excited states
... • Deactivation processes involved in converting a substance from excited state to ground state: • the emission of heat, • activation of a chemical reaction or • emission of radiation of the same or a modified wavelength. • Forms of photoluminescence (luminescence after absorption) are fluorescence ( ...
... • Deactivation processes involved in converting a substance from excited state to ground state: • the emission of heat, • activation of a chemical reaction or • emission of radiation of the same or a modified wavelength. • Forms of photoluminescence (luminescence after absorption) are fluorescence ( ...
Undergraduate physical chemistry final examination topics 1
... rotor; energy levels and selection rules. Different types of spinning tops. Applications of rotational spectroscopy. Classical and quantum mechanical description of a diatomic molecule as a harmonic oscillator; energy levels and selection rules. Generalisation to multiatomic molecules’ vibration. In ...
... rotor; energy levels and selection rules. Different types of spinning tops. Applications of rotational spectroscopy. Classical and quantum mechanical description of a diatomic molecule as a harmonic oscillator; energy levels and selection rules. Generalisation to multiatomic molecules’ vibration. In ...
Quantum Harmonic Oscillator Eigenvalues and Wavefunctions:
... Quantum harmonic oscillator is an important model system taught in upper level physics and physical chemistry courses. In chemistry, quantum harmonic oscillator is often used to as a simple, analytically solvable model of a vibrating diatomic molecule. The model captures well the essence of harmonic ...
... Quantum harmonic oscillator is an important model system taught in upper level physics and physical chemistry courses. In chemistry, quantum harmonic oscillator is often used to as a simple, analytically solvable model of a vibrating diatomic molecule. The model captures well the essence of harmonic ...
Energy Levels and Light Absorption
... Light absorption • If photons of the right energy are incident on a material, they can cause the promotion of electrons – excited states – The photons are absorbed by the molecules – If the sample is thick enough, the particular wavelengths can be completely absorbed – If white light is used, the a ...
... Light absorption • If photons of the right energy are incident on a material, they can cause the promotion of electrons – excited states – The photons are absorbed by the molecules – If the sample is thick enough, the particular wavelengths can be completely absorbed – If white light is used, the a ...
Molecular Luminescence Spectroscopy
... Recombination mechanisms. The return to equilibrium, also known as "recombination," can involve both radiative and nonradiative processes. The amount of photoluminescence and its dependence on the level of photo-excitation and temperature are directly related to the dominant recombination process. ...
... Recombination mechanisms. The return to equilibrium, also known as "recombination," can involve both radiative and nonradiative processes. The amount of photoluminescence and its dependence on the level of photo-excitation and temperature are directly related to the dominant recombination process. ...
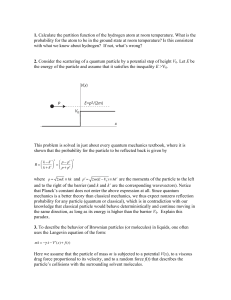
1. Calculate the partition function of the hydrogen atom at room
... where p = 2mE ≡ k and p′ = 2m(E − V0 ) ≡ k ′ are the momenta of the particle to the left and to the right of the barrier (and k and k’ are the corresponding wavevectors). Notice that Planck’s constant does not enter the above expression at all. Since quantum mechanics is a better theory than class ...
... where p = 2mE ≡ k and p′ = 2m(E − V0 ) ≡ k ′ are the momenta of the particle to the left and to the right of the barrier (and k and k’ are the corresponding wavevectors). Notice that Planck’s constant does not enter the above expression at all. Since quantum mechanics is a better theory than class ...
transport1
... metal: decreases as T is raised semiconductor: increases as T is raised Note that an insulator appears as a semiconductor with very low conductivity. ...
... metal: decreases as T is raised semiconductor: increases as T is raised Note that an insulator appears as a semiconductor with very low conductivity. ...
Lesson01
... radiation, since the absorptions of their major constituents are generally strong at the short wavelengths. • As a result, photochemically active radiation that penetrates into an atmosphere is of longer wavelengths, and the chemistry is characterized by lower energies. For example, the dissociation ...
... radiation, since the absorptions of their major constituents are generally strong at the short wavelengths. • As a result, photochemically active radiation that penetrates into an atmosphere is of longer wavelengths, and the chemistry is characterized by lower energies. For example, the dissociation ...
Franck–Condon principle
The Franck–Condon principle is a rule in spectroscopy and quantum chemistry that explains the intensity of vibronic transitions. Vibronic transitions are the simultaneous changes in electronic and vibrational energy levels of a molecule due to the absorption or emission of a photon of the appropriate energy. The principle states that during an electronic transition, a change from one vibrational energy level to another will be more likely to happen if the two vibrational wave functions overlap more significantly.