchange Force/Pauli Exclusion Principle. The balance between attractive and repulsive potential often creates a net-potential with an energy minimum. The energy minimum defines the classical (!) equilibrium separation or bond length. The depth of the potential well defines the classical (!) molecu ...
... •Exchange Force/Pauli Exclusion Principle. The balance between attractive and repulsive potential often creates a net-potential with an energy minimum. The energy minimum defines the classical (!) equilibrium separation or bond length. The depth of the potential well defines the classical (!) molecu ...
Franck–Condon principle
The Franck–Condon principle is a rule in spectroscopy and quantum chemistry that explains the intensity of vibronic transitions. Vibronic transitions are the simultaneous changes in electronic and vibrational energy levels of a molecule due to the absorption or emission of a photon of the appropriate energy. The principle states that during an electronic transition, a change from one vibrational energy level to another will be more likely to happen if the two vibrational wave functions overlap more significantly.