esca studies of core and valence electrons in gases and solids
... The 32 valence electrons in CF, are distributed among 16 molecular orbitals but due to the high symmetry of the molecule several of these orbitals are degenerate and only 7 different ionization energies are observable in the valence electron spectrum. Three of these states have previously been studi ...
... The 32 valence electrons in CF, are distributed among 16 molecular orbitals but due to the high symmetry of the molecule several of these orbitals are degenerate and only 7 different ionization energies are observable in the valence electron spectrum. Three of these states have previously been studi ...
1 | Page Chemistry Lecture #35 Chemistry Lecture #35: Names and
... Fe2+ and Fe3+ could each be called “iron cation” but this name does not distinguish the two. numerals. ...
... Fe2+ and Fe3+ could each be called “iron cation” but this name does not distinguish the two. numerals. ...
Energy and Inorganic Chemistry
... solar electricity provides only approximately 1 millionth of the total electricity supply, and renewable biomass provides less than 0.1% of the total energy consumed. The huge gap between our present use of solar energy and its enormous undeveloped potential defines a grand challenge in energy resea ...
... solar electricity provides only approximately 1 millionth of the total electricity supply, and renewable biomass provides less than 0.1% of the total energy consumed. The huge gap between our present use of solar energy and its enormous undeveloped potential defines a grand challenge in energy resea ...
Synthesis [UO (HMBUD)] ,[UO
... Schiff bases have often been used as chelating ligands in the field of coordination chemistry and their metal complexes are of great interest for many years. It is well known that N and S atoms play a key role in the coordination of metals at the active sites of numerous metallobiomolecules [1]. Sch ...
... Schiff bases have often been used as chelating ligands in the field of coordination chemistry and their metal complexes are of great interest for many years. It is well known that N and S atoms play a key role in the coordination of metals at the active sites of numerous metallobiomolecules [1]. Sch ...
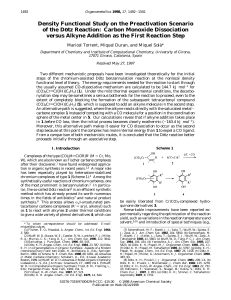
Density Functional Study on the Preactivation Scenario of the
... would be the insertion of an alkyne ligand into the metal coordination sphere prior to CO elimination (associative mechanism). Such a mechanism is not unknown in the field of transition-metal chemistry; e.g., carbonylmetal complexes with a 17-VE shell such as V(CO)6 undergo substitution via an assoc ...
... would be the insertion of an alkyne ligand into the metal coordination sphere prior to CO elimination (associative mechanism). Such a mechanism is not unknown in the field of transition-metal chemistry; e.g., carbonylmetal complexes with a 17-VE shell such as V(CO)6 undergo substitution via an assoc ...
Coordination Number 2 - Department of Chemistry, UWI, Mona
... file://C:\WWW\Courses\C10Kcoordnum.html ...
... file://C:\WWW\Courses\C10Kcoordnum.html ...
draft material draft material - Pearson Schools and FE Colleges
... Although it is often useful to think about diagrams like this, when writing equations it is more usual to abbreviate them. The example above would be shown as [Fe(H2O)6]2+. Notice that the square brackets and the position of the charge are the same in this abbreviated form. These water molecules, an ...
... Although it is often useful to think about diagrams like this, when writing equations it is more usual to abbreviate them. The example above would be shown as [Fe(H2O)6]2+. Notice that the square brackets and the position of the charge are the same in this abbreviated form. These water molecules, an ...
Corynebactin and Enterobactin: Related Siderophores of Opposite
... The major role of siderophores in microbial iron transport and bacterial pathogenicity is now well established.1 These low molecular weight chelators are expressed to overcome the insolubility of Fe3+ at pH 7 (∼10-18 M).2 The ferric complexes enter the bacterial cell via specific receptor proteins o ...
... The major role of siderophores in microbial iron transport and bacterial pathogenicity is now well established.1 These low molecular weight chelators are expressed to overcome the insolubility of Fe3+ at pH 7 (∼10-18 M).2 The ferric complexes enter the bacterial cell via specific receptor proteins o ...
b - PianetaChimica
... Fiona, an earnest young analytical chemist, decided to make some 0.500 mol L–1 vanadous sulfate (VSO4) solution. She had a bottle of vanadyl sulfate (VOSO4.2H2O), which she stirred with an excess of zinc metal (amalgamated with a small amount of mercury(II) catalyst). Since it was getting late, Fion ...
... Fiona, an earnest young analytical chemist, decided to make some 0.500 mol L–1 vanadous sulfate (VSO4) solution. She had a bottle of vanadyl sulfate (VOSO4.2H2O), which she stirred with an excess of zinc metal (amalgamated with a small amount of mercury(II) catalyst). Since it was getting late, Fion ...
Blue_Solids_LO
... 3. YIn1-xMnxO3is made by a common procedure for the synthesis of thermodynamically stable solid state materials. Describe how these materials are made. Why do you think this method produces thermodynamically stable materials? 4. How is the hexagonal YMnO3 structure similar to and different from the ...
... 3. YIn1-xMnxO3is made by a common procedure for the synthesis of thermodynamically stable solid state materials. Describe how these materials are made. Why do you think this method produces thermodynamically stable materials? 4. How is the hexagonal YMnO3 structure similar to and different from the ...
296
... that bent uranyl complexes exist.12,13 Not only do our calculations indicate that there are minima on the UO2(OH)2 potential energy surface corresponding to bent uranyl complexes but our results suggest that these compounds, 2a and 2b, may be accessible at high temperatures. Isomerization Reactions. ...
... that bent uranyl complexes exist.12,13 Not only do our calculations indicate that there are minima on the UO2(OH)2 potential energy surface corresponding to bent uranyl complexes but our results suggest that these compounds, 2a and 2b, may be accessible at high temperatures. Isomerization Reactions. ...
Coordination Compounds (NCERT)
... formed when the carbonyl carbon donates a lone pair of electrons to the vacant orbital of the metal. A π bond is formed by the donation of a pair of electrons from the filled metal d orbital into the vacant anti-bonding π* orbital (also known as back bonding of thecarbonyl group). The σ bond strengt ...
... formed when the carbonyl carbon donates a lone pair of electrons to the vacant orbital of the metal. A π bond is formed by the donation of a pair of electrons from the filled metal d orbital into the vacant anti-bonding π* orbital (also known as back bonding of thecarbonyl group). The σ bond strengt ...
Organic Chemistry
... • The attraction of anions and cations leads to the formation of ionic solids. This ionic interaction is often referred to as an ionic bond. • An atom may share electrons with one or more atoms to complete its valence shell; a chemical bond formed by sharing electrons is called a covalent bond. Bond ...
... • The attraction of anions and cations leads to the formation of ionic solids. This ionic interaction is often referred to as an ionic bond. • An atom may share electrons with one or more atoms to complete its valence shell; a chemical bond formed by sharing electrons is called a covalent bond. Bond ...
Spin crossover

Spin Crossover (SCO), sometimes referred to as spin transition or spin equilibrium behavior, is a phenomenon that occurs in some metal complexes wherein the spin state of the complex changes due to external stimuli such as a variation of temperature, pressure, light irradiation or an influence of a magnetic field.With regard to a ligand field and ligand field theory, the change in spin state is a transition from a low spin (LS) ground state electron configuration to a high spin (HS) ground state electron configuration of the metal’s d atomic orbitals (AOs), or vice versa. The magnitude of the ligand field splitting along with the pairing energy of the complex determines whether it will have a LS or HS electron configuration. A LS state occurs because the ligand field splitting (Δ) is greater than the pairing energy of the complex (which is an unfavorable process).Figure 1 is a simplified illustration of the metal’s d orbital splitting in the presence of an octahedral ligand field. A large splitting between the t2g and eg AOs requires a substantial amount of energy for the electrons to overcome the energy gap (Δ) to comply with Hund’s Rule. Therefore, electrons will fill the lower energy t2g orbitals completely before populating the higher energy eg orbitals. Conversely, a HS state occurs with weaker ligand fields and smaller orbital splitting. In this case the energy required to populate the higher levels is substantially less than the pairing energy and the electrons fill the orbitals according to Hund’s Rule by populating the higher energy orbitals before pairing with electrons in the lower lying orbitals. An example of a metal ion that can exist in either a LS or HS state is Fe3+ in an octahedral ligand field. Depending on the ligands that are coordinated to this complex the Fe3+ can attain a LS or a HS state, as in Figure 1.Spin crossover refers to the transitions between high to low, or low to high, spin states. This phenomenon is commonly observed with some first row transition metal complexes with a d4 through d7 electron configuration in an octahedral ligand geometry. Spin transition curves are a common representation of SCO phenomenon with the most commonly observed types depicted in Figure 2 in which γHS (the high-spin molar fraction) is plotted vs. T. The figure shows a gradual spin transition (left), an abrupt transition with hysteresis (middle) and a two-step transition (right). For a transition to be considered gradual, it typically takes place over a large temperature range, even up to several hundred K, whereas for a transition to be considered abrupt, it should take place within 10 K or less.These curves indicate that a spin transition has occurred in a metal complex as temperature changed. The gradual transition curve is an indication that not all metal centers within the complex are undergoing the transition at the same temperature. The abrupt spin change with hysteresis indicates a strong cooperativity, or “communication”, between neighboring metal complexes. In the latter case, the material is bistable and can exist in the two different spin states with a different range of external stimuli (temperature in this case) for the two phenomena, namely LS → HS and HS → LS. The two-step transition is relatively rare but is observed, for example, with dinuclear SCO complexes for which the spin transition in one metal center renders the transition in the second metal center less favorable.There are several types of spin crossover that can occur in a complex; some of them are light induced excited state spin trapping (LIESST), ligand-driven light induced spin change (LD-LISC), and charge transfer induced spin transition (CTIST).




![Synthesis [UO (HMBUD)] ,[UO](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008903642_1-f363073bed72529363e14045dbcef517-300x300.png)