The Correct Derivation of Magnetism from Electrostatics
... The magnetic force of an infinitely long straight wire for nonrelativistic speeds can be obtained by applying the formulation: ...
... The magnetic force of an infinitely long straight wire for nonrelativistic speeds can be obtained by applying the formulation: ...
Many-Minds Quantum Mechanics
... select useful information. Quantum computers are based on the existence of complete wave functions, which may not exist for many-electron systems, and therefore it is not (at all) clear that a quantum computer can be brought to existence, (except very simple ones consisting of a few so called quantu ...
... select useful information. Quantum computers are based on the existence of complete wave functions, which may not exist for many-electron systems, and therefore it is not (at all) clear that a quantum computer can be brought to existence, (except very simple ones consisting of a few so called quantu ...
Chapter 10 The Deaths of Stars
... • The length of an object (as observed from “rest”) decreases in the direction of its motion as its speed increases. Length contraction • Clocks that you see as moving run more slowly than do clocks at rest. Biological processes slow down. Time dilation • Space and time cannot be considered as two s ...
... • The length of an object (as observed from “rest”) decreases in the direction of its motion as its speed increases. Length contraction • Clocks that you see as moving run more slowly than do clocks at rest. Biological processes slow down. Time dilation • Space and time cannot be considered as two s ...
Slide 1
... rolling on the flat? And if you were at the edge of a Yo-yo that was falling under gravity? What would it feel like in both cases? ...
... rolling on the flat? And if you were at the edge of a Yo-yo that was falling under gravity? What would it feel like in both cases? ...
On the Experimental Proofs of Relativistic Length Contraction and
... set in translational motion [9,10], Thus, according to Einstein, not only clocks run slow, but time itself is "dilated" in systems that move with respect to the system considered to be stationary (laboratory). The idea of the slowing down of moving clocks as a strictly kinematic effect was unaccepta ...
... set in translational motion [9,10], Thus, according to Einstein, not only clocks run slow, but time itself is "dilated" in systems that move with respect to the system considered to be stationary (laboratory). The idea of the slowing down of moving clocks as a strictly kinematic effect was unaccepta ...
Ch 6 Homework Name: edition. Follow the instructions and show your
... Two shuffleboard disks of equal mass, one orange and the other green, are involved in a perfectly elastic glancing collision. The green disk is initially at rest and is struck by the orange disk moving initially to the right at 5.00 m/s as in Figure (a) below. After the collision, the orange disk mo ...
... Two shuffleboard disks of equal mass, one orange and the other green, are involved in a perfectly elastic glancing collision. The green disk is initially at rest and is struck by the orange disk moving initially to the right at 5.00 m/s as in Figure (a) below. After the collision, the orange disk mo ...
Module 11
... What are some of the things that we should notice about these expressions for these physical quantities? First of all, remember that all of them revert to the classical, Newtonian expressions if u << c. We can get by just fine with saying that mass doesn’t change with speed and that kinetic energy ...
... What are some of the things that we should notice about these expressions for these physical quantities? First of all, remember that all of them revert to the classical, Newtonian expressions if u << c. We can get by just fine with saying that mass doesn’t change with speed and that kinetic energy ...
Frame of Reference
... A non‐iner.al frame of reference is one that is accelera%ng and Newton’s laws of mo%on appear invalid unless fic%%ous forces are used to describe the mo%on of objects observed in the non‐iner%al reference frame. Example: If you are in an automobile when the brakes are abruptly applied, then you wi ...
... A non‐iner.al frame of reference is one that is accelera%ng and Newton’s laws of mo%on appear invalid unless fic%%ous forces are used to describe the mo%on of objects observed in the non‐iner%al reference frame. Example: If you are in an automobile when the brakes are abruptly applied, then you wi ...
Earlier examination problems
... contravariant tensor, and use the fact that the inverse of a matrix is unique.) 3. A fluid is consisting of point particles of rest mass m moving to the right along the xaxis with a gamma-factor of 2 and number density n, as seen from a certain coordinate system. What is the (space-averaged) energy ...
... contravariant tensor, and use the fact that the inverse of a matrix is unique.) 3. A fluid is consisting of point particles of rest mass m moving to the right along the xaxis with a gamma-factor of 2 and number density n, as seen from a certain coordinate system. What is the (space-averaged) energy ...
magnet experiment to measuring space propulsion heim
... cessful in constructing a quantum theory of gravity. In how far string theory [1, 3], ST, that uses a background metric will be able to recover background independence is something that seems undecided at present. On the contrary, according to Einstein, one should start with GR and incorporate the ...
... cessful in constructing a quantum theory of gravity. In how far string theory [1, 3], ST, that uses a background metric will be able to recover background independence is something that seems undecided at present. On the contrary, according to Einstein, one should start with GR and incorporate the ...
7 Radiation of relativistic particles 7.1 General properties of relativistic radiation sources
... Transit time effect. If the source is moving near the speed of light along a direction which lies close to the line of sight, then the source almost catches up with its own radiation but not quite. Consider an object which moves from a point P1 to a point P2 in a time ∆t in the observers frame. If t ...
... Transit time effect. If the source is moving near the speed of light along a direction which lies close to the line of sight, then the source almost catches up with its own radiation but not quite. Consider an object which moves from a point P1 to a point P2 in a time ∆t in the observers frame. If t ...
Physics 106a/196a – Problem Set 2 – Due Oct 13,...
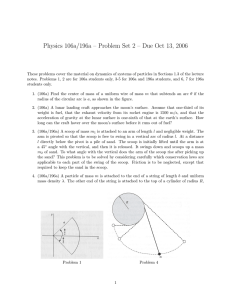
... 1. (106a) Find the center of mass of a uniform wire of mass m that subtends an arc θ if the radius of the circular arc is a, as shown in the figure. 2. (106a) A lunar landing craft approaches the moon’s surface. Assume that one-third of its weight is fuel, that the exhaust velocity from its rocket e ...
... 1. (106a) Find the center of mass of a uniform wire of mass m that subtends an arc θ if the radius of the circular arc is a, as shown in the figure. 2. (106a) A lunar landing craft approaches the moon’s surface. Assume that one-third of its weight is fuel, that the exhaust velocity from its rocket e ...
General Relativity for Pedestrians-
... Gravity is universal. Everything creates gravity as well as gets affected by gravity since everything has mass (or, equivalently, energy). However, unless the mass of an object is very large, the gravity it generates is very weak. According to Newton’s laws of gravity, acceleration of a test particl ...
... Gravity is universal. Everything creates gravity as well as gets affected by gravity since everything has mass (or, equivalently, energy). However, unless the mass of an object is very large, the gravity it generates is very weak. According to Newton’s laws of gravity, acceleration of a test particl ...
Review questions for ISU old book Word document
... and therefore an absolute reference frame, did not exist? Describe the device used to perform the experiment and how it showed there was no ether. b) According to scientists before 1887, what properties did the so-called “ether” possess? c) Before 1887, what two reasons did scientists have for belie ...
... and therefore an absolute reference frame, did not exist? Describe the device used to perform the experiment and how it showed there was no ether. b) According to scientists before 1887, what properties did the so-called “ether” possess? c) Before 1887, what two reasons did scientists have for belie ...
lectures 2015
... have a strong notion that time and space are absolute quantities. We think that we can define a point in ‘absolute’ space and ‘absolute’ time, and that space and time are the same for everyone, no matter how they are moving with respect to each other. These ideas obviously work very well in everyday ...
... have a strong notion that time and space are absolute quantities. We think that we can define a point in ‘absolute’ space and ‘absolute’ time, and that space and time are the same for everyone, no matter how they are moving with respect to each other. These ideas obviously work very well in everyday ...
Physics Final Review Problems 2013 *Note: the following problems
... speed and accuracy and you only get one throw. Which option would you choose? Why? 22. A 40 kg skater traveling at 4 m/s overtakes a 60 kg skater traveling at 2 m/s in the same direction and collides with her. If they remain in contact after the collision, what is their final velocity? Work and Ener ...
... speed and accuracy and you only get one throw. Which option would you choose? Why? 22. A 40 kg skater traveling at 4 m/s overtakes a 60 kg skater traveling at 2 m/s in the same direction and collides with her. If they remain in contact after the collision, what is their final velocity? Work and Ener ...
Sects. 4.9 & 4.10
... Non-Inertial Frames • The most common example of a non-inertial frame = Earth’s surface! Another is rigid body rotation. • We usually assume Earth’s surface is inertial, when it is not! – A coord system fixed on the Earth is accelerating (Earth’s rotation + orbital motion) & is thus non-inertial! – ...
... Non-Inertial Frames • The most common example of a non-inertial frame = Earth’s surface! Another is rigid body rotation. • We usually assume Earth’s surface is inertial, when it is not! – A coord system fixed on the Earth is accelerating (Earth’s rotation + orbital motion) & is thus non-inertial! – ...
Special relativity

In physics, special relativity (SR, also known as the special theory of relativity or STR) is the generally accepted physical theory regarding the relationship between space and time. It is based on two postulates: (1) that the laws of physics are invariant (i.e. identical) in all inertial systems (non-accelerating frames of reference); and (2) that the speed of light in a vacuum is the same for all observers, regardless of the motion of the light source. It was originally proposed in 1905 by Albert Einstein in the paper ""On the Electrodynamics of Moving Bodies"". The inconsistency of Newtonian mechanics with Maxwell’s equations of electromagnetism and the inability to discover Earth's motion through a luminiferous aether led to the development of special relativity, which corrects mechanics to handle situations involving motions nearing the speed of light. As of today, special relativity is the most accurate model of motion at any speed. Even so, Newtonian mechanics is still useful (due to its simplicity and high accuracy) as an approximation at small velocities relative to the speed of light.Special relativity implies a wide range of consequences, which have been experimentally verified, including length contraction, time dilation, relativistic mass, mass–energy equivalence, a universal speed limit, and relativity of simultaneity. It has replaced the conventional notion of an absolute universal time with the notion of a time that is dependent on reference frame and spatial position. Rather than an invariant time interval between two events, there is an invariant spacetime interval. Combined with other laws of physics, the two postulates of special relativity predict the equivalence of mass and energy, as expressed in the mass–energy equivalence formula E = mc2, where c is the speed of light in vacuum.A defining feature of special relativity is the replacement of the Galilean transformations of Newtonian mechanics with the Lorentz transformations. Time and space cannot be defined separately from each other. Rather space and time are interwoven into a single continuum known as spacetime. Events that occur at the same time for one observer could occur at different times for another.The theory is ""special"" in that it only applies in the special case where the curvature of spacetime due to gravity is negligible. In order to include gravity, Einstein formulated general relativity in 1915. (Special relativity, contrary to some outdated descriptions, is capable of handling accelerated frames of reference.)As Galilean relativity is now considered an approximation of special relativity that is valid for low speeds, special relativity is considered an approximation of general relativity that is valid for weak gravitational fields, i.e. at a sufficiently small scale and in conditions of free fall. Whereas general relativity incorporates noneuclidean geometry in order to represent gravitational effects as the geometric curvature of spacetime, special relativity is restricted to the flat spacetime known as Minkowski space. A locally Lorentz-invariant frame that abides by special relativity can be defined at sufficiently small scales, even in curved spacetime.Galileo Galilei had already postulated that there is no absolute and well-defined state of rest (no privileged reference frames), a principle now called Galileo's principle of relativity. Einstein extended this principle so that it accounted for the constant speed of light, a phenomenon that had been recently observed in the Michelson–Morley experiment. He also postulated that it holds for all the laws of physics, including both the laws of mechanics and of electrodynamics.