Relativity without tears - Philsci
... Now c is an invariant velocity, as (14) shows. However, in the above derivation nothing as yet indicates that c is the velocity of light. Only when we invoke the Maxwell equations it becomes clear that the velocity of electromagnetic waves implied by these equations must coincide with c if we want t ...
... Now c is an invariant velocity, as (14) shows. However, in the above derivation nothing as yet indicates that c is the velocity of light. Only when we invoke the Maxwell equations it becomes clear that the velocity of electromagnetic waves implied by these equations must coincide with c if we want t ...
Waves & Oscillations Physics 42200 Spring 2015 Semester
... • An accelerated reference frame is one way to provide a periodic driving force. • Analyzing mechanical systems in accelerated reference frames can be very convenient. • An accelerated reference frame is an example of a non-inertial reference frame. • Let’s analyze the motion of a particle in an acc ...
... • An accelerated reference frame is one way to provide a periodic driving force. • Analyzing mechanical systems in accelerated reference frames can be very convenient. • An accelerated reference frame is an example of a non-inertial reference frame. • Let’s analyze the motion of a particle in an acc ...
The Velocity of Light - Gravitational Relativity
... subatomic charges extend into infinity, supplying an electromagnetic medium for light to travel through the universe, howbeit weak in deep space. Maxwell’s derivation of the speed of light states that the speed of light is inversely proportional to the electromagnetic strength of light’s transport ...
... subatomic charges extend into infinity, supplying an electromagnetic medium for light to travel through the universe, howbeit weak in deep space. Maxwell’s derivation of the speed of light states that the speed of light is inversely proportional to the electromagnetic strength of light’s transport ...
The Velocity of Light - Gravitational Relativity
... subatomic charges extend into infinity, supplying an electromagnetic medium for light to travel through the universe, howbeit weak in deep space. Maxwell’s derivation of the speed of light states that the speed of light is inversely proportional to the electromagnetic strength of light’s transport ...
... subatomic charges extend into infinity, supplying an electromagnetic medium for light to travel through the universe, howbeit weak in deep space. Maxwell’s derivation of the speed of light states that the speed of light is inversely proportional to the electromagnetic strength of light’s transport ...
... After a presentation of the postulates used, a matrix notation which is most convenient for the four-dimensional formulation of the theory is developed. This notation is applied to derive relativistic mechanics and electrodynamics as a consequence of the postulates. An investigation of the fields in ...
Syllabus
... the audience asked him what the value of this was. Faraday’s famous response was “Madam, of what value is a newborn child?” Faraday’s curt response shows his passion for his research; however, the question the lady asked was actually a very good question and is the type of question that needs to be ...
... the audience asked him what the value of this was. Faraday’s famous response was “Madam, of what value is a newborn child?” Faraday’s curt response shows his passion for his research; however, the question the lady asked was actually a very good question and is the type of question that needs to be ...
Forces II
... Equation (8) shows how the derivative of a vector can be transformed between an inertial and a rotating reference frame. Even though the derivation was done for a vector in only two dimensions, it works regardless of the number of dimensions. ...
... Equation (8) shows how the derivative of a vector can be transformed between an inertial and a rotating reference frame. Even though the derivation was done for a vector in only two dimensions, it works regardless of the number of dimensions. ...
AP Summer Assignment - York County School Division
... (1) The potential difference across the 6 ohm resistor is half as great as the potential difference across the 3 ohm resistor. (2) The potential difference across the 6 ohm resistor is four times as great as the potential difference across the 3 ohm resistor. (3) The potential difference across the ...
... (1) The potential difference across the 6 ohm resistor is half as great as the potential difference across the 3 ohm resistor. (2) The potential difference across the 6 ohm resistor is four times as great as the potential difference across the 3 ohm resistor. (3) The potential difference across the ...
The effective mass tensor in the General Relativity
... material, the force between other atoms will affect its movement and it will not be described by Newton's law. So we introduce the concept of effective mass to describe the movement of electron in Newton's law. The effective mass can be negative or different due to circumstances. Generally, in the a ...
... material, the force between other atoms will affect its movement and it will not be described by Newton's law. So we introduce the concept of effective mass to describe the movement of electron in Newton's law. The effective mass can be negative or different due to circumstances. Generally, in the a ...
Special_Relativity_7
... light has anything to do with the problem. That’s actually wrong. The resolution of the problem has everything to do with the speed of light; it’s just that the way it works is exceedingly subtle. To short circuit the full story, photons carry momentum as well as energy (as we found in SR6). In esse ...
... light has anything to do with the problem. That’s actually wrong. The resolution of the problem has everything to do with the speed of light; it’s just that the way it works is exceedingly subtle. To short circuit the full story, photons carry momentum as well as energy (as we found in SR6). In esse ...
physics space notes File
... The launch begins with the rocket producing thrust by burning fuel and expelling the resulting hot gases out one end. These hot gases have a momentum in one direction, and since the total momentum of the rocket-fuel system is zero, the rocket itself has an equal momentum in the opposite direction. T ...
... The launch begins with the rocket producing thrust by burning fuel and expelling the resulting hot gases out one end. These hot gases have a momentum in one direction, and since the total momentum of the rocket-fuel system is zero, the rocket itself has an equal momentum in the opposite direction. T ...
MCA PPT Review - Math On Monday
... Freely Falling Bodies Free fall is motion under the influence of gravity. When you toss an object in the air it is in free fall, whether it is going up or down. Its velocity will decrease as it goes up and increase as it goes down because the Earth pulls on it due to its gravity. Close to the surfa ...
... Freely Falling Bodies Free fall is motion under the influence of gravity. When you toss an object in the air it is in free fall, whether it is going up or down. Its velocity will decrease as it goes up and increase as it goes down because the Earth pulls on it due to its gravity. Close to the surfa ...
this PDF file - Canadian Center of Science and Education
... created by a moving electric charge, differs from the gravitational four-vector created by a moving massive point by only a constant multiplicative coefficient. From a) and b), it appears that for non-small , Maxwell’s electromagnetism could be generalized as a case of Einstein’s general relativity. ...
... created by a moving electric charge, differs from the gravitational four-vector created by a moving massive point by only a constant multiplicative coefficient. From a) and b), it appears that for non-small , Maxwell’s electromagnetism could be generalized as a case of Einstein’s general relativity. ...
Changing Coordinate Systems
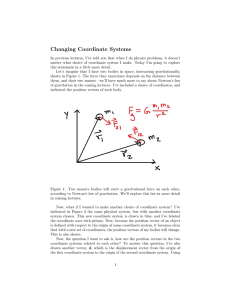
... that I’m moving to the right. I can verify this claim pretty easily from looking at Figure 2. If d is the position vector of the new frame with respect to the old frame, then certainly, −d must be the position vector of the old frame, as viewed by the new frame, since −d points in the opposite direc ...
... that I’m moving to the right. I can verify this claim pretty easily from looking at Figure 2. If d is the position vector of the new frame with respect to the old frame, then certainly, −d must be the position vector of the old frame, as viewed by the new frame, since −d points in the opposite direc ...
Inertial and Non-inertial Reference Frames
... Imagine a ball dropped from the roof of a building. It falls straight down with an acceleration of 9.8 m/s2. Now consider a ball dropped from an airplane in level flight with a constant velocity. To an observer stationary on the ground, the ball appears to follow a parabolic path. However, according ...
... Imagine a ball dropped from the roof of a building. It falls straight down with an acceleration of 9.8 m/s2. Now consider a ball dropped from an airplane in level flight with a constant velocity. To an observer stationary on the ground, the ball appears to follow a parabolic path. However, according ...
HSC Physics Notes - Space
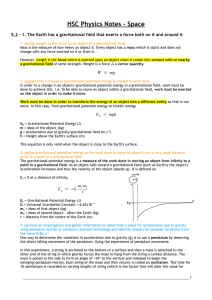
... To reduce the effect that g-forces have on the astronauts, they are made to lie down in specialised seats which minimise the effect of the feeling of g-forces. By lying down, the force is spread out across the body and also prevents the eye balls of astronauts popping under the intense stress. The ...
... To reduce the effect that g-forces have on the astronauts, they are made to lie down in specialised seats which minimise the effect of the feeling of g-forces. By lying down, the force is spread out across the body and also prevents the eye balls of astronauts popping under the intense stress. The ...
A New Astronomical Quranic Method for The Determination Of The
... "GOD is the ONE who made the sun a shining glory and the moon a light and for her ordained mansions, so that you might know the number of years and the reckoning" (10:5) The lunar year is twelve months, the month is defined recently as the time of one revolution of the moon in its orbit around the e ...
... "GOD is the ONE who made the sun a shining glory and the moon a light and for her ordained mansions, so that you might know the number of years and the reckoning" (10:5) The lunar year is twelve months, the month is defined recently as the time of one revolution of the moon in its orbit around the e ...
Frames of Reference Apparent Forces
... that is fixed in space. • A coordinate system fixed in space is known as an inertial (or absolute) frame of reference. • A coordinate system that is not fixed in space, such as one defined with respect to the rotating earth, is a noninertial frame of reference. • Because we are interested in atmosph ...
... that is fixed in space. • A coordinate system fixed in space is known as an inertial (or absolute) frame of reference. • A coordinate system that is not fixed in space, such as one defined with respect to the rotating earth, is a noninertial frame of reference. • Because we are interested in atmosph ...
Special relativity

In physics, special relativity (SR, also known as the special theory of relativity or STR) is the generally accepted physical theory regarding the relationship between space and time. It is based on two postulates: (1) that the laws of physics are invariant (i.e. identical) in all inertial systems (non-accelerating frames of reference); and (2) that the speed of light in a vacuum is the same for all observers, regardless of the motion of the light source. It was originally proposed in 1905 by Albert Einstein in the paper ""On the Electrodynamics of Moving Bodies"". The inconsistency of Newtonian mechanics with Maxwell’s equations of electromagnetism and the inability to discover Earth's motion through a luminiferous aether led to the development of special relativity, which corrects mechanics to handle situations involving motions nearing the speed of light. As of today, special relativity is the most accurate model of motion at any speed. Even so, Newtonian mechanics is still useful (due to its simplicity and high accuracy) as an approximation at small velocities relative to the speed of light.Special relativity implies a wide range of consequences, which have been experimentally verified, including length contraction, time dilation, relativistic mass, mass–energy equivalence, a universal speed limit, and relativity of simultaneity. It has replaced the conventional notion of an absolute universal time with the notion of a time that is dependent on reference frame and spatial position. Rather than an invariant time interval between two events, there is an invariant spacetime interval. Combined with other laws of physics, the two postulates of special relativity predict the equivalence of mass and energy, as expressed in the mass–energy equivalence formula E = mc2, where c is the speed of light in vacuum.A defining feature of special relativity is the replacement of the Galilean transformations of Newtonian mechanics with the Lorentz transformations. Time and space cannot be defined separately from each other. Rather space and time are interwoven into a single continuum known as spacetime. Events that occur at the same time for one observer could occur at different times for another.The theory is ""special"" in that it only applies in the special case where the curvature of spacetime due to gravity is negligible. In order to include gravity, Einstein formulated general relativity in 1915. (Special relativity, contrary to some outdated descriptions, is capable of handling accelerated frames of reference.)As Galilean relativity is now considered an approximation of special relativity that is valid for low speeds, special relativity is considered an approximation of general relativity that is valid for weak gravitational fields, i.e. at a sufficiently small scale and in conditions of free fall. Whereas general relativity incorporates noneuclidean geometry in order to represent gravitational effects as the geometric curvature of spacetime, special relativity is restricted to the flat spacetime known as Minkowski space. A locally Lorentz-invariant frame that abides by special relativity can be defined at sufficiently small scales, even in curved spacetime.Galileo Galilei had already postulated that there is no absolute and well-defined state of rest (no privileged reference frames), a principle now called Galileo's principle of relativity. Einstein extended this principle so that it accounted for the constant speed of light, a phenomenon that had been recently observed in the Michelson–Morley experiment. He also postulated that it holds for all the laws of physics, including both the laws of mechanics and of electrodynamics.