Stationarity Principle for Non-Equilibrium States
... Université de Montréal C.P. 6128, succ. Centre-Ville Montréal, Québec H3C 3J7 (Canada) ...
... Université de Montréal C.P. 6128, succ. Centre-Ville Montréal, Québec H3C 3J7 (Canada) ...
Quantum mechanics – an introduction
... displaced about the Rayleigh band; however, the intensity of the anti-Stokes bands is much weaker than the Stokes bands and they ...
... displaced about the Rayleigh band; however, the intensity of the anti-Stokes bands is much weaker than the Stokes bands and they ...
powerpoint - University of Illinois Urbana
... Permeation of wave functions Probability in the classically forbidden region gets smaller with increasing v (quantum number). Another correspondence principle result. ...
... Permeation of wave functions Probability in the classically forbidden region gets smaller with increasing v (quantum number). Another correspondence principle result. ...
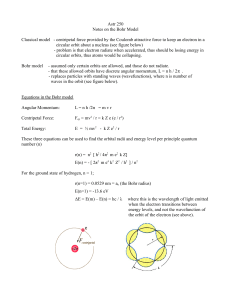
Astr 250 Notes on the Bohr Model Classical model
... circular orbit about a nucleus (see figure below) - problem is that electron radiate when accelerated, thus should be losing energy in circular orbits, thus atoms would be collapsing. Bohr model ...
... circular orbit about a nucleus (see figure below) - problem is that electron radiate when accelerated, thus should be losing energy in circular orbits, thus atoms would be collapsing. Bohr model ...
HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT 12
... This is just a harmonic oscillator Hamiltonian, with Mef f = M r02 , and ω = 2M r0 , so that the energy levels are r ...
... This is just a harmonic oscillator Hamiltonian, with Mef f = M r02 , and ω = 2M r0 , so that the energy levels are r ...
ap chemistry review – multiple choice
... (a) Lithium (b) Nickel (c) Bromine (d) Uranium (e) Fluorine 13. Is a gas in its standard state at 298 K. 14. Reacts with water to form a strong base. ...
... (a) Lithium (b) Nickel (c) Bromine (d) Uranium (e) Fluorine 13. Is a gas in its standard state at 298 K. 14. Reacts with water to form a strong base. ...
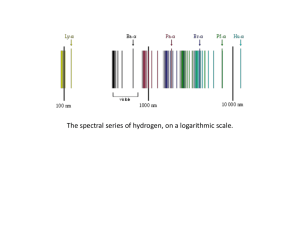
Rutherford–Bohr model
... atomic nucleus and where an electron jump between orbits is accompanied by an emitted or absorbed amount of electromagnetic energy (hν).[1] The orbits in which the electron may travel are shown as grey circles; their radius increases as n2, where n is the principal quantum number. The 3 → 2 transiti ...
... atomic nucleus and where an electron jump between orbits is accompanied by an emitted or absorbed amount of electromagnetic energy (hν).[1] The orbits in which the electron may travel are shown as grey circles; their radius increases as n2, where n is the principal quantum number. The 3 → 2 transiti ...
MOLECULAR ENERGY LEVELS
... • Can also refer to energy levels of nuclei or vibrational or rotational energy levels in molecules. ...
... • Can also refer to energy levels of nuclei or vibrational or rotational energy levels in molecules. ...
Section1 Final Key
... 5. (10 pts) Postulates and Principles: True/False. T / F : According to the variational principle, the quantum mechanical energy is always lower than the classical energy. T / F: A spherical harmonic function Ylm (θ, φ) is an eigenfunction of the L̂2 operator with eigenvalue h̄2 l(l + 1). T / F : A ...
... 5. (10 pts) Postulates and Principles: True/False. T / F : According to the variational principle, the quantum mechanical energy is always lower than the classical energy. T / F: A spherical harmonic function Ylm (θ, φ) is an eigenfunction of the L̂2 operator with eigenvalue h̄2 l(l + 1). T / F : A ...
Exam 2 Review - Iowa State University
... 14. A neon atom emits light at many wavelengths, two of which are at 616.4 and 638.3 nm. Both of these transitions are to the same final state. a) What is the energy difference between the two states for each transition? ...
... 14. A neon atom emits light at many wavelengths, two of which are at 616.4 and 638.3 nm. Both of these transitions are to the same final state. a) What is the energy difference between the two states for each transition? ...
Slide 1
... Spectroscopic techniques all work on the principle of that, under certain conditions, materials absorb or emit energy Quantized energy: photon ...
... Spectroscopic techniques all work on the principle of that, under certain conditions, materials absorb or emit energy Quantized energy: photon ...
Final Exam Solutions - University of California San Diego
... Photons of wavelength 450nm are incident on a metal. The most energetic electrons ejected from the metal are bent into a circular arc of radius 20cm in a magnetic field whose strength is equal to 2.0!10-5T. What is the work function of the metal? Problem 2: Quantum Pool:[20 pts] An x-ray photon of w ...
... Photons of wavelength 450nm are incident on a metal. The most energetic electrons ejected from the metal are bent into a circular arc of radius 20cm in a magnetic field whose strength is equal to 2.0!10-5T. What is the work function of the metal? Problem 2: Quantum Pool:[20 pts] An x-ray photon of w ...
Chapter 7, 8, and 9 Exam 2014 Name I. 50% of your grade will come
... Name _____________________________________ ...
... Name _____________________________________ ...
Franck–Condon principle
The Franck–Condon principle is a rule in spectroscopy and quantum chemistry that explains the intensity of vibronic transitions. Vibronic transitions are the simultaneous changes in electronic and vibrational energy levels of a molecule due to the absorption or emission of a photon of the appropriate energy. The principle states that during an electronic transition, a change from one vibrational energy level to another will be more likely to happen if the two vibrational wave functions overlap more significantly.