EFFECT OF CENTRIFUGAL AND CORIOLIS FORCES DUE TO
... have their usual meaning. When a particle is at rest on the surface of earth which rotates with constant angular velocity ω about its polar axis, then: ...
... have their usual meaning. When a particle is at rest on the surface of earth which rotates with constant angular velocity ω about its polar axis, then: ...
FE6
... Frames of reference If you want to describe the motion of an object you need a coordinate system, or something equivalent, to which you can relate your measurements of position; it doesn't make sense to give position coordinates (x, y, z) unless you know where the origin is and the directions of the ...
... Frames of reference If you want to describe the motion of an object you need a coordinate system, or something equivalent, to which you can relate your measurements of position; it doesn't make sense to give position coordinates (x, y, z) unless you know where the origin is and the directions of the ...
newton`s laws of motion
... the velocity of the object is constant. Velocity is a vector quantity which expresses both the object’s speed and the direction of its motion; therefore, the statement that the object’s velocity is constant is a statement that both its speed and the direction of its motion are constant. After Galile ...
... the velocity of the object is constant. Velocity is a vector quantity which expresses both the object’s speed and the direction of its motion; therefore, the statement that the object’s velocity is constant is a statement that both its speed and the direction of its motion are constant. After Galile ...
Name
... a The inside horse b The outside horse c Neither—they both have the same linear speed. 3. "Centrifugal forces" are an apparent reality to observers in a reference frame that is a rotating. b an inertial reference frame. c moving at constant velocity. d at rest. e none of the above 4. If you whirl a ...
... a The inside horse b The outside horse c Neither—they both have the same linear speed. 3. "Centrifugal forces" are an apparent reality to observers in a reference frame that is a rotating. b an inertial reference frame. c moving at constant velocity. d at rest. e none of the above 4. If you whirl a ...
PHYS 1443 – Section 501 Lecture #1
... Newton’s laws are valid only when observations are made in an inertial frame of reference. What happens in a non-inertial frame? Fictitious forces are needed to apply Newton’s second law in an accelerated frame. ...
... Newton’s laws are valid only when observations are made in an inertial frame of reference. What happens in a non-inertial frame? Fictitious forces are needed to apply Newton’s second law in an accelerated frame. ...
Sample pages 2 PDF
... reference that is anchored to a rocket-ship while its rockets are propelling it to higher and higher speeds. Newton’s laws do not hold in such a reference frame. After all, if you were to gently release a coin in such a frame, it would not stay put but rather it would move with accelerated motion in ...
... reference that is anchored to a rocket-ship while its rockets are propelling it to higher and higher speeds. Newton’s laws do not hold in such a reference frame. After all, if you were to gently release a coin in such a frame, it would not stay put but rather it would move with accelerated motion in ...
Worksheet - 2
... a) With what velocity will it strike the ground? b) After what time will it strike the ground? 10. A car accelerating uniformly from 15m/sec to 20 m/sec in 8 sec. calculate a) its acceleration b)The distance covered by the car in that time. 11. Define the following terms a) Force b) Balanced forces. ...
... a) With what velocity will it strike the ground? b) After what time will it strike the ground? 10. A car accelerating uniformly from 15m/sec to 20 m/sec in 8 sec. calculate a) its acceleration b)The distance covered by the car in that time. 11. Define the following terms a) Force b) Balanced forces. ...
Physics 106b/196b – Problem Set 9 – Due Jan 19,... Version 3: January 18, 2007
... Problem 5b. Also, the explanation of the axis orientation, “At t = 0, the xz plane is normal to the x0 y 0 -plane with the x axis in the first quadrant of the x0 z 0 -plane” is incorrect in an obvious way: the x axis is in the third quadrant of the x0 z 0 -plane at t = 0. Given the late date of thes ...
... Problem 5b. Also, the explanation of the axis orientation, “At t = 0, the xz plane is normal to the x0 y 0 -plane with the x axis in the first quadrant of the x0 z 0 -plane” is incorrect in an obvious way: the x axis is in the third quadrant of the x0 z 0 -plane at t = 0. Given the late date of thes ...
Document
... Analyze motion in different frames of reference (nonaccelerated) Identify the types of forces Distinguish Newton’s Three Laws of Motion Use a Free Body Diagram to solve 1D and 2D problems with forces in equilibrium and non-equilibrium (i.e., acceleration) using Newton’ 1st and 2nd laws. ...
... Analyze motion in different frames of reference (nonaccelerated) Identify the types of forces Distinguish Newton’s Three Laws of Motion Use a Free Body Diagram to solve 1D and 2D problems with forces in equilibrium and non-equilibrium (i.e., acceleration) using Newton’ 1st and 2nd laws. ...
Document
... The objects/bodies in the universe interact via Gravitational Forces and are present everywhere but are very weak. Hence we can neglect these forces. Best Approximation: Intergalatic space Non-Inertial Reference Frame: Is a frame of reference with a changing velocity. The velocity of a frame will ch ...
... The objects/bodies in the universe interact via Gravitational Forces and are present everywhere but are very weak. Hence we can neglect these forces. Best Approximation: Intergalatic space Non-Inertial Reference Frame: Is a frame of reference with a changing velocity. The velocity of a frame will ch ...
PPT
... • Newtonian physics does not allow massless objects. They would always have zero energy and momentum, and would be unobservable. • Now in SR imagine an object with zero invariant mass: E2= c2p2 so E=pc, like for Maxwell’s light. Any object with zero invariant mass moves at the speed of light. Gluons ...
... • Newtonian physics does not allow massless objects. They would always have zero energy and momentum, and would be unobservable. • Now in SR imagine an object with zero invariant mass: E2= c2p2 so E=pc, like for Maxwell’s light. Any object with zero invariant mass moves at the speed of light. Gluons ...
Dynamics: Interactions of Forces
... •The second image shows just the object of interest (the climber) and has vectors drawn representing the different forces on the climber, which are labeled with everyday language. •The third image is a force diagram; the object of interest is simply represented by a dot, and the vectors are labeled ...
... •The second image shows just the object of interest (the climber) and has vectors drawn representing the different forces on the climber, which are labeled with everyday language. •The third image is a force diagram; the object of interest is simply represented by a dot, and the vectors are labeled ...
Lecture 1 Forces on a rotating planet Lecture 2 We will describe the
... relative to the stars appears to move when viewed from the Earth. 2. An object moving at constant velocity relative to the stars seems to change direction when viewed from the rotating Earth. ...
... relative to the stars appears to move when viewed from the Earth. 2. An object moving at constant velocity relative to the stars seems to change direction when viewed from the rotating Earth. ...
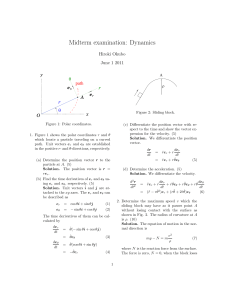
Midterm examination: Dynamics
... 4. The collar A is free to slide along the smooth shaft B mounted in the frame in Fig. 3. The plane of the frame is vertical. Determine the horizontal acceleration a of the frame necessary to maintain the collar in a fixed position on the shaft. (10) Solution. The equations of motion of the collar g ...
... 4. The collar A is free to slide along the smooth shaft B mounted in the frame in Fig. 3. The plane of the frame is vertical. Determine the horizontal acceleration a of the frame necessary to maintain the collar in a fixed position on the shaft. (10) Solution. The equations of motion of the collar g ...
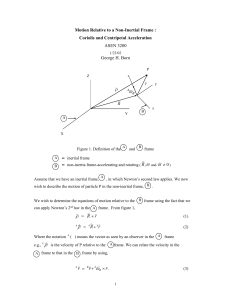
Motion Relative to a non-inertial frame
... In Eq. (19), we have moved the centripetal and Coriolis accelerations to the force side of the equation. In this situation they are referred to as the centripetal and Coriolis apparent forces per unit mass. Hence, the signs of the centripetal and Coriolis apparent forces per unit mass are opposite t ...
... In Eq. (19), we have moved the centripetal and Coriolis accelerations to the force side of the equation. In this situation they are referred to as the centripetal and Coriolis apparent forces per unit mass. Hence, the signs of the centripetal and Coriolis apparent forces per unit mass are opposite t ...
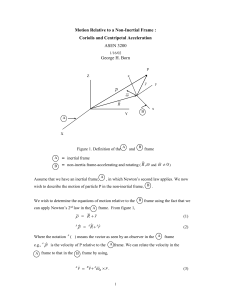
Motion Relative to a non-inertial frame
... In Eq. (19), we have moved the centripetal and Coriolis accelerations to the force side of the equation. In this situation they are referred to as the centripetal and Coriolis apparent forces per unit mass. Hence, the signs of the centripetal and Coriolis apparent forces per unit mass are opposite t ...
... In Eq. (19), we have moved the centripetal and Coriolis accelerations to the force side of the equation. In this situation they are referred to as the centripetal and Coriolis apparent forces per unit mass. Hence, the signs of the centripetal and Coriolis apparent forces per unit mass are opposite t ...
Relative Motion
... This law can be viewed as a specific example of Newton’s second law, F~ = m~a, where F~ = 0. Does this law always holds ? Consider a ball moving in space at a constant velocity, ~v , as viewed by an observer at rest. The ball thus have no forces acting upon it, F~ = 0. Consider now a second observer ...
... This law can be viewed as a specific example of Newton’s second law, F~ = m~a, where F~ = 0. Does this law always holds ? Consider a ball moving in space at a constant velocity, ~v , as viewed by an observer at rest. The ball thus have no forces acting upon it, F~ = 0. Consider now a second observer ...
Chapter 7 Rotating Frames
... which equals mω 2 x (radially outwards) — this is called the “centrifugal force”. As far as the observer in S 0 is concerned, the “centrifugal force” is cancelled by N. The most physically important rotating system is the Earth itself. Our weather patterns are strongly influenced by the Earth’s rota ...
... which equals mω 2 x (radially outwards) — this is called the “centrifugal force”. As far as the observer in S 0 is concerned, the “centrifugal force” is cancelled by N. The most physically important rotating system is the Earth itself. Our weather patterns are strongly influenced by the Earth’s rota ...
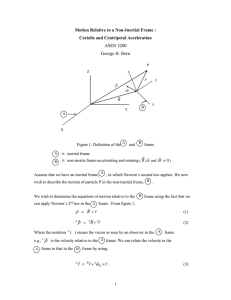
Motion Relative to a non-inertial frame
... In Eq. (19), we have moved the centripetal and Coriolis accelerations to the force side of the equation. In this situation they are referred to as the centripetal and Coriolis apparent forces per unit mass. Hence, the signs of the centripetal and Coriolis apparent forces per unit mass are opposite t ...
... In Eq. (19), we have moved the centripetal and Coriolis accelerations to the force side of the equation. In this situation they are referred to as the centripetal and Coriolis apparent forces per unit mass. Hence, the signs of the centripetal and Coriolis apparent forces per unit mass are opposite t ...