3.2 Adapting to environment
... It is closely linked to primary productivity, which is the amount of energy provided by the producers in an ecosystem. A greater number of producers can support a more complex and diverse community of consumers. The greatest biodiversity on Earth occurs in tropical rainforests, where primary product ...
... It is closely linked to primary productivity, which is the amount of energy provided by the producers in an ecosystem. A greater number of producers can support a more complex and diverse community of consumers. The greatest biodiversity on Earth occurs in tropical rainforests, where primary product ...
SCIENCE NOTES - ECOSYSTEMS LESSON 1 What is an
... - An ecosystem is all the living and nonliving things in an area. Some ecosystems are small and some are large. - All living things need nonliving things (called abiotic factors) to survive. Some examples of this are water, soil, sunlight, and air. - The living things in an ecosystem are biotic fact ...
... - An ecosystem is all the living and nonliving things in an area. Some ecosystems are small and some are large. - All living things need nonliving things (called abiotic factors) to survive. Some examples of this are water, soil, sunlight, and air. - The living things in an ecosystem are biotic fact ...
What is an Ecosystem?
... Earth has three basic structural zones: the lithosphere (land) the hydrosphere (water) the atmosphere (air) ...
... Earth has three basic structural zones: the lithosphere (land) the hydrosphere (water) the atmosphere (air) ...
Use & Abuse of the Environment
... Abuse of the environment – 5 ways that humans damage the environment ...
... Abuse of the environment – 5 ways that humans damage the environment ...
Chapter 21 The Living Planet (SP09)
... succession – the gradual change in the organisms that make up a community. From bare ground, the first organisms (pioneer organisms) to inhabit the area are normally lichen, mosses and grasses. These trap sand particles and donate organic matter to produce the area’s first soils. This prepares the w ...
... succession – the gradual change in the organisms that make up a community. From bare ground, the first organisms (pioneer organisms) to inhabit the area are normally lichen, mosses and grasses. These trap sand particles and donate organic matter to produce the area’s first soils. This prepares the w ...
Changes Over Time
... Biotic vs. Abiotic Factors • Biotic-living (plants, worms, bacteria, etc.) -Abiotic-nonliving (soil, water, oxygen, etc.) ...
... Biotic vs. Abiotic Factors • Biotic-living (plants, worms, bacteria, etc.) -Abiotic-nonliving (soil, water, oxygen, etc.) ...
Introduction to Ecology
... Resources that cannot be replaced or are being used much faster than they are forming. Example: Coal, oil, natural gas (fossil fuel) ...
... Resources that cannot be replaced or are being used much faster than they are forming. Example: Coal, oil, natural gas (fossil fuel) ...
Notes Chapter18 Ecology
... • To appreciate how an ecosystem worksthink about other things depend on hundreds of individual parts. • If one part is missing or breaks, the entire thing does not work. ...
... • To appreciate how an ecosystem worksthink about other things depend on hundreds of individual parts. • If one part is missing or breaks, the entire thing does not work. ...
between two or more different species
... __Fossil__ ___record___: A historical sequence of life provided by fossils is known as this. ...
... __Fossil__ ___record___: A historical sequence of life provided by fossils is known as this. ...
Concepts in contemporary ecological theory Ecology is the study of
... Habitat is a concrete idea whereas niche is more abstract concept; since it includes how the population interacts with both natural resources and other populations. Adaptation is the process by which organisms or populations make biological or behavioral adjustments that facilitate their survival an ...
... Habitat is a concrete idea whereas niche is more abstract concept; since it includes how the population interacts with both natural resources and other populations. Adaptation is the process by which organisms or populations make biological or behavioral adjustments that facilitate their survival an ...
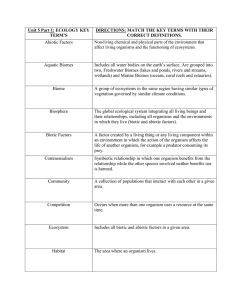
Unit 5 Part 1: ECOLOGY KEY TERM`S DIRECTIONS: MATCH THE
... Includes all water bodies on the earth’s surface. Are grouped into two, Freshwater Biomes (lakes and ponds, rivers and streams, wetlands) and Marine Biomes (oceans, coral reefs and estuaries). ...
... Includes all water bodies on the earth’s surface. Are grouped into two, Freshwater Biomes (lakes and ponds, rivers and streams, wetlands) and Marine Biomes (oceans, coral reefs and estuaries). ...
Ecology - Dominican
... Abiotic factors: The non-living components of an ecosystem. Biotic factors: The living components of an ecosystem. Climatic factors: Aspects of the weather that influence an ecosystem. Edaphic factors: Aspects of the soil that influence an ecosystem. Niche: The functional role of an organism in an e ...
... Abiotic factors: The non-living components of an ecosystem. Biotic factors: The living components of an ecosystem. Climatic factors: Aspects of the weather that influence an ecosystem. Edaphic factors: Aspects of the soil that influence an ecosystem. Niche: The functional role of an organism in an e ...
Biodiversity Program Related Key Terms for Students
... Diversity- relates to things that are different from one another in one or many different ways. Ecosystem- is a community of organisms that rely on each other within an environment. Environment- is a complex of living and non-living things (such as plants, animals, water, soil and weather) that inte ...
... Diversity- relates to things that are different from one another in one or many different ways. Ecosystem- is a community of organisms that rely on each other within an environment. Environment- is a complex of living and non-living things (such as plants, animals, water, soil and weather) that inte ...
Chapter 19 – Introduction to Ecology
... • Biosphere: the broadest and most inclusive level of organization – The Earth and its atmosphere make up our biosphere • Extends from 8 to 10 km (5-6 miles) above the Earth’s surface to the deepest parts of the ocean ...
... • Biosphere: the broadest and most inclusive level of organization – The Earth and its atmosphere make up our biosphere • Extends from 8 to 10 km (5-6 miles) above the Earth’s surface to the deepest parts of the ocean ...
DINEEnv Science Chapter 1 Science and the Environment Section 1
... _______________________________________________, which cannot be broken down by natural processes and include materials such as mercury. ...
... _______________________________________________, which cannot be broken down by natural processes and include materials such as mercury. ...
Chapter 6 Humans in the Biosphere
... These holes were caused by CFCs, which were used in aerosol cans, Styrofoam, and coolants. The use of CFCs have been phased out. ...
... These holes were caused by CFCs, which were used in aerosol cans, Styrofoam, and coolants. The use of CFCs have been phased out. ...
Introduction to Environmental Science PowerPoint
... The supply of nonrenewable resources is replenished extremely slowly, if at all. These can be used up. Coal, oil, minerals. ...
... The supply of nonrenewable resources is replenished extremely slowly, if at all. These can be used up. Coal, oil, minerals. ...
Earth Systems Crossword
... of its path (counterclockwise). It is greatest at the poles, North and South, and almost nonexistent at the equator. 4. -The movement of matter due to differences in density that are caused by temperature variations. The transfer of energy of heat when a liquid or a gas moves from place to place. 7. ...
... of its path (counterclockwise). It is greatest at the poles, North and South, and almost nonexistent at the equator. 4. -The movement of matter due to differences in density that are caused by temperature variations. The transfer of energy of heat when a liquid or a gas moves from place to place. 7. ...
Unit 9: Ecology A. Definitions 1. biotic(bio = living)
... 1. invasive nonnative species (aka exotic species) were brought here for use as ornamental lawn or garden plants 2. when the invasive organism is able to survive and reproduce, it can invade the natural habitat and crowd out the native species reducing biodiversity 3. habitats with low plant ...
... 1. invasive nonnative species (aka exotic species) were brought here for use as ornamental lawn or garden plants 2. when the invasive organism is able to survive and reproduce, it can invade the natural habitat and crowd out the native species reducing biodiversity 3. habitats with low plant ...
Human Impacts on the Environment and the 3Rs
... – Trees are cut down for paper, fuel, or as a building material – Trees SHOULD BE replanted, however many forests in tropical regions are not being replaced ...
... – Trees are cut down for paper, fuel, or as a building material – Trees SHOULD BE replanted, however many forests in tropical regions are not being replaced ...
PPT_Ecosystem Organization and Limiting Factors
... What is Ecology? The study of interactions between ...
... What is Ecology? The study of interactions between ...
section_1.1_notes_and_discussion
... Species are going extinct from the planet at a dramatic rate Extinction is the result of a species under stress – which can be natural or humanrelated Latest projections are now being seen as humans causing extinction 1000x’s faster ...
... Species are going extinct from the planet at a dramatic rate Extinction is the result of a species under stress – which can be natural or humanrelated Latest projections are now being seen as humans causing extinction 1000x’s faster ...
Natural environment

The natural environment encompasses all living and non-living things occurring naturally on Earth or some region thereof. It is an environment that encompasses the interaction of all living species. Climate, weather, and natural resources that affect human survival and economic activity.The concept of the natural environment can be distinguished by components: Complete ecological units that function as natural systems without massive civilized human intervention, including all vegetation, microorganisms, soil, rocks, atmosphere, and natural phenomena that occur within their boundaries Universal natural resources and physical phenomena that lack clear-cut boundaries, such as air, water, and climate, as well as energy, radiation, electric charge, and magnetism, not originating from civilized human activityIn contrast to the natural environment is the built environment. In such areas where man has fundamentally transformed landscapes such as urban settings and agricultural land conversion, the natural environment is greatly modified and diminished, with a much more simplified human environment largely replacing it. Even events which seem less extreme such as hydroelectric dam construction, or photovoltaic system construction in the desert, the natural environment is substantially altered.It is difficult to find absolutely natural environments, and it is common that the naturalness varies in a continuum, from ideally 100% natural in one extreme to 0% natural in the other. More precisely, we can consider the different aspects or components of an environment, and see that their degree of naturalness is not uniform. If, for instance, we take an agricultural field, and consider the mineralogic composition and the structure of its soil, we will find that whereas the first is quite similar to that of an undisturbed forest soil, the structure is quite different.Natural environment is often used as a synonym for habitat. For instance, when we say that the natural environment of giraffes is the savanna.