Kellogg Chapter 1. Introduction (Neurological structures)
... Visual Neglect (cortical neglect) = visual information in the contralateral field is not noticed or attended (this phenomena also occurs with visual imagery - the Piazza in Milan) Blindsight = contralateral field shows visual neglect but still has an influence Amnesia - the loss of memory or memory ...
... Visual Neglect (cortical neglect) = visual information in the contralateral field is not noticed or attended (this phenomena also occurs with visual imagery - the Piazza in Milan) Blindsight = contralateral field shows visual neglect but still has an influence Amnesia - the loss of memory or memory ...
How Psychologists Study the Brain
... produces various images. No ionizing radiation is used in MRI. MRI cannot be done if the person has certain metal devices inside their body (such as a pacemaker, implanted port or pump). The magnetic force is so strong that it can damage or dislodge these devices. In most cases, MRI can be done on p ...
... produces various images. No ionizing radiation is used in MRI. MRI cannot be done if the person has certain metal devices inside their body (such as a pacemaker, implanted port or pump). The magnetic force is so strong that it can damage or dislodge these devices. In most cases, MRI can be done on p ...
Name: Date: ______ 1. The self-examination of
... 1. The self-examination of one's own emotional and mental processes is called: a) introspection. b) humanism. c) cognitive neuroscience. d) behaviorism. 2. Humanistic psychologists focused attention on the importance of people's: a) potential for healthy growth. b) unconscious thought processes. c) ...
... 1. The self-examination of one's own emotional and mental processes is called: a) introspection. b) humanism. c) cognitive neuroscience. d) behaviorism. 2. Humanistic psychologists focused attention on the importance of people's: a) potential for healthy growth. b) unconscious thought processes. c) ...
Nervous System - KidsHealth in the Classroom
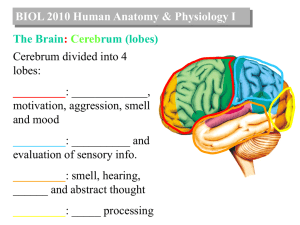
... cerebellum, balance or coordination brain stem, breathing or circulation or digestion hypothalamus, body temperature or appetite or sleep pituitary gland, growth or metabolism ...
... cerebellum, balance or coordination brain stem, breathing or circulation or digestion hypothalamus, body temperature or appetite or sleep pituitary gland, growth or metabolism ...
Advanced MRI Center (AMRIC)
... The Advanced MRI Center is a research core facility providing the latest ...
... The Advanced MRI Center is a research core facility providing the latest ...
The Nervous System
... • Aka the “little brain” • Responsible for coordination of motor functions • Also involved in language (although poorly understood) Brain Stem • Two parts: pons and medulla oblongata • Mediates flow between body and brain Medulla ...
... • Aka the “little brain” • Responsible for coordination of motor functions • Also involved in language (although poorly understood) Brain Stem • Two parts: pons and medulla oblongata • Mediates flow between body and brain Medulla ...
Notes-Brain and Memory
... Damage to both sides of the hippocampus can stop the ability to form new memories, known as anterograde amnesia ...
... Damage to both sides of the hippocampus can stop the ability to form new memories, known as anterograde amnesia ...
No Slide Title
... frontal and parietal lobes is ______ ________. Ridges on either side are ____ & _____ _____ ...
... frontal and parietal lobes is ______ ________. Ridges on either side are ____ & _____ _____ ...
Unit 3 Cerqueira guide
... interneurons) , PNS (autonomic + somatic). Autonomic is subdivided into sympathetic and parasympathetic (“fight or flight”). How reflexes work. The advantages of neural networks. How the endocrine systems differs from the nervous system (slow v. fast!) – “the distinction is no longer clear.” Hormone ...
... interneurons) , PNS (autonomic + somatic). Autonomic is subdivided into sympathetic and parasympathetic (“fight or flight”). How reflexes work. The advantages of neural networks. How the endocrine systems differs from the nervous system (slow v. fast!) – “the distinction is no longer clear.” Hormone ...
Barrier is Deficient in Human Brain Tumors Moore, Peyton, French
... In 45 years about 900,000 – 1,000,000 patients in the US In 1959 mortality was 10-30% - 90,000-300,000 deaths With steroids morality dropped to 3-10% - 27,000-100,000 deaths The effect upon morbidity can not be qualified but is substantial: XRT Between 60,000 and 200,000 lives saved in US Worldwide ...
... In 45 years about 900,000 – 1,000,000 patients in the US In 1959 mortality was 10-30% - 90,000-300,000 deaths With steroids morality dropped to 3-10% - 27,000-100,000 deaths The effect upon morbidity can not be qualified but is substantial: XRT Between 60,000 and 200,000 lives saved in US Worldwide ...
Functional neuroimaging
... PET radioisotopes emit a positron (a positively charged electron) in the process of decay. When this positron collides with an electron, the 2 particles annihilate each other, and produce 2 photons traveling in opposite directions. This induces electromagnetic radiation which is what can be detected ...
... PET radioisotopes emit a positron (a positively charged electron) in the process of decay. When this positron collides with an electron, the 2 particles annihilate each other, and produce 2 photons traveling in opposite directions. This induces electromagnetic radiation which is what can be detected ...
Chapter 12
... determines which of these signals to forward to the cerebral cortex Hypothalamus - regulates the pituitary gland, body T, food intake, emotion, sleep-wake cycle and memory; controls autonomic functions (heart rate, respiration, blood pressure) ...
... determines which of these signals to forward to the cerebral cortex Hypothalamus - regulates the pituitary gland, body T, food intake, emotion, sleep-wake cycle and memory; controls autonomic functions (heart rate, respiration, blood pressure) ...
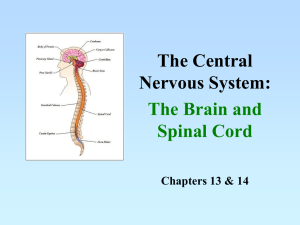
CNS: Spinal Cord Function
... • You will be provided with three diagrams of the brain. The image of the brain is a lateral view including the brain stem. On the other side you will see A) a posterio-lateral external view and B) a cross-section of a lateral view. • Identify, label and differentiate with color the lobes of the cer ...
... • You will be provided with three diagrams of the brain. The image of the brain is a lateral view including the brain stem. On the other side you will see A) a posterio-lateral external view and B) a cross-section of a lateral view. • Identify, label and differentiate with color the lobes of the cer ...
mapping the brain - Scholastic Heads Up
... We know this, and much more, from advancements in neuroscience—the study of the nervous system, including the brain. Neuroscientists use brainimaging tools—MRI, fMRI, and PET—to study the brain’s structures and functions. With these technologies, neuroscientists have ...
... We know this, and much more, from advancements in neuroscience—the study of the nervous system, including the brain. Neuroscientists use brainimaging tools—MRI, fMRI, and PET—to study the brain’s structures and functions. With these technologies, neuroscientists have ...
Central Nervous System
... “The Brain observatory at the University of California” • Jacopo Annese is looking for 1,000 brains. The director of the brain library is on a quest to collect, dissect, and digitize images of the human brain for the Digital Brain Library, which was launched with support from the National Science F ...
... “The Brain observatory at the University of California” • Jacopo Annese is looking for 1,000 brains. The director of the brain library is on a quest to collect, dissect, and digitize images of the human brain for the Digital Brain Library, which was launched with support from the National Science F ...
The Brain for Not-So
... The provided no nourishment, but was soft and warm Infants greatly preferred the “cloth mother” Retreated to the soft mother when anxious Were more outgoing, adventurous, able to meet new monkeys in presence of “cloth mother” Touch (e.g., “skin to skin”) now an important part of ...
... The provided no nourishment, but was soft and warm Infants greatly preferred the “cloth mother” Retreated to the soft mother when anxious Were more outgoing, adventurous, able to meet new monkeys in presence of “cloth mother” Touch (e.g., “skin to skin”) now an important part of ...
ElectroEncephaloGram (EEG) - MIT Biology
... amplifier reveals variation in voltage over time. MEG systems measure the magnetic fields emanating from the brain with a Superconducting QUantum Interference Device (SQUID) biomagnetometers. EEG and MEG can be used in clinical applications such as localization of epilepsy sources, psychiatry, to d ...
... amplifier reveals variation in voltage over time. MEG systems measure the magnetic fields emanating from the brain with a Superconducting QUantum Interference Device (SQUID) biomagnetometers. EEG and MEG can be used in clinical applications such as localization of epilepsy sources, psychiatry, to d ...
EEG - mitbrain
... amplifier reveals variation in voltage over time. MEG systems measure the magnetic fields emanating from the brain with a Superconducting QUantum Interference Device (SQUID) biomagnetometers. EEG and MEG can be used in clinical applications such as localization of epilepsy sources, psychiatry, to d ...
... amplifier reveals variation in voltage over time. MEG systems measure the magnetic fields emanating from the brain with a Superconducting QUantum Interference Device (SQUID) biomagnetometers. EEG and MEG can be used in clinical applications such as localization of epilepsy sources, psychiatry, to d ...
Chapter 03 - Jen Wright
... 16. What is the difference between an EEG, a CT scan, and an fMRI? How do these machines help us to better understand the brain? How do they help us to better understand the mind? GROUP Extra Credit – 2.5 pts: The limbic system includes both the hippocampus and the amygdala. What do you think the si ...
... 16. What is the difference between an EEG, a CT scan, and an fMRI? How do these machines help us to better understand the brain? How do they help us to better understand the mind? GROUP Extra Credit – 2.5 pts: The limbic system includes both the hippocampus and the amygdala. What do you think the si ...
Behavioural Neuroscience Lecture 2: History
... • Thought heart was a vase of the mind • Reflected religious/moral views • Limited study methods • Finds from chance discoveries • Controversial 2. Hippocrates (Greece, 450BC) • First to suggest that the brain is the center of the body (not heart, contrary to Aristotle) • Four bodily “humours” 3. G ...
... • Thought heart was a vase of the mind • Reflected religious/moral views • Limited study methods • Finds from chance discoveries • Controversial 2. Hippocrates (Greece, 450BC) • First to suggest that the brain is the center of the body (not heart, contrary to Aristotle) • Four bodily “humours” 3. G ...
Study Guide
... The individual nerve cell is called a neuron. Impulses going to a nerve cell travel along feelers called dendrites. Impulses leaving a nerve cell travel along feelers called axons. Involuntary responses are performed without our brain becoming involved. Voluntary responses are performed when you wan ...
... The individual nerve cell is called a neuron. Impulses going to a nerve cell travel along feelers called dendrites. Impulses leaving a nerve cell travel along feelers called axons. Involuntary responses are performed without our brain becoming involved. Voluntary responses are performed when you wan ...
brain09.3
... Although much progress has been made in understanding the brain in recent decades, scientists still know relatively little about how these processes function. The two key problems in making progress in this field are that there will never be enough real data in terms of measuring what the brain actu ...
... Although much progress has been made in understanding the brain in recent decades, scientists still know relatively little about how these processes function. The two key problems in making progress in this field are that there will never be enough real data in terms of measuring what the brain actu ...
Document
... Drowsiness is becoming a severe issue in case of traffic accident. Normally, Sleeping can be identified from several factors like eyeblink level, yawning ,gripping force on wheel and so on. But all these measuring techniques will check only the physical activities of the human. In some cases , peopl ...
... Drowsiness is becoming a severe issue in case of traffic accident. Normally, Sleeping can be identified from several factors like eyeblink level, yawning ,gripping force on wheel and so on. But all these measuring techniques will check only the physical activities of the human. In some cases , peopl ...
Quiz Chapter 3 Brain Neural Communication Dr Myer How do
... Quiz Chapter 3 Brain Neural Communication Dr Myer How do scientists learn about the inner workings of the human brain? Who is Phinneas Gage? How is what happened to him significant for neuroscience? You will need to know the structures and their functions of the brain as discussed in the video ...
... Quiz Chapter 3 Brain Neural Communication Dr Myer How do scientists learn about the inner workings of the human brain? Who is Phinneas Gage? How is what happened to him significant for neuroscience? You will need to know the structures and their functions of the brain as discussed in the video ...