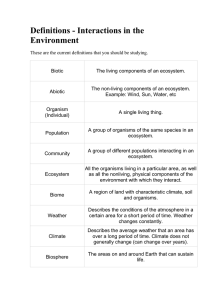
Definitions - Interactions in the Environment These are the current
... All the organisms living in a particular area, as well as all the nonliving, physical components of the environment with which they interact. ...
... All the organisms living in a particular area, as well as all the nonliving, physical components of the environment with which they interact. ...
Ecosystems - St. Joan of Arc School
... Habitats ~ the place in an ecosystem where an organism lives. Different ecosystems have different types of habitats. A forest ecosystem has fallen logs and trees. The logs provide a habitat for spiders and mushrooms. The trees provide a habitat for birds and squirrels. Ecosystems come in different s ...
... Habitats ~ the place in an ecosystem where an organism lives. Different ecosystems have different types of habitats. A forest ecosystem has fallen logs and trees. The logs provide a habitat for spiders and mushrooms. The trees provide a habitat for birds and squirrels. Ecosystems come in different s ...
Lecture 4-Biomes and the Physical Environment
... Air flowing toward the equator will be deflected west—it will be spinning more slowly than the earth and lag behind poleward flow will be deflected east—it will be spining faster than the earth and surge forward ...
... Air flowing toward the equator will be deflected west—it will be spinning more slowly than the earth and lag behind poleward flow will be deflected east—it will be spining faster than the earth and surge forward ...
Slide 1
... called natural selection (4) that the millions of species present on Earth today arose from a single original life form through a branching process called speciation, by which one species can give rise to two or more species (Coyne, 2007). ...
... called natural selection (4) that the millions of species present on Earth today arose from a single original life form through a branching process called speciation, by which one species can give rise to two or more species (Coyne, 2007). ...
A. Ecology
... Ecotone – an area where different terrestrial biomes grade into each other. Fires – Many plants and animal communities adapt to these. Fires also can change species composition within biological communities. ...
... Ecotone – an area where different terrestrial biomes grade into each other. Fires – Many plants and animal communities adapt to these. Fires also can change species composition within biological communities. ...
People and their enviornment Arabian Peninsula
... • Oil is a nonrenewable resource, yet it is the most widely used energy source today. • Burning fossil fuels creates greenhouse gases, which contribute to a rise in air temperature. • This climate change negatively affects the environment by decreasing the amount of rainfall and causing a rise in se ...
... • Oil is a nonrenewable resource, yet it is the most widely used energy source today. • Burning fossil fuels creates greenhouse gases, which contribute to a rise in air temperature. • This climate change negatively affects the environment by decreasing the amount of rainfall and causing a rise in se ...
Ecology Section 1 Notes
... and their environments, focusing on energy transfer • It is a science of relationships. ...
... and their environments, focusing on energy transfer • It is a science of relationships. ...
Chapter 4 Summary
... Ecology is a study of the connections among organisms and their living and nonliving environment. Prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms are composed of cells. Organisms may reproduce by asexual reproduction or sexual reproduction. Organisms that reproduce sexually are classified as members of the sam ...
... Ecology is a study of the connections among organisms and their living and nonliving environment. Prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms are composed of cells. Organisms may reproduce by asexual reproduction or sexual reproduction. Organisms that reproduce sexually are classified as members of the sam ...
Biome:
... The biosphere extends to the upper areas of the atmosphere where birds and insects can be found. It also reaches deep into the ground at a dark cave or to the bottom of the ocean at hydrothermal vents. The biosphere extends to any place that life (of any kind) can exist on Earth. ...
... The biosphere extends to the upper areas of the atmosphere where birds and insects can be found. It also reaches deep into the ground at a dark cave or to the bottom of the ocean at hydrothermal vents. The biosphere extends to any place that life (of any kind) can exist on Earth. ...
Unit 8 CW Puzzle Biosphere
... altitude Elevation; especially above sea level or above the earth's surface biodiversity The degree of variation of life forms within a given ecosystem, biome, or an entire planet biome A group of ecosystems that share similar climates and typical organisms biosphere All the parts of the earth where ...
... altitude Elevation; especially above sea level or above the earth's surface biodiversity The degree of variation of life forms within a given ecosystem, biome, or an entire planet biome A group of ecosystems that share similar climates and typical organisms biosphere All the parts of the earth where ...
Ecology
... • All organisms interact with other organisms – Plant, animal, bacteria, fungi, protists, & archaea ...
... • All organisms interact with other organisms – Plant, animal, bacteria, fungi, protists, & archaea ...
Unit 2: Multi-cellular organisms
... Biotic factors such as grazing and PREDATION are caused by living things; abiotic factors such as pH and TEMPERATURE are non-living. ...
... Biotic factors such as grazing and PREDATION are caused by living things; abiotic factors such as pH and TEMPERATURE are non-living. ...
Introduction to Ecology
... Changes in rainfall and weather patterns will lead to famine, starvation, and disease ...
... Changes in rainfall and weather patterns will lead to famine, starvation, and disease ...
Level of organization
... Levels of Organization All living things have a structure that is based on specific organization of materials (chemicals). Example ...
... Levels of Organization All living things have a structure that is based on specific organization of materials (chemicals). Example ...
Ecosystem Notes - Alvin Independent School District
... growing, metabolizing nutrients, and usually reproducing. ...
... growing, metabolizing nutrients, and usually reproducing. ...
1.03_Ecological Levels of Organization_11
... Levels of Studying Ecology Biosphere: The earth’s ecosystem interacting with the physical environment as a whole to maintain a steady state system intermediate in the flow of energy between the high energy input of the sun and the thermal sink of space (merges with atmosphere, lithosphere, hydrosp ...
... Levels of Studying Ecology Biosphere: The earth’s ecosystem interacting with the physical environment as a whole to maintain a steady state system intermediate in the flow of energy between the high energy input of the sun and the thermal sink of space (merges with atmosphere, lithosphere, hydrosp ...
File
... characteristics that help it survive in its environment (ex: ducks have webbed feet to make them better swimmers). 3) Where an organism lives is called its ________________________ and it includes all of the things that they organism needs (food, water, shelter). 4) The non-living parts of an enviro ...
... characteristics that help it survive in its environment (ex: ducks have webbed feet to make them better swimmers). 3) Where an organism lives is called its ________________________ and it includes all of the things that they organism needs (food, water, shelter). 4) The non-living parts of an enviro ...
Why do organisms change? - Rabun County School District
... and change so quickly? They have very short generation times. Generation time is the period between the birth of one generation and the birth of the next generation. ...
... and change so quickly? They have very short generation times. Generation time is the period between the birth of one generation and the birth of the next generation. ...
unit 6 vocabulary: ecology
... 5. Water shed- area of land that drains water from higher land to lower land and into a stream 6. Transpiration- loss of water through a plant’s leaves 7. Precipitation –water falling in any form, such as snow, ice, or rain 8. Evaporation- change of matter from a liquid state to a gaseous state (vap ...
... 5. Water shed- area of land that drains water from higher land to lower land and into a stream 6. Transpiration- loss of water through a plant’s leaves 7. Precipitation –water falling in any form, such as snow, ice, or rain 8. Evaporation- change of matter from a liquid state to a gaseous state (vap ...
Environmental Systems Scope and Sequence
... Land and Water Biomes Energy Flow-Food Webs and Food Chains Succession 2nd Six Weeks Population Dynamics Animal Population Growth Carrying Capacity and Resources Invasive and Extinct Species Protecting Biodiversity Maintaining the Balance The Dynamic Earth Parts of the Earth and Atmosphere Biogeoche ...
... Land and Water Biomes Energy Flow-Food Webs and Food Chains Succession 2nd Six Weeks Population Dynamics Animal Population Growth Carrying Capacity and Resources Invasive and Extinct Species Protecting Biodiversity Maintaining the Balance The Dynamic Earth Parts of the Earth and Atmosphere Biogeoche ...
Natural environment

The natural environment encompasses all living and non-living things occurring naturally on Earth or some region thereof. It is an environment that encompasses the interaction of all living species. Climate, weather, and natural resources that affect human survival and economic activity.The concept of the natural environment can be distinguished by components: Complete ecological units that function as natural systems without massive civilized human intervention, including all vegetation, microorganisms, soil, rocks, atmosphere, and natural phenomena that occur within their boundaries Universal natural resources and physical phenomena that lack clear-cut boundaries, such as air, water, and climate, as well as energy, radiation, electric charge, and magnetism, not originating from civilized human activityIn contrast to the natural environment is the built environment. In such areas where man has fundamentally transformed landscapes such as urban settings and agricultural land conversion, the natural environment is greatly modified and diminished, with a much more simplified human environment largely replacing it. Even events which seem less extreme such as hydroelectric dam construction, or photovoltaic system construction in the desert, the natural environment is substantially altered.It is difficult to find absolutely natural environments, and it is common that the naturalness varies in a continuum, from ideally 100% natural in one extreme to 0% natural in the other. More precisely, we can consider the different aspects or components of an environment, and see that their degree of naturalness is not uniform. If, for instance, we take an agricultural field, and consider the mineralogic composition and the structure of its soil, we will find that whereas the first is quite similar to that of an undisturbed forest soil, the structure is quite different.Natural environment is often used as a synonym for habitat. For instance, when we say that the natural environment of giraffes is the savanna.