Joe`s Relatively Small Book of Special Relativity
... same order of magnitude as the speed of light. In this course, we will always refer to this speed as c, where c ≈ 2.99 × 108 m/sec. In fact, we will almost always approximate this as c = 3 × 108 m/sec. If we consider a car traveling on the motorway at a speed of 100 km/hr, Galilean-Newtonian mechani ...
... same order of magnitude as the speed of light. In this course, we will always refer to this speed as c, where c ≈ 2.99 × 108 m/sec. In fact, we will almost always approximate this as c = 3 × 108 m/sec. If we consider a car traveling on the motorway at a speed of 100 km/hr, Galilean-Newtonian mechani ...
conservation of momentum in two dimensions
... forces are at the core of momentum changes. However in this case both parts of the system are moving as opposed to a car’s movement where the road is stationary. ...
... forces are at the core of momentum changes. However in this case both parts of the system are moving as opposed to a car’s movement where the road is stationary. ...
Motion Relative to a non-inertial frame
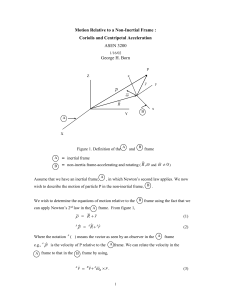
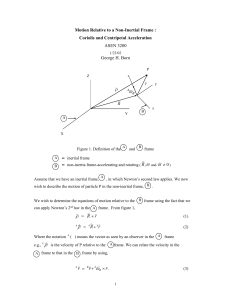
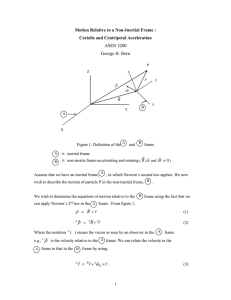
... The term A B r does not have a specific name. In order for B to be an inertial frame it is required that A ...
... The term A B r does not have a specific name. In order for B to be an inertial frame it is required that A ...
Open Ended Questions OEQ 1 The car manufacturer SATSUMA
... with that of the alpha particle? (no need for a calculation) (3,3) (c) If an electron and an alpha particle were then passed at identical speeds between the poles of a magnet, sketch how their paths would differ. (2) ...
... with that of the alpha particle? (no need for a calculation) (3,3) (c) If an electron and an alpha particle were then passed at identical speeds between the poles of a magnet, sketch how their paths would differ. (2) ...
COURSE INFORMATION
... PHYSICS 142 is the second and final semester of an introductory, calculus-based Physics course designed primarily for chemistry and zoology majors and satisfies the physics requirements for medical and dental schools. The course presents a survey of Electrodynamics – Electric and Magnetic phenomena, ...
... PHYSICS 142 is the second and final semester of an introductory, calculus-based Physics course designed primarily for chemistry and zoology majors and satisfies the physics requirements for medical and dental schools. The course presents a survey of Electrodynamics – Electric and Magnetic phenomena, ...
File - PhysicsLovers
... joule. Energy can be classified further into various well defined forms such as (a) mechanical (b) heat (c) electrical (d) chemical (e) atomic energy etc. In many processes that occur in nature energy may be transformed from one form to other. Mass can also be transformed into energy and vice-versa ...
... joule. Energy can be classified further into various well defined forms such as (a) mechanical (b) heat (c) electrical (d) chemical (e) atomic energy etc. In many processes that occur in nature energy may be transformed from one form to other. Mass can also be transformed into energy and vice-versa ...
1994 AAPT/Metrologic Physics Bowl Exam
... Answer sheet: Enter your information and answers on the answer sheet provided. Be sure to use a #2 pencil, fill the area completely, and make no stray marks on the sheet. In the indicated spaces, write in and encode your name (last name first). In the block labeled "IDENTIFICATION NUMBER," write in ...
... Answer sheet: Enter your information and answers on the answer sheet provided. Be sure to use a #2 pencil, fill the area completely, and make no stray marks on the sheet. In the indicated spaces, write in and encode your name (last name first). In the block labeled "IDENTIFICATION NUMBER," write in ...
lcp 14: the physics of star trek
... would naturally occur to Captain Kirk and Mr. Spock in travelling on their journeys or planning them. Since this is an advanced assignment it will not be specifically spelled out what you must know before attempting to solve the problems. The physics required beyond elementary relativity theory, how ...
... would naturally occur to Captain Kirk and Mr. Spock in travelling on their journeys or planning them. Since this is an advanced assignment it will not be specifically spelled out what you must know before attempting to solve the problems. The physics required beyond elementary relativity theory, how ...
Abraham-Solution to Schwarzschild Metric Implies
... holes [1]. The hoped-for miniholes are only 10–32 cm large – as small compared to an atom (10–8 cm) as the latter is to the whole solar system (1016 cm) – and are expected to “evaporate“ within less than a picosecond while leaving behind a much hoped-for “signature“ of secondary particles [1]. The f ...
... holes [1]. The hoped-for miniholes are only 10–32 cm large – as small compared to an atom (10–8 cm) as the latter is to the whole solar system (1016 cm) – and are expected to “evaporate“ within less than a picosecond while leaving behind a much hoped-for “signature“ of secondary particles [1]. The f ...
INTRODUCTION TO THE THEORY OF BLACK HOLES∗
... soon as their Compton wavelengths approach the dimensions of the black hole itself. This so-called “Hawking radiation” would be a property that all black holes have in common, though for the astronomical black holes it would be far too weak to be observed directly. The radiation is purely thermal. T ...
... soon as their Compton wavelengths approach the dimensions of the black hole itself. This so-called “Hawking radiation” would be a property that all black holes have in common, though for the astronomical black holes it would be far too weak to be observed directly. The radiation is purely thermal. T ...
The gravitational interaction of light: from weak to strong fields
... overall attraction factor of four appears. An independent motivation for our work comes from the subject of electromagnetic geons [7, 8]. Wheeler [7] adopted TEP’s result as the cornerstone of his electromagnetic geon model. He went beyond TEP’s findings by generalizing them to the case of two ligh ...
... overall attraction factor of four appears. An independent motivation for our work comes from the subject of electromagnetic geons [7, 8]. Wheeler [7] adopted TEP’s result as the cornerstone of his electromagnetic geon model. He went beyond TEP’s findings by generalizing them to the case of two ligh ...
2 Spacetime and General - Farmingdale State College
... future light cone. When (dx)2 > (d)2, (ds)2 is negative. Because the space term predominates in this case, the world line is called spacelike. A spacelike world line lies outside the light cone in the region called elsewhere, figure 2.4. When (dx)2 = (d)2, (ds)2 is equal to zero. In this case, (dx ...
... future light cone. When (dx)2 > (d)2, (ds)2 is negative. Because the space term predominates in this case, the world line is called spacelike. A spacelike world line lies outside the light cone in the region called elsewhere, figure 2.4. When (dx)2 = (d)2, (ds)2 is equal to zero. In this case, (dx ...
Physics 235 Chapter 10 Motion in a Non-Inertial Reference Frame
... account the rotation of the Earth around its axis, the rotation of the Earth around the sun, the rotation of our solar system around the center of our galaxy, etc. etc. The motion of the book will all of a sudden be a lot more complicated! For many experiments, the effect of the Earth not being an i ...
... account the rotation of the Earth around its axis, the rotation of the Earth around the sun, the rotation of our solar system around the center of our galaxy, etc. etc. The motion of the book will all of a sudden be a lot more complicated! For many experiments, the effect of the Earth not being an i ...
Chapter 8 and 9 Study Guide
... 2. A 30-kg girl and a 50-kg boy face each other on friction-free roller skates. The girl pushes the boy, who moves away at a speed of 3 m/s. What is the girl's speed? 3. A 40-kg football player leaps through the air to collide with and tackle a 50-kg player heading toward him, also in the air. If th ...
... 2. A 30-kg girl and a 50-kg boy face each other on friction-free roller skates. The girl pushes the boy, who moves away at a speed of 3 m/s. What is the girl's speed? 3. A 40-kg football player leaps through the air to collide with and tackle a 50-kg player heading toward him, also in the air. If th ...
Relativity
... motion of the reference frame. He examined Maxwell’s ideas as applied to a frame-ofreference experiment that required only a magnet and a closed coil of wire. Einstein used a method called a thought experiment, which is an experiment carried out in the imagination but not actually performed. A thoug ...
... motion of the reference frame. He examined Maxwell’s ideas as applied to a frame-ofreference experiment that required only a magnet and a closed coil of wire. Einstein used a method called a thought experiment, which is an experiment carried out in the imagination but not actually performed. A thoug ...
Special relativity

In physics, special relativity (SR, also known as the special theory of relativity or STR) is the generally accepted physical theory regarding the relationship between space and time. It is based on two postulates: (1) that the laws of physics are invariant (i.e. identical) in all inertial systems (non-accelerating frames of reference); and (2) that the speed of light in a vacuum is the same for all observers, regardless of the motion of the light source. It was originally proposed in 1905 by Albert Einstein in the paper ""On the Electrodynamics of Moving Bodies"". The inconsistency of Newtonian mechanics with Maxwell’s equations of electromagnetism and the inability to discover Earth's motion through a luminiferous aether led to the development of special relativity, which corrects mechanics to handle situations involving motions nearing the speed of light. As of today, special relativity is the most accurate model of motion at any speed. Even so, Newtonian mechanics is still useful (due to its simplicity and high accuracy) as an approximation at small velocities relative to the speed of light.Special relativity implies a wide range of consequences, which have been experimentally verified, including length contraction, time dilation, relativistic mass, mass–energy equivalence, a universal speed limit, and relativity of simultaneity. It has replaced the conventional notion of an absolute universal time with the notion of a time that is dependent on reference frame and spatial position. Rather than an invariant time interval between two events, there is an invariant spacetime interval. Combined with other laws of physics, the two postulates of special relativity predict the equivalence of mass and energy, as expressed in the mass–energy equivalence formula E = mc2, where c is the speed of light in vacuum.A defining feature of special relativity is the replacement of the Galilean transformations of Newtonian mechanics with the Lorentz transformations. Time and space cannot be defined separately from each other. Rather space and time are interwoven into a single continuum known as spacetime. Events that occur at the same time for one observer could occur at different times for another.The theory is ""special"" in that it only applies in the special case where the curvature of spacetime due to gravity is negligible. In order to include gravity, Einstein formulated general relativity in 1915. (Special relativity, contrary to some outdated descriptions, is capable of handling accelerated frames of reference.)As Galilean relativity is now considered an approximation of special relativity that is valid for low speeds, special relativity is considered an approximation of general relativity that is valid for weak gravitational fields, i.e. at a sufficiently small scale and in conditions of free fall. Whereas general relativity incorporates noneuclidean geometry in order to represent gravitational effects as the geometric curvature of spacetime, special relativity is restricted to the flat spacetime known as Minkowski space. A locally Lorentz-invariant frame that abides by special relativity can be defined at sufficiently small scales, even in curved spacetime.Galileo Galilei had already postulated that there is no absolute and well-defined state of rest (no privileged reference frames), a principle now called Galileo's principle of relativity. Einstein extended this principle so that it accounted for the constant speed of light, a phenomenon that had been recently observed in the Michelson–Morley experiment. He also postulated that it holds for all the laws of physics, including both the laws of mechanics and of electrodynamics.