Turkle (177) - units.miamioh.edu
... “One the one hand we insist that we are different from machines because we have emotions, bodies and an intellect that cannot be captured in rules, but on the other we play with computer programs that we think of as alive or almost alive. Images of machines have come ever closer to images of people, ...
... “One the one hand we insist that we are different from machines because we have emotions, bodies and an intellect that cannot be captured in rules, but on the other we play with computer programs that we think of as alive or almost alive. Images of machines have come ever closer to images of people, ...
Central nervous system (CNS)
... Brain: the mass of nerve tissue that is the main control center of the nervous system. Largest organ in the nervous system. Is responsible for voluntary and involuntary control. Has three main parts: ...
... Brain: the mass of nerve tissue that is the main control center of the nervous system. Largest organ in the nervous system. Is responsible for voluntary and involuntary control. Has three main parts: ...
Endocrine and nervous system - Glasgow Independent Schools
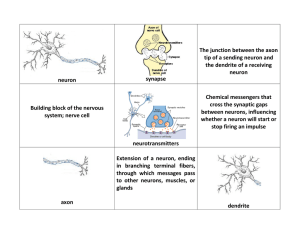
... 3. Axon: long projection that carries impulses away from cell body ...
... 3. Axon: long projection that carries impulses away from cell body ...
Cognitive Psychology
... When they die, study their brain for where the damaged tissue was. (Phineas Gage, Broca’s & Wernicke’s areas) • Human-lesion studies - These days, we can take pictures of the brain while it’s still in the skull (CAT, MRI) an determine where the lesions are while someone is still alive. (Prosopagnosi ...
... When they die, study their brain for where the damaged tissue was. (Phineas Gage, Broca’s & Wernicke’s areas) • Human-lesion studies - These days, we can take pictures of the brain while it’s still in the skull (CAT, MRI) an determine where the lesions are while someone is still alive. (Prosopagnosi ...
Magnetic-resonance-imaging
... technique providing rich information about the human soft tissue anatomy. It has several advantages over other imaging techniques enabling it to provide three-dimensional (3-D) data with high contrast between soft tissues. However, the amount of data is far too much for manual analysis/interpretatio ...
... technique providing rich information about the human soft tissue anatomy. It has several advantages over other imaging techniques enabling it to provide three-dimensional (3-D) data with high contrast between soft tissues. However, the amount of data is far too much for manual analysis/interpretatio ...
Nervous System
... Keeps the CNS constantly informed of events going on both inside and outside the body Nerve fibers convey impulses to the CNS from sensory receptors located in various parts of the body. Somatic sensory – delivers impulses from the skin, skeletal muscles, and joints. Visceral sensory – transmits imp ...
... Keeps the CNS constantly informed of events going on both inside and outside the body Nerve fibers convey impulses to the CNS from sensory receptors located in various parts of the body. Somatic sensory – delivers impulses from the skin, skeletal muscles, and joints. Visceral sensory – transmits imp ...
CNS Brain 241North
... • Balance; maintains muscle tone; coordinates fine muscle movement • Comparator: integrates proposed movements with current body position to produce smooth, exact movement • Involved in learning new balance-intensive activities – Riding a bike, yoga, climbing ...
... • Balance; maintains muscle tone; coordinates fine muscle movement • Comparator: integrates proposed movements with current body position to produce smooth, exact movement • Involved in learning new balance-intensive activities – Riding a bike, yoga, climbing ...
Functions of the Nervous System
... Types of Neurons Reflex- an involuntary response to a stimulus (change in environment) that allows the body to respond quickly without thinking about it ...
... Types of Neurons Reflex- an involuntary response to a stimulus (change in environment) that allows the body to respond quickly without thinking about it ...
The Nervous System
... Types of Neurons Reflex- an involuntary response to a stimulus (change in environment) that allows the body to respond quickly without thinking about it ...
... Types of Neurons Reflex- an involuntary response to a stimulus (change in environment) that allows the body to respond quickly without thinking about it ...
Nervous System
... Uses hormones that travel through the bloodstream. Takes longer to get there but lasts a long time ...
... Uses hormones that travel through the bloodstream. Takes longer to get there but lasts a long time ...
Chapter 2 Notes Packet (Part 1)
... o Like all cells, they are made up of: __________________: the complete set of chromosomes and genes Cytoplasm: keeps the cells alive Cell Membrane: encloses the whole cell o What makes them different? ________________: short fibers that branch out from the cell body and pick up incoming mes ...
... o Like all cells, they are made up of: __________________: the complete set of chromosomes and genes Cytoplasm: keeps the cells alive Cell Membrane: encloses the whole cell o What makes them different? ________________: short fibers that branch out from the cell body and pick up incoming mes ...
Georgetown MRI Reading Center (GMRC)
... planning radiation therapy based on the image data. From this experience was born his first publication in 1987 (meeting abstract that can be searched on the "Web of Science") was on manganese chloride's and nickel chloride's effect as contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging studied at variou ...
... planning radiation therapy based on the image data. From this experience was born his first publication in 1987 (meeting abstract that can be searched on the "Web of Science") was on manganese chloride's and nickel chloride's effect as contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging studied at variou ...
Biology 3201 - Corner Brook Regional High
... • Commonly used in Radiology to visualize the structure and function of the body. • provides detailed images of the body in any plane. • provides much greater contrast between different tissues of the body than does CT, making it especially useful in neurological (brain), ...
... • Commonly used in Radiology to visualize the structure and function of the body. • provides detailed images of the body in any plane. • provides much greater contrast between different tissues of the body than does CT, making it especially useful in neurological (brain), ...
Chapter 2: Neuroscience and Behavior
... communicate with the rest of the body, specifically the neuron Neurons are highly specialized cells that receive and transmit information from one part of the body to another They communicate information in electrical and chemical form Your entire brain has an estimated 100 billion neurons Glial Cel ...
... communicate with the rest of the body, specifically the neuron Neurons are highly specialized cells that receive and transmit information from one part of the body to another They communicate information in electrical and chemical form Your entire brain has an estimated 100 billion neurons Glial Cel ...
CE7427: Cognitive Neuroscience and Embedded Intelligence
... What is the structure, mechanism, function of … • specific gen or protein, like hemoglobin; • bacteria in our bodies; • specific neurotransmitters and neuromodulators; • cells in our body, like blood cells or astrocytes; • hairs in the inner ear, hairs in the retina; • nucleus accumbens, orbitofront ...
... What is the structure, mechanism, function of … • specific gen or protein, like hemoglobin; • bacteria in our bodies; • specific neurotransmitters and neuromodulators; • cells in our body, like blood cells or astrocytes; • hairs in the inner ear, hairs in the retina; • nucleus accumbens, orbitofront ...
PPT10Chapter10TheNervousSystem
... forms the outermost portion of the cerebrum. The gray matter of the cerebral cortex allows us to perform higher mental tasks such as learning, reasoning, language, and memory. The bulk of the cerebrum is composed of white matter located directly below the cortex. ...
... forms the outermost portion of the cerebrum. The gray matter of the cerebral cortex allows us to perform higher mental tasks such as learning, reasoning, language, and memory. The bulk of the cerebrum is composed of white matter located directly below the cortex. ...
bYTEBoss brain_notes
... • When the body gets dehydrated, a higher concentration of salt in the bloodstream causes the stress response and learning may be impaired. ...
... • When the body gets dehydrated, a higher concentration of salt in the bloodstream causes the stress response and learning may be impaired. ...
AChE inhibitor
... For further information on brain plasticity in old age and factors which may enhance this plasticity, see the below papers (full texts are available on the course website under “Relevant Articles”): • Merabet LB et al. What blindness can tell us about seeing again: merging neuroplasticity and neuro ...
... For further information on brain plasticity in old age and factors which may enhance this plasticity, see the below papers (full texts are available on the course website under “Relevant Articles”): • Merabet LB et al. What blindness can tell us about seeing again: merging neuroplasticity and neuro ...
neuron synapse The junction between the axon tip of a sending
... 2. Remove all the definition/description cards and place them to the side. With the picture cards try the following: Nervous System Organization: categorize the cards to mirror the how the parts of the nervous system and brain are organized Pick two: each person picks two cards and explains to t ...
... 2. Remove all the definition/description cards and place them to the side. With the picture cards try the following: Nervous System Organization: categorize the cards to mirror the how the parts of the nervous system and brain are organized Pick two: each person picks two cards and explains to t ...
Fly Fishing 101-
... Areas in the cerebral cortex that are not involved in primary motor or sensory functions; are involved in higher mental ...
... Areas in the cerebral cortex that are not involved in primary motor or sensory functions; are involved in higher mental ...
Michael J. Fisher, MD – Research Investment
... Michael J. Fisher, MD, is chief of the Section of Neuro-Oncology in the Cancer Center at The Children's Hospital of Philadelphia and director of the Neuro-Oncology Fellowship Program. He has a special interest in brain tumors and neurofibromatosis. After graduating from Harvard Medical School, he di ...
... Michael J. Fisher, MD, is chief of the Section of Neuro-Oncology in the Cancer Center at The Children's Hospital of Philadelphia and director of the Neuro-Oncology Fellowship Program. He has a special interest in brain tumors and neurofibromatosis. After graduating from Harvard Medical School, he di ...
What is Neuroscience?
... The brain is the most complex living structure in the universe. We each have 100,000,000,000 (ie. 100 billion) nerve cells in our brain. These are called ‘neurons’. They make 100 trillion connections (‘synapses’). ...
... The brain is the most complex living structure in the universe. We each have 100,000,000,000 (ie. 100 billion) nerve cells in our brain. These are called ‘neurons’. They make 100 trillion connections (‘synapses’). ...
Scientific American
... mental activities give rise to changing patterns of activity in different parts of the brain. This has been shown in neurophysiology through EEG, magneto-encephalogram (MEG) and at present also through magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and positron emission tomography (PET-scan). (9-11) Also an incre ...
... mental activities give rise to changing patterns of activity in different parts of the brain. This has been shown in neurophysiology through EEG, magneto-encephalogram (MEG) and at present also through magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and positron emission tomography (PET-scan). (9-11) Also an incre ...