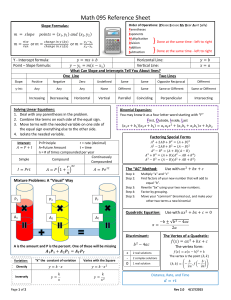
Student Activity DOC
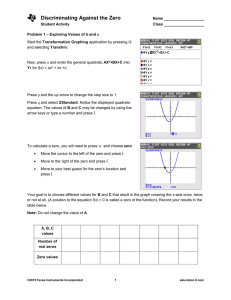
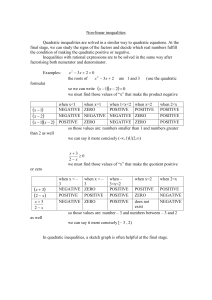
... 9. Why do some decimals under the square root, like 12.25, make the zeros rational, but other decimals make the zeros irrational? ...
... 9. Why do some decimals under the square root, like 12.25, make the zeros rational, but other decimals make the zeros irrational? ...
The Math-abet Book - TerrenceGraduatePortfolio
... The bottom of a plane figure or three-dimensional figure. ...
... The bottom of a plane figure or three-dimensional figure. ...
Division by zero
In mathematics, division by zero is division where the divisor (denominator) is zero. Such a division can be formally expressed as a/0 where a is the dividend (numerator). In ordinary arithmetic, the expression has no meaning, as there is no number which, multiplied by 0, gives a (assuming a≠0), and so division by zero is undefined. Since any number multiplied by zero is zero, the expression 0/0 also has no defined value and is called an indeterminate form. Historically, one of the earliest recorded references to the mathematical impossibility of assigning a value to a/0 is contained in George Berkeley's criticism of infinitesimal calculus in The Analyst (""ghosts of departed quantities"").There are mathematical structures in which a/0 is defined for some a such as in Riemann spheres and real projective lines; however, such structures cannot satisfy every ordinary rule of arithmetic (the field axioms).In computing, a program error may result from an attempt to divide by zero. Depending on the programming environment and the type of number (e.g. floating point, integer) being divided by zero, it may generate positive or negative infinity by the IEEE 754 floating point standard, generate an exception, generate an error message, cause the program to terminate, or result in a special not-a-number value.