Class X Episode 5 A. P State HUMAN NERVOUS SYSTEM The
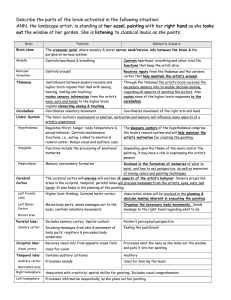
... Let us now examine each part of the brain. 1. Fore Brain – Cerebrum The cerebrum is the largest part of brain and is made up of two halves. Each half of cerebrum is known as Cerebral hemispere The two hemispheres are connected by a sheet of nerve fibres known as Corpus Collusum The wall of cerebrum ...
... Let us now examine each part of the brain. 1. Fore Brain – Cerebrum The cerebrum is the largest part of brain and is made up of two halves. Each half of cerebrum is known as Cerebral hemispere The two hemispheres are connected by a sheet of nerve fibres known as Corpus Collusum The wall of cerebrum ...
signals in a storm - Columbia University
... molecules, one neuron communicates with anthe volume in this region of the brain is nothing other by spitting out chemical neurotransmitbut the space between neighboring cells— ters that carry its message across a thin gap to space through which neurotransmitters can apa receptive surface on its par ...
... molecules, one neuron communicates with anthe volume in this region of the brain is nothing other by spitting out chemical neurotransmitbut the space between neighboring cells— ters that carry its message across a thin gap to space through which neurotransmitters can apa receptive surface on its par ...
The use of Models - NAU jan.ucc.nau.edu web server
... • The study of human thought, using all available scientific techniques and including all relevant scientific disciplines for exploring and investigating cognition. ...
... • The study of human thought, using all available scientific techniques and including all relevant scientific disciplines for exploring and investigating cognition. ...
Brain Facts
... – paralysis – crippling disease involving permanent damage to motor control areas of the brain ...
... – paralysis – crippling disease involving permanent damage to motor control areas of the brain ...
Summary of: Stevens, Alison P. "Learning Rewires the Brain
... make it easier, but it actually changes the brain. Exactly how these processes happen though is still unknown, however scientists have known that the brain continues to develop up through our adolescence to adulthood. What we have learned is that our brain never stops growing even when it is fully m ...
... make it easier, but it actually changes the brain. Exactly how these processes happen though is still unknown, however scientists have known that the brain continues to develop up through our adolescence to adulthood. What we have learned is that our brain never stops growing even when it is fully m ...
Know Your Brain
... degenerative diseases of adult life (such as Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease), metabolic diseases (such as Gaucher’s disease), cerebrovascular diseases (such as stroke and vascular dementia), trauma (such as ...
... degenerative diseases of adult life (such as Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease), metabolic diseases (such as Gaucher’s disease), cerebrovascular diseases (such as stroke and vascular dementia), trauma (such as ...
Design Overview - Computer Science & Engineering
... Graphical User Interface for easy construction of brain models and simulation parameters Web based application for easy access from any location or ...
... Graphical User Interface for easy construction of brain models and simulation parameters Web based application for easy access from any location or ...
Nervous and Endocrine Systems
... Midbrain and Pons = pathways connecting various parts of the brain with each other Medulla = controls involuntary actions ...
... Midbrain and Pons = pathways connecting various parts of the brain with each other Medulla = controls involuntary actions ...
Bio Bases 2014 - Doral Academy Preparatory
... Cerebellum located on the bottom rear of the brain Literally means little brain Coordinates some habitual muscle movements, such as tracking objects in space and playing a musical instrument o Midbrain Coordinates simple movements with sensory information Located above the hindbrain, but ...
... Cerebellum located on the bottom rear of the brain Literally means little brain Coordinates some habitual muscle movements, such as tracking objects in space and playing a musical instrument o Midbrain Coordinates simple movements with sensory information Located above the hindbrain, but ...
Neurons and the Brain
... It’s the most common neurotransmitter. It is located in both the central nervous and peripheral nervous system. It acts on basic autonomic and muscular functions Plays an important role in arousal and attention ...
... It’s the most common neurotransmitter. It is located in both the central nervous and peripheral nervous system. It acts on basic autonomic and muscular functions Plays an important role in arousal and attention ...
session1vocabulary
... Is in the skull, and is part of the central nervous system. Controls most functions in the body. About 100bill. neurons. Has 12 pairs of nerves. Main command center like a captain. Spinal Cord Thick column of nerve tissue. Links the brain to most of the nerves in the peripheral nervous system. Like ...
... Is in the skull, and is part of the central nervous system. Controls most functions in the body. About 100bill. neurons. Has 12 pairs of nerves. Main command center like a captain. Spinal Cord Thick column of nerve tissue. Links the brain to most of the nerves in the peripheral nervous system. Like ...
The Brain
... contains ALL ascending and descending tracts – White matter only (myelinated axons) – All communication between brain and spinal cord passes through the Medulla Oblongata – Both pyramidal tracts cross over in the Medulla • Decussation of pyramids: one side of brain controls the other side of the bod ...
... contains ALL ascending and descending tracts – White matter only (myelinated axons) – All communication between brain and spinal cord passes through the Medulla Oblongata – Both pyramidal tracts cross over in the Medulla • Decussation of pyramids: one side of brain controls the other side of the bod ...
Nervous System - Berlin High School
... Cephalization = Brain evolution Cephalization = clustering of neurons in “brain” at front (anterior) end of bilaterally symmetrical animals where sense organs are associative neurons nerve cords ...
... Cephalization = Brain evolution Cephalization = clustering of neurons in “brain” at front (anterior) end of bilaterally symmetrical animals where sense organs are associative neurons nerve cords ...
Nervous System
... Cephalization = Brain evolution Cephalization = clustering of neurons in “brain” at front (anterior) end of bilaterally symmetrical animals where sense organs are associative neurons nerve cords ...
... Cephalization = Brain evolution Cephalization = clustering of neurons in “brain” at front (anterior) end of bilaterally symmetrical animals where sense organs are associative neurons nerve cords ...
C2 - The Biological Perspective
... Our Divided Brain Our brain is divided into two hemispheres. The left hemisphere processes reading, writing, speaking, mathematics, and comprehension skills. In the 1960s, it was termed as the dominant brain. ...
... Our Divided Brain Our brain is divided into two hemispheres. The left hemisphere processes reading, writing, speaking, mathematics, and comprehension skills. In the 1960s, it was termed as the dominant brain. ...
File
... with each other and with muscle and gland cells they can coordinate, regulate, and integrate many body functions. The nervous tissue includes neurological cells. These cells support and bind components of nervous tissue, carry on phagocytosis, and help support nutrients to neurons by connecting them ...
... with each other and with muscle and gland cells they can coordinate, regulate, and integrate many body functions. The nervous tissue includes neurological cells. These cells support and bind components of nervous tissue, carry on phagocytosis, and help support nutrients to neurons by connecting them ...
Brain, Cognition and Language
... memory abilities –, how they learn to judge or understand how other people preceive the world. What the mature adult brain is capable of and how these capabilities worsen with age is also being studied. The results are compared with those from behavioural research conducted on non-human primates. Th ...
... memory abilities –, how they learn to judge or understand how other people preceive the world. What the mature adult brain is capable of and how these capabilities worsen with age is also being studied. The results are compared with those from behavioural research conducted on non-human primates. Th ...
Bio 111 Lab 8: The Nervous System and the Senses
... liquid: at this point sound waves in air are transformed to fluid waves. The fluid waves pass through the spiral cochlea, which is lined with tiny hair cells. The hair cells move in the current (just like seaweed in waves), which excites neurons located at their bases. Nerve impulses travel from her ...
... liquid: at this point sound waves in air are transformed to fluid waves. The fluid waves pass through the spiral cochlea, which is lined with tiny hair cells. The hair cells move in the current (just like seaweed in waves), which excites neurons located at their bases. Nerve impulses travel from her ...
Unit VIII: Animal Structure and Function, Part II
... Excretory System Nitrogen-containing wastes • toxic by-products of protein and nucleic acid metabolism + ammonia - small and very toxic - no energy required - must be diluted + urea - 100,000 times less toxic - formed by combining CO2 and NH2 + uric acid - excreted in paste-like form - conserve eve ...
... Excretory System Nitrogen-containing wastes • toxic by-products of protein and nucleic acid metabolism + ammonia - small and very toxic - no energy required - must be diluted + urea - 100,000 times less toxic - formed by combining CO2 and NH2 + uric acid - excreted in paste-like form - conserve eve ...
Neuronal Development
... – When growth cone reaches its target • Vesicles are produced • Synapse forms ...
... – When growth cone reaches its target • Vesicles are produced • Synapse forms ...
Terminology and Diagnoses - Academy for Coaching Parents
... Specializes in higher levels of functioning that involve complex abilities of organization and regulation Sometimes called the new brain with functions to help govern personal and social behavior and inhibit impulsive or inappropriate behaviors that result in difficulties related to social interac ...
... Specializes in higher levels of functioning that involve complex abilities of organization and regulation Sometimes called the new brain with functions to help govern personal and social behavior and inhibit impulsive or inappropriate behaviors that result in difficulties related to social interac ...