Document
... – A coord system fixed on the Earth is accelerating (Earth’s rotation + orbital motion) & is thus non-inertial! – For many problems, this is not important. For some, we cannot ignore it! ...
... – A coord system fixed on the Earth is accelerating (Earth’s rotation + orbital motion) & is thus non-inertial! – For many problems, this is not important. For some, we cannot ignore it! ...
Need for the General Theory
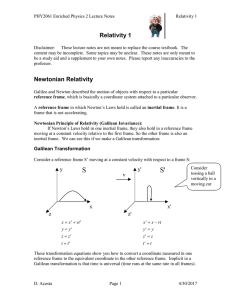
... Newtonian Mechanics and Inertial Frames of Reference Newtonian particle mechanics is based on Newton's laws of motion. Newton's first law may be written: "Reference frames exist in which all free particles have zero acceleration". Here a free particle is defined to be one on which no net force acts. ...
... Newtonian Mechanics and Inertial Frames of Reference Newtonian particle mechanics is based on Newton's laws of motion. Newton's first law may be written: "Reference frames exist in which all free particles have zero acceleration". Here a free particle is defined to be one on which no net force acts. ...
Relativity1
... Maxwell’s Equations. Maxwell’s Equations state that the speed of light is c and only c, but for which reference frame does it refer to? For clarification of the issue, let’s consider sound waves, which are another form of a traveling wave. Sound waves are pressure waves. Pressure is a measure of how ...
... Maxwell’s Equations. Maxwell’s Equations state that the speed of light is c and only c, but for which reference frame does it refer to? For clarification of the issue, let’s consider sound waves, which are another form of a traveling wave. Sound waves are pressure waves. Pressure is a measure of how ...
The Coriolis effect is a deflection of moving objects when
... and long periods of time, such as large-scale movements of air in the atmosphere or water in the ocean. Such motions are constrained by the surface of the earth, so generally only the horizontalcomponent of the Coriolis force is important. This force causes moving objects on the surface of the Earth ...
... and long periods of time, such as large-scale movements of air in the atmosphere or water in the ocean. Such motions are constrained by the surface of the earth, so generally only the horizontalcomponent of the Coriolis force is important. This force causes moving objects on the surface of the Earth ...
Document
... To record the event, each observer uses a reference frame that consists of a coordinate system and a clock. Each observer is at rest relative to her own reference frame. ...
... To record the event, each observer uses a reference frame that consists of a coordinate system and a clock. Each observer is at rest relative to her own reference frame. ...
ATM 316 - Augmentation of Newton`s 2nd law for Earth`s rotation
... A quickie example is provided in the left panel of the figure above. The space-based observer sees the coordinate axis we call east as shifting in time, and this change in direction implies the ...
... A quickie example is provided in the left panel of the figure above. The space-based observer sees the coordinate axis we call east as shifting in time, and this change in direction implies the ...
Frame of Reference
... the car is moving at a constant speed of 30 km/hr rela%ve to a person standing on the sidewalk. In fact, you would say the person on the sidewalk is moving toward or away from you at 30 km/hr! The two frames of reference are the ground and the car. Example 2: You are floa%ng down a river on a ra ...
... the car is moving at a constant speed of 30 km/hr rela%ve to a person standing on the sidewalk. In fact, you would say the person on the sidewalk is moving toward or away from you at 30 km/hr! The two frames of reference are the ground and the car. Example 2: You are floa%ng down a river on a ra ...
PPTX - University of Toronto Physics
... Self-adjusting forces • Gravity, FG, has an equation for it which predicts the correct magnitude (it’s always mg here on Earth). • Normal force, Tension and Static friction are all selfadjusting forces: there is no equation for these!! • Normal force is whatever is needed to keep the object from cr ...
... Self-adjusting forces • Gravity, FG, has an equation for it which predicts the correct magnitude (it’s always mg here on Earth). • Normal force, Tension and Static friction are all selfadjusting forces: there is no equation for these!! • Normal force is whatever is needed to keep the object from cr ...
Newton and Leibniz – Absolute and Relative Motion
... If we transform Newton’s second law to a rotating frame, and we find the centrifugal and Coriolis terms appear. Physicists, as opposed to high school teachers, tend to regard inertial forces as real. After all, they’re indistinguishable from gravity. And they can squash you flat. But a Newtonian mu ...
... If we transform Newton’s second law to a rotating frame, and we find the centrifugal and Coriolis terms appear. Physicists, as opposed to high school teachers, tend to regard inertial forces as real. After all, they’re indistinguishable from gravity. And they can squash you flat. But a Newtonian mu ...
Physics 321 Theoretical Mechanics I
... – They also require an understanding of concepts such as position and time, but those definitions are obvious • …or at least we thought they were – quantum mechanics and relativity have shown otherwise ...
... – They also require an understanding of concepts such as position and time, but those definitions are obvious • …or at least we thought they were – quantum mechanics and relativity have shown otherwise ...
Sects. 4.9 & 4.10
... side & we get: “F” = manoninertial. where “F” = F + terms from coord transformation “Fictitious Forces” ! ...
... side & we get: “F” = manoninertial. where “F” = F + terms from coord transformation “Fictitious Forces” ! ...
The Spring 2013 Qualifying Exam, Part 2
... instantaneously changes the nucleus into He3, which consists of two protons and one neutron. Calculate the probability that the electron remains in the ground state of the new atom. Problem 2: (a) Consider a circular cylinder of radius R and length L, rotating about its symmetry axis with angular ve ...
... instantaneously changes the nucleus into He3, which consists of two protons and one neutron. Calculate the probability that the electron remains in the ground state of the new atom. Problem 2: (a) Consider a circular cylinder of radius R and length L, rotating about its symmetry axis with angular ve ...
CHAPTER XI
... each other can be used as the basis for detecting and describing motion this collection of objects is called reference system - the most common reference system: Earth - example of other reference systems…. - describing motion in a given reference system Motions viewed in different Reference Syste ...
... each other can be used as the basis for detecting and describing motion this collection of objects is called reference system - the most common reference system: Earth - example of other reference systems…. - describing motion in a given reference system Motions viewed in different Reference Syste ...
MATH10222, Chapter 4: Frames of Reference 1 Motion relative to a
... Quite often a particle will be referred to as being ‘weightless’ when in fact it is still being acted upon by a gravitational acceleration. This is commonly the case in non-inertial frames of reference where the ‘observer’ and the particle are both in free fall. For example, consider a particle P of ...
... Quite often a particle will be referred to as being ‘weightless’ when in fact it is still being acted upon by a gravitational acceleration. This is commonly the case in non-inertial frames of reference where the ‘observer’ and the particle are both in free fall. For example, consider a particle P of ...
Chapter_6_In-class_problems_(section_by_section_notes)
... arc of radius 100 meters while the dip in the road is a part of a circular arc of radius 150 meters. In both variable form and as a numerical answer, find… a) the apparent weight of the car at the top of the bump. b) the apparent weight of the car at the bottom of the dip. 3. The same 2000 kg car hi ...
... arc of radius 100 meters while the dip in the road is a part of a circular arc of radius 150 meters. In both variable form and as a numerical answer, find… a) the apparent weight of the car at the top of the bump. b) the apparent weight of the car at the bottom of the dip. 3. The same 2000 kg car hi ...
Frames of Reference Apparent Forces
... center of earth; gravity is not, except at poles and equator. ...
... center of earth; gravity is not, except at poles and equator. ...
Non-Inertial Frames
... We are now going to discuss accelerating frames where the non-inertial frame is rotating (relative to the inertial frames). Before we can discuss these, we must introduce some concepts and notation for handling rotation. Many rotation problems involve axes fixed in a rigid body (e.g. the rotation of ...
... We are now going to discuss accelerating frames where the non-inertial frame is rotating (relative to the inertial frames). Before we can discuss these, we must introduce some concepts and notation for handling rotation. Many rotation problems involve axes fixed in a rigid body (e.g. the rotation of ...
Homework 6
... It is important to understand that the effects of special relativity are in no way due to the fact that light travels at a finite speed, but rather due to the fact that the speed of light is the same finite quantity in any inertial reference frame. We can always take into account the time it takes f ...
... It is important to understand that the effects of special relativity are in no way due to the fact that light travels at a finite speed, but rather due to the fact that the speed of light is the same finite quantity in any inertial reference frame. We can always take into account the time it takes f ...
Relativity 1 - UCF College of Sciences
... However, the S’ observer measured and additional force due to the magnetic field at y1’ arising from the motion of the wire in the -x’ direction. Thus, the electromagnetic force does not have the same form in different inertial systems, implying that Maxwell’s equations are not invariant under a Gal ...
... However, the S’ observer measured and additional force due to the magnetic field at y1’ arising from the motion of the wire in the -x’ direction. Thus, the electromagnetic force does not have the same form in different inertial systems, implying that Maxwell’s equations are not invariant under a Gal ...
Inertial and Non-inertial Reference Frames
... discussed within the context of the 3rd Law. According to the 3rd law, every force is actually a two-way interaction. In the example above, if a force does truly push on the cup, then the cup must also push back on something else (whatever is causing the cup to accelerate). However, since there are ...
... discussed within the context of the 3rd Law. According to the 3rd law, every force is actually a two-way interaction. In the example above, if a force does truly push on the cup, then the cup must also push back on something else (whatever is causing the cup to accelerate). However, since there are ...