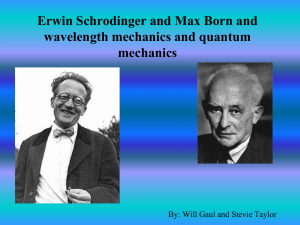Quantum Mechanics: Introduction
... but time periodicity of oscillator Additionally Laws of thermodynamics E = kT Fundamental constants : 1. velocity of light c 2. Avogadro Number N 3. Boltzman constant k 4. Unit of charge e ...
... but time periodicity of oscillator Additionally Laws of thermodynamics E = kT Fundamental constants : 1. velocity of light c 2. Avogadro Number N 3. Boltzman constant k 4. Unit of charge e ...
Erwin Schrodinger an Max Born and wavelength
... Erwin Schrodinger and wavelength mechanics • In 1926 he determined that a particle or an atom would vibrate in circles with activity • The atom contained, “Waves of Chance” • When an electron passed through the nucleus these waves would ripple back and forth • They would ripple in a straight line w ...
... Erwin Schrodinger and wavelength mechanics • In 1926 he determined that a particle or an atom would vibrate in circles with activity • The atom contained, “Waves of Chance” • When an electron passed through the nucleus these waves would ripple back and forth • They would ripple in a straight line w ...
Please look over the following review questions
... quite different from the radius predicted by Bohr that agrees with the orbital radius of Bohr ...
... quite different from the radius predicted by Bohr that agrees with the orbital radius of Bohr ...
Quantum Theory
... When two particles or events affect each other without any signal or force. Determinism, and our common sense, says that this is totally impossible. Quantum mechanics predicts when it will or will not happen, and what the probability of the outcome will be. ...
... When two particles or events affect each other without any signal or force. Determinism, and our common sense, says that this is totally impossible. Quantum mechanics predicts when it will or will not happen, and what the probability of the outcome will be. ...
Open Questions in Physics
... 1. Where and what is dark matter? 2. How massive are neutrinos? 3. What are the implications of neutrino mass? 4. What are the origins of mass? 5. Why is gravity so weak? 6. Why is the universe made of matter and not antimatter? 7. Where do ultrahigh-energy cosmic rays come from? ...
... 1. Where and what is dark matter? 2. How massive are neutrinos? 3. What are the implications of neutrino mass? 4. What are the origins of mass? 5. Why is gravity so weak? 6. Why is the universe made of matter and not antimatter? 7. Where do ultrahigh-energy cosmic rays come from? ...
INTRODUCTION TO ELEMENTARY PARTICLE PHYSICS
... However, some general features of this behavior have nothing to do with the detailed form of the interactions. Instead they follow directly from relativity, from quantum mechanics, or from the combination of the two. For example, in relativity, energy and momentum are always conserved, but (rest) ma ...
... However, some general features of this behavior have nothing to do with the detailed form of the interactions. Instead they follow directly from relativity, from quantum mechanics, or from the combination of the two. For example, in relativity, energy and momentum are always conserved, but (rest) ma ...
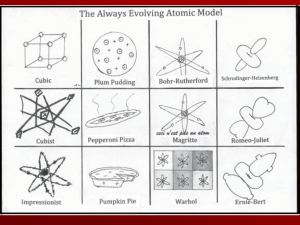
4.2 The Quantum Model of the Atom Vocab Electromagnetic
... - A unit or quantum of light a particle of electromagnetic radiation that has zero rest mass and carries a quantum of energy. Ground State - The lowest energy state of a quantized system. Excited State - A state in which an atom has more energy than it does at its ground state. Emission-Line Spectru ...
... - A unit or quantum of light a particle of electromagnetic radiation that has zero rest mass and carries a quantum of energy. Ground State - The lowest energy state of a quantized system. Excited State - A state in which an atom has more energy than it does at its ground state. Emission-Line Spectru ...
powerpoint
... Superposition creates regions of constructive and destructive diffraction according to the relative incidence of the waves. The light intensity is distributed by the square of the wave envelope: ...
... Superposition creates regions of constructive and destructive diffraction according to the relative incidence of the waves. The light intensity is distributed by the square of the wave envelope: ...
HTPIB27O The Einstein-Bohr Debate
... “God does not play dice” Attacked either Heisenberg uncertainty, or complementarity ...
... “God does not play dice” Attacked either Heisenberg uncertainty, or complementarity ...