SANS
... Classified as either direct or indirect acting agents. Direct acting drugs act directly on the parasympathetic receptors (Eg. Pilocarpine acts on Nicotinic). Indirect acting drugs either cause release of neurotransmitter which then goes to the receptor site OR they inhibit the enzyme cholinest ...
... Classified as either direct or indirect acting agents. Direct acting drugs act directly on the parasympathetic receptors (Eg. Pilocarpine acts on Nicotinic). Indirect acting drugs either cause release of neurotransmitter which then goes to the receptor site OR they inhibit the enzyme cholinest ...
Motivation - HomePage Server for UT Psychology
... • Activate the sympathetic nervous system • Interfere with the normal reuptake of dopamine by the releasing neuron • Some stimulants also increase the release of dopamine • Caffeine, cocaine, amphetamines ...
... • Activate the sympathetic nervous system • Interfere with the normal reuptake of dopamine by the releasing neuron • Some stimulants also increase the release of dopamine • Caffeine, cocaine, amphetamines ...
illegal drugs
... Substance abuse includes the use of illegal substances, as well as the misuse of legal substances Factors that influence teens o Peer pressure o Family members o Role models o Media messages o Perceptions of drug behavior o Misleading information How drugs affect your health o Physical health ...
... Substance abuse includes the use of illegal substances, as well as the misuse of legal substances Factors that influence teens o Peer pressure o Family members o Role models o Media messages o Perceptions of drug behavior o Misleading information How drugs affect your health o Physical health ...
NERVOUS SYSTEM - Spring Branch ISD
... 12. The skeleton is divided into two parts: List the name and function of each a. b. 13. Label the 3 types of muscle tissue below: ...
... 12. The skeleton is divided into two parts: List the name and function of each a. b. 13. Label the 3 types of muscle tissue below: ...
Chapter 13-Toxicology
... and “glue sniffing” (toluene, gasoline, freon, etc.) - all effect central nervous system. Major problems chemical eposures cause permanent liver, kidney, heart and brain damage. ...
... and “glue sniffing” (toluene, gasoline, freon, etc.) - all effect central nervous system. Major problems chemical eposures cause permanent liver, kidney, heart and brain damage. ...
Opioid Presentation pt2(updated) [Read
... Metoclopramide (Maxalon) acts centrally at dopamine receptors and has prokinetic action on gut to increase drug absorption. (useful in migraine) Also has some effect at 5HT3 receptor sites. Most commonly used and least effective anti emetic(some studies indicate little better than placebo). ...
... Metoclopramide (Maxalon) acts centrally at dopamine receptors and has prokinetic action on gut to increase drug absorption. (useful in migraine) Also has some effect at 5HT3 receptor sites. Most commonly used and least effective anti emetic(some studies indicate little better than placebo). ...
HST-151 Final Exam p
... 12. The medicinal chemistry department of your company has come up with a statin that is 10x more potent than atorvastatin and twice as efficacious. Does this sound like a promising drug for development? Explain [5] Probably not, since lack of potency and efficacy aren’t the major drawbacks for exis ...
... 12. The medicinal chemistry department of your company has come up with a statin that is 10x more potent than atorvastatin and twice as efficacious. Does this sound like a promising drug for development? Explain [5] Probably not, since lack of potency and efficacy aren’t the major drawbacks for exis ...
BuSpar (buspirone)
... BuSpar’s effectiveness for treating anxiety may be explained by its pharmacological action in the brain at specific receptor sites. Receptors are specific sites on the nerve cell membrane that receive a signal from a neurochemical called the neurotransmitter. Once a neurotransmitter locks in on the ...
... BuSpar’s effectiveness for treating anxiety may be explained by its pharmacological action in the brain at specific receptor sites. Receptors are specific sites on the nerve cell membrane that receive a signal from a neurochemical called the neurotransmitter. Once a neurotransmitter locks in on the ...
THE UNIVERSITY OF AUCKLAND
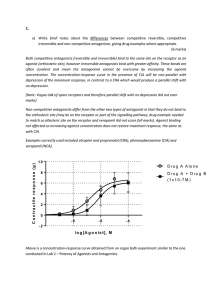
... a) Write brief notes about the differences between competitive reversible, competitive irreversible and non-competitive antagonism, giving drug examples where appropriate. (6 marks) Both competitive antagonists (reversible and irreversible) bind to the same site on the receptor as an agonist (orthos ...
... a) Write brief notes about the differences between competitive reversible, competitive irreversible and non-competitive antagonism, giving drug examples where appropriate. (6 marks) Both competitive antagonists (reversible and irreversible) bind to the same site on the receptor as an agonist (orthos ...
UNESCO Course on Benefit and Harm CASE STUDY: USE OF NEW
... and effective cancer drug, but various proponents of the drug have claimed that it can cure or control the spread of cancer, or at least can mitigate the symptoms of the disease without curing it. This drug has not been approved by the Food and Drug Administration or the National Cancer Society. It ...
... and effective cancer drug, but various proponents of the drug have claimed that it can cure or control the spread of cancer, or at least can mitigate the symptoms of the disease without curing it. This drug has not been approved by the Food and Drug Administration or the National Cancer Society. It ...
cholinergic agonists - Nursing Pharmacology
... her memory. The patient has a history of arthritis, type 2 diabetes, thyroid disease, and hypertension. She is currently taking NSAIDs for arthritis, oral antidiabetic medications, thyroid replacement hormone, and a beta blocker for blood pressure. What potential adverse effect from the gingko would ...
... her memory. The patient has a history of arthritis, type 2 diabetes, thyroid disease, and hypertension. She is currently taking NSAIDs for arthritis, oral antidiabetic medications, thyroid replacement hormone, and a beta blocker for blood pressure. What potential adverse effect from the gingko would ...
Antidepressant drugs - Dr Lynch
... Disability adjusted life years All causes Unipolar major depression Iron deficiency anaemia Falls Alcohol use COPD Bipolar disorder Congenital anomalies Osteoarthritis Schizophrenia Obsessive compulsive disorders ...
... Disability adjusted life years All causes Unipolar major depression Iron deficiency anaemia Falls Alcohol use COPD Bipolar disorder Congenital anomalies Osteoarthritis Schizophrenia Obsessive compulsive disorders ...
Depression and Suicide
... Disability adjusted life years All causes Unipolar major depression Iron deficiency anaemia Falls Alcohol use COPD Bipolar disorder Congenital anomalies Osteoarthritis Schizophrenia Obsessive compulsive disorders ...
... Disability adjusted life years All causes Unipolar major depression Iron deficiency anaemia Falls Alcohol use COPD Bipolar disorder Congenital anomalies Osteoarthritis Schizophrenia Obsessive compulsive disorders ...
CH4 part 2
... Animals with less protein have more free drug. This may allow the drug to be excreted before it has time to take effect. ...
... Animals with less protein have more free drug. This may allow the drug to be excreted before it has time to take effect. ...
Addiction
... Incentive Sensitization • Drug-induced sensitization of brain systems (DA) that mediate incentive-salience causes drugs and drugassociated stimuli to become compulsively “wanted” • The activation of the sensitized system can occur both implicitly or explicitly • These systems can be dissociated fro ...
... Incentive Sensitization • Drug-induced sensitization of brain systems (DA) that mediate incentive-salience causes drugs and drugassociated stimuli to become compulsively “wanted” • The activation of the sensitized system can occur both implicitly or explicitly • These systems can be dissociated fro ...
Ch1 and 2 student
... Precautions, warnings, and contraindications (ADR) How to treat an overdose Dosage and administration Pharmacology (Pharmacodynamics and Pharmacokinetics) ...
... Precautions, warnings, and contraindications (ADR) How to treat an overdose Dosage and administration Pharmacology (Pharmacodynamics and Pharmacokinetics) ...
Adverse_Reactions_Slideshow
... • Significant untoward risks, costs, and increased hospital stays associated with ADRs • Allergy, atopy, or asthma pts have been suggested to be at an increased risk • Antibiotics, blood products, drug preservatives and polypeptides may be associated with a higher incidence of reactions • Drug avoid ...
... • Significant untoward risks, costs, and increased hospital stays associated with ADRs • Allergy, atopy, or asthma pts have been suggested to be at an increased risk • Antibiotics, blood products, drug preservatives and polypeptides may be associated with a higher incidence of reactions • Drug avoid ...
SOC 12 - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... A. Physiological Effects - Alcohol is absorbed through the stomach & small intestine into the blood stream, then distributed throughout the body; this small chemical messenger easily crosses the blood/brain barrier. In the brain, alcohol depresses functioning of the reticular formation (a.k.a. retic ...
... A. Physiological Effects - Alcohol is absorbed through the stomach & small intestine into the blood stream, then distributed throughout the body; this small chemical messenger easily crosses the blood/brain barrier. In the brain, alcohol depresses functioning of the reticular formation (a.k.a. retic ...
Pharmacological Treatment of Alcoholism: Has Something New
... such as heroin. When taken orally does not produce “high” and allows individual to function. Adequate dose important, > 80 mg/d. Clearly shown to reduce relapse to heroin use, reduce HIV transmission and ...
... such as heroin. When taken orally does not produce “high” and allows individual to function. Adequate dose important, > 80 mg/d. Clearly shown to reduce relapse to heroin use, reduce HIV transmission and ...
biological treatments for schizophrenia gapfill
... relieve the...................... symptoms of schizophrenia and subsequently used in the treatment of schizophrenia. C............................... antipsychotics are more commonly administered and .................................. antipsychotics were later developed which are believed to be more ...
... relieve the...................... symptoms of schizophrenia and subsequently used in the treatment of schizophrenia. C............................... antipsychotics are more commonly administered and .................................. antipsychotics were later developed which are believed to be more ...
movement disorders and ataxia
... 1. DA receptors: a. D1 receptors: Cause vasodilation. b. D2 receptors: inhibit sympathetic transmission, inhibit prolactin release, cause vomiting. c. D3, 4, 5 receptors: Less well-characterized; limbic more than motor effects. 2. DA agonists: Used for Parkinson’s disease, alertness disorders. a. Le ...
... 1. DA receptors: a. D1 receptors: Cause vasodilation. b. D2 receptors: inhibit sympathetic transmission, inhibit prolactin release, cause vomiting. c. D3, 4, 5 receptors: Less well-characterized; limbic more than motor effects. 2. DA agonists: Used for Parkinson’s disease, alertness disorders. a. Le ...