Analyzed by Symptoms and history Diagnosis 1. Walking down a
... specific part of Johnny’s brain might have resulted in an inability of the brain to regulate normal alertness? ...
... specific part of Johnny’s brain might have resulted in an inability of the brain to regulate normal alertness? ...
The Brain - PSYCHOUT
... spinal cord, brain stem, cerebellum and parts of the cerebrum to the cerebral cortex. Sensory information entering the body through the eyes, ears, or skin travels in the form of spikes to the thalamus, in the centre of the brain. Filters information and passes it along, as more spikes, to the corte ...
... spinal cord, brain stem, cerebellum and parts of the cerebrum to the cerebral cortex. Sensory information entering the body through the eyes, ears, or skin travels in the form of spikes to the thalamus, in the centre of the brain. Filters information and passes it along, as more spikes, to the corte ...
optional biology 1 study packet the brain
... motor fibers extending from the cerebrum. These fibers cross each other in this area of the brain stem and results in the right half of the brain controlling the left side of the body and the left half of the brain controlling the right side of the body. The Medulla Oblongata contains vital clusters ...
... motor fibers extending from the cerebrum. These fibers cross each other in this area of the brain stem and results in the right half of the brain controlling the left side of the body and the left half of the brain controlling the right side of the body. The Medulla Oblongata contains vital clusters ...
Psychology 10th Edition David Myers
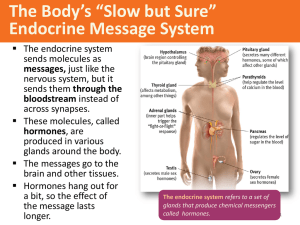
... messages, just like the nervous system, but it sends them through the bloodstream instead of across synapses. These molecules, called hormones, are produced in various glands around the body. The messages go to the brain and other tissues. Hormones hang out for a bit, so the effect of the mess ...
... messages, just like the nervous system, but it sends them through the bloodstream instead of across synapses. These molecules, called hormones, are produced in various glands around the body. The messages go to the brain and other tissues. Hormones hang out for a bit, so the effect of the mess ...
Alcohol on the nervous system
... liver and other organs. • The cells become weaker to alcohol. These unhealthy cells weaken the nervous system a lot. Also, the high tolerance level of a person to the alcohol, makes him more prone to various kinds of infections. Severe consequences like - heart attacks, brain strokes and dementia ma ...
... liver and other organs. • The cells become weaker to alcohol. These unhealthy cells weaken the nervous system a lot. Also, the high tolerance level of a person to the alcohol, makes him more prone to various kinds of infections. Severe consequences like - heart attacks, brain strokes and dementia ma ...
Cognitive neuroscience
... Neuroscientists have to discover neural mechanisms that implement computational processes from psychological level → Autonomy of psychology • Piccinini - “Nature has been uncooperative with this approach.” = There has been impossible to discover implementation • Neural networks are unable to help th ...
... Neuroscientists have to discover neural mechanisms that implement computational processes from psychological level → Autonomy of psychology • Piccinini - “Nature has been uncooperative with this approach.” = There has been impossible to discover implementation • Neural networks are unable to help th ...
Lecture 1 (Neuroscience History)
... He saw the effects of brain and spinal injuries. By poking on the brain he noticed that the front was soft and back was hard, and concluded that the front dealt with memories and back dealt with movement. He dissected sheep brains and noted they had hollow cavities ...
... He saw the effects of brain and spinal injuries. By poking on the brain he noticed that the front was soft and back was hard, and concluded that the front dealt with memories and back dealt with movement. He dissected sheep brains and noted they had hollow cavities ...
glossary - HBO.com
... Cerebral cortex—the outermost layer of the cerebral hemispheres sometimes referred to as the gray matter. It is composed of neurons and nerve fibers and associated support cells called glia. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)—the fluid found in and around the brain and spinal cord. Its function is to transpo ...
... Cerebral cortex—the outermost layer of the cerebral hemispheres sometimes referred to as the gray matter. It is composed of neurons and nerve fibers and associated support cells called glia. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)—the fluid found in and around the brain and spinal cord. Its function is to transpo ...
Chapter 51 Disorders of Brain Function
... • Most small aneurysms are asymptomatic. • Large aneurysms may cause chronic headache, neurologic deficits, or both. • Other manifestations include signs of meningeal irritation, cranial nerve deficits, stroke syndrome, cerebral edema and increased ICP, and pituitary dysfunction. • Hypertension and ...
... • Most small aneurysms are asymptomatic. • Large aneurysms may cause chronic headache, neurologic deficits, or both. • Other manifestations include signs of meningeal irritation, cranial nerve deficits, stroke syndrome, cerebral edema and increased ICP, and pituitary dysfunction. • Hypertension and ...
Deanne Boules presentation pdf
... • The scientific study of the nervous system • Traditionally seen as a branch of biology • Currently an interdisciplinary science that collaborates with other fields such as chemistry, cognitive science, computer science, engineering, linguistics, mathematics, medicine, genetics and applied discipli ...
... • The scientific study of the nervous system • Traditionally seen as a branch of biology • Currently an interdisciplinary science that collaborates with other fields such as chemistry, cognitive science, computer science, engineering, linguistics, mathematics, medicine, genetics and applied discipli ...
Behavioral Neuroscience
... More intelligent animals have increased “uncommitted” or association areas of the cortex. ...
... More intelligent animals have increased “uncommitted” or association areas of the cortex. ...
Chapter 1 lec 1
... This happened even when the nerve and muscle were separated from the rest of the body Brain did not inflate muscles with fluids ...
... This happened even when the nerve and muscle were separated from the rest of the body Brain did not inflate muscles with fluids ...
Building the Brain - Urban Child Institute
... years that the brain demonstrates its greatest plasticity. ...
... years that the brain demonstrates its greatest plasticity. ...
Glossary
... The largest and most complicated region of the brain, encompassing a variety of structures, including the thalamus, hypothalamus, limbic system, and cerebrum. ...
... The largest and most complicated region of the brain, encompassing a variety of structures, including the thalamus, hypothalamus, limbic system, and cerebrum. ...
The History and Scope of Psychology Module 1
... hemispheric differences in mental abilities. A number of brain scan studies show normal individuals engage their right brain when completing a perceptual task and their left brain when carrying out a linguistic task. ...
... hemispheric differences in mental abilities. A number of brain scan studies show normal individuals engage their right brain when completing a perceptual task and their left brain when carrying out a linguistic task. ...
05First2yearsBiosocial
... • What are some of the basic immunizations a child should receive? • How do the risks from disease relate to the risks from immunization? • What is the difference between colostrum and milk? ...
... • What are some of the basic immunizations a child should receive? • How do the risks from disease relate to the risks from immunization? • What is the difference between colostrum and milk? ...
Lecture 2b - Rio Hondo College
... Eating, drinking, sex, circadian rhythms, temperature control Emotional behavior Fight or flight responses Termed a “pleasure center” ...
... Eating, drinking, sex, circadian rhythms, temperature control Emotional behavior Fight or flight responses Termed a “pleasure center” ...
Now!
... c. Discuss the effect of the endocrine system on behavior. d. Describe the nervous system and its subdivisions and functions: — central and peripheral nervous systems; — major brain regions, lobes, and cortical areas; — brain lateralization and hemispheric specialization. e. Discuss the role of neur ...
... c. Discuss the effect of the endocrine system on behavior. d. Describe the nervous system and its subdivisions and functions: — central and peripheral nervous systems; — major brain regions, lobes, and cortical areas; — brain lateralization and hemispheric specialization. e. Discuss the role of neur ...
File
... cortex that are not involved in primary motor or sensory functions. They are involved in higher mental functions such as learning remembering, thinking and speaking. ...
... cortex that are not involved in primary motor or sensory functions. They are involved in higher mental functions such as learning remembering, thinking and speaking. ...
Brain, Consciousness and free will Idan Segev
... consciousness. If they might not have---minds." "Don't get fantastic," snorted the scientist. "But how do you know?" persisted the visitor. "Look, your feedback arrangement is closely analogous to a human nervous system. How do you know that your individual computers, even if they are constrained by ...
... consciousness. If they might not have---minds." "Don't get fantastic," snorted the scientist. "But how do you know?" persisted the visitor. "Look, your feedback arrangement is closely analogous to a human nervous system. How do you know that your individual computers, even if they are constrained by ...
Parts of a Neuron
... Adrenal glands consist of the adrenal medulla and the cortex. The medulla secretes hormones (epinephrine and norepinephrine) during stressful and emotional situations, while the adrenal cortex regulates salt and carbohydrate ...
... Adrenal glands consist of the adrenal medulla and the cortex. The medulla secretes hormones (epinephrine and norepinephrine) during stressful and emotional situations, while the adrenal cortex regulates salt and carbohydrate ...
The Brain
... A. It separates positive ions and places them all inside the axon. B. It is responsible for keeping the axon charged by returning and keeping sodium ions outside the axon membrane. C. It generates an electrical current when the positive ions rush into the axon. D. It generates an electrical current ...
... A. It separates positive ions and places them all inside the axon. B. It is responsible for keeping the axon charged by returning and keeping sodium ions outside the axon membrane. C. It generates an electrical current when the positive ions rush into the axon. D. It generates an electrical current ...
File
... Sleep is a state in which external stimuli are received but not consciously perceived Sleep is also an active state Although sleep is essential for survival, we still know very little about its function, one hypothesis is that sleep and dreams are involved in consolidating learning and memory The co ...
... Sleep is a state in which external stimuli are received but not consciously perceived Sleep is also an active state Although sleep is essential for survival, we still know very little about its function, one hypothesis is that sleep and dreams are involved in consolidating learning and memory The co ...
Unit 3 "Cliff Notes" Review
... In particular, it studies the evolution of behavior and mind using principles of natural selection. Traits that contribute to reproduction and survival are more likely to be passed on. 15.2 – An Evolutionary Explanation of Human Sexuality Gender Differences in Sexuality Males and females, to a large ...
... In particular, it studies the evolution of behavior and mind using principles of natural selection. Traits that contribute to reproduction and survival are more likely to be passed on. 15.2 – An Evolutionary Explanation of Human Sexuality Gender Differences in Sexuality Males and females, to a large ...
Nervous System Outline
... b. Motor - As information is carried to muscles and glands in order to have a response, it must travel along motor neurons. They carry motor, or movement, information away from the CNS. 1-Somatic - If that motor information is going to skeletal muscles, such as a Biceps muscle, it travels in a somat ...
... b. Motor - As information is carried to muscles and glands in order to have a response, it must travel along motor neurons. They carry motor, or movement, information away from the CNS. 1-Somatic - If that motor information is going to skeletal muscles, such as a Biceps muscle, it travels in a somat ...