Psych 9A. Lec. 07 PP Slides: Brain and Nervous System, Part 3
... Mike D’Zmura Department of Cognitive Sciences, UCI ...
... Mike D’Zmura Department of Cognitive Sciences, UCI ...
primary somatosensory cortex
... What are the major areas of the brain that are associated with the perception of touch? (continued) • The majority of thalamic neurons that receive touch information subsequently project the information to the primary somatosensory cortex (SI). Thereafter, information is projected to the secondary ...
... What are the major areas of the brain that are associated with the perception of touch? (continued) • The majority of thalamic neurons that receive touch information subsequently project the information to the primary somatosensory cortex (SI). Thereafter, information is projected to the secondary ...
IV. PSYCHOBIOLOGY
... carries messages between them. – If severed, demonstrates how both sides work together. ...
... carries messages between them. – If severed, demonstrates how both sides work together. ...
Brain Power Point
... concentration and attention Thinking about the information in the last slides, explain what happens in the brain with people who are depressed ...
... concentration and attention Thinking about the information in the last slides, explain what happens in the brain with people who are depressed ...
Slide ()
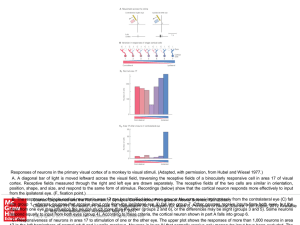
... Responses of neurons in the primary visual cortex of a monkey to visual stimuli. (Adapted, with permission, from Hubel and Wiesel 1977.) A. A diagonal bar of light is moved leftward across the visual field, traversing the receptive fields of a binocularly responsive cell in area 17 of visual cortex. ...
... Responses of neurons in the primary visual cortex of a monkey to visual stimuli. (Adapted, with permission, from Hubel and Wiesel 1977.) A. A diagonal bar of light is moved leftward across the visual field, traversing the receptive fields of a binocularly responsive cell in area 17 of visual cortex. ...
04/09 PPT
... -- Depth Perception for near objects (<100 ft). binocular disparity The difference between the images of an object on the two retinas due to the slightly different location of the two eyes relative to the viewed object (Look at one figure with alternative closing of the left and right eye). Cues for ...
... -- Depth Perception for near objects (<100 ft). binocular disparity The difference between the images of an object on the two retinas due to the slightly different location of the two eyes relative to the viewed object (Look at one figure with alternative closing of the left and right eye). Cues for ...
The Teenage Brain - Welcome to Senior Biology
... continues from back to front through early 20’s ...
... continues from back to front through early 20’s ...
Unit 03B
... can be identified by the text being underlined and a different color (usually purple). – Unit subsections hyperlinks: Immediately after the unit title slide, a page (slide #3) can be found listing all of the unit’s subsections. While in slide show mode, clicking on any of these hyperlinks will take ...
... can be identified by the text being underlined and a different color (usually purple). – Unit subsections hyperlinks: Immediately after the unit title slide, a page (slide #3) can be found listing all of the unit’s subsections. While in slide show mode, clicking on any of these hyperlinks will take ...
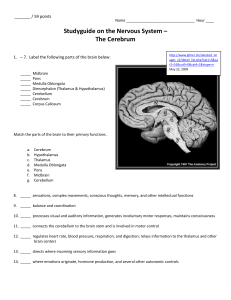
Major Parts of the Brain:
... 34. _____ Receives signals for hearing 35. _____ Interprets what you are hearing 36. _____ Receives visual signals 37. _____ Interprets what you are seeing 38. _____ Receives messages about taste 39. _____ Receives signals about scent 40. _____ Controls direct voluntary movements 41. _____ Coordinat ...
... 34. _____ Receives signals for hearing 35. _____ Interprets what you are hearing 36. _____ Receives visual signals 37. _____ Interprets what you are seeing 38. _____ Receives messages about taste 39. _____ Receives signals about scent 40. _____ Controls direct voluntary movements 41. _____ Coordinat ...
Eagleman Ch 5. Vision
... Most activity within the brain is produced on the inside and is only modified by sensory input. Patients who lose their vision hallucinate that they still see objects around them. ...
... Most activity within the brain is produced on the inside and is only modified by sensory input. Patients who lose their vision hallucinate that they still see objects around them. ...
module 6 The Cerebral Cortex and Our Divided Brain Module
... cortical space. In an effort to find the source of motor control, researchers have recorded messages from brain areas involved in planning and intention, leading to the testing of neural prosthetics for paralyzed patients. The sensory cortex, a region at the front of the parietal lobes, registers an ...
... cortical space. In an effort to find the source of motor control, researchers have recorded messages from brain areas involved in planning and intention, leading to the testing of neural prosthetics for paralyzed patients. The sensory cortex, a region at the front of the parietal lobes, registers an ...
UNIT 4: Sensation and Perception I. Overview A. Sensation
... Sensory analysis that starts at the entry level as “bottom-up processing” ...
... Sensory analysis that starts at the entry level as “bottom-up processing” ...
Quiz - psychm5
... Scott was challenged to catch a dollar bill as fast as he could with his thumb and index finger as it fell between the. Scott was successful one time out of five trials. Which statement best explains why Scott failed to catch the dollar bill? a. Scott’s injury to the temporal lobe has caused him to ...
... Scott was challenged to catch a dollar bill as fast as he could with his thumb and index finger as it fell between the. Scott was successful one time out of five trials. Which statement best explains why Scott failed to catch the dollar bill? a. Scott’s injury to the temporal lobe has caused him to ...
The gustatory pathway - West Virginia University
... The insular cortex projects to the orbitofrontal cortex Both cortices are part of the limbic system The limbic system is responsible for the behavioral and emotional significance of taste ...
... The insular cortex projects to the orbitofrontal cortex Both cortices are part of the limbic system The limbic system is responsible for the behavioral and emotional significance of taste ...
Brain Notes Most complex organ in the body It allows us to think
... b. wrinkles are called cortex i. where the majority of brain cells (neurons) are c. Job: i. speech ii. senses iii. emotional response iv. memory d. divided into several sections called lobes i. Frontal Lobe(white house): reasoning, problem solving, judgement, impulse control 1. last thing to develop ...
... b. wrinkles are called cortex i. where the majority of brain cells (neurons) are c. Job: i. speech ii. senses iii. emotional response iv. memory d. divided into several sections called lobes i. Frontal Lobe(white house): reasoning, problem solving, judgement, impulse control 1. last thing to develop ...
FIGURE LEGENDS FIGURE 26.1 Schematic diagram of the human
... (as in B) are taken with a CCD camera while the anesthetized, paralyzed animal is viewing a visual stimulus. These images are stored on a second computer for further analysis. (B) Individual image (9 by 6 mm) of a region of V1 and a portion of V2 taken with a special filter so that blood vessels sta ...
... (as in B) are taken with a CCD camera while the anesthetized, paralyzed animal is viewing a visual stimulus. These images are stored on a second computer for further analysis. (B) Individual image (9 by 6 mm) of a region of V1 and a portion of V2 taken with a special filter so that blood vessels sta ...
Biological and Psychology Why are psychologists concerned about
... Broca’s area (impaired speaking) or to Wernicke’s area (impaired understanding). Damage to the right brain often had an effect of stopping spatial recognition of faces and objects Right Hemisphere - Generally considered to be the hemisphere more adept at visual spatial abilities and at interpreting ...
... Broca’s area (impaired speaking) or to Wernicke’s area (impaired understanding). Damage to the right brain often had an effect of stopping spatial recognition of faces and objects Right Hemisphere - Generally considered to be the hemisphere more adept at visual spatial abilities and at interpreting ...
Document
... • the dorsal tract brings sensory information into the spinal cord and the ventral tract carries motor information from the spinal cord to the muscles, organs and glands. • the brain and spinal cord are protected by protective membrane, the meninges and surrounded by cerebrospinal fluid. The Brain • ...
... • the dorsal tract brings sensory information into the spinal cord and the ventral tract carries motor information from the spinal cord to the muscles, organs and glands. • the brain and spinal cord are protected by protective membrane, the meninges and surrounded by cerebrospinal fluid. The Brain • ...
CNS
... • the dorsal tract brings sensory information into the spinal cord and the ventral tract carries motor information from the spinal cord to the muscles, organs and glands. • the brain and spinal cord are protected by protective membrane, the meninges and surrounded by cerebrospinal fluid. The Brain • ...
... • the dorsal tract brings sensory information into the spinal cord and the ventral tract carries motor information from the spinal cord to the muscles, organs and glands. • the brain and spinal cord are protected by protective membrane, the meninges and surrounded by cerebrospinal fluid. The Brain • ...
Chapter 2
... The Cerebral Cortex 2.Parietal Lobe- sensory cortex • Sensory Cortex-registers and processes body sensations • Receives info from skin receptors • More sensitive= bigger area 3.Occipital Lobe- receives visual from opposite sides ...
... The Cerebral Cortex 2.Parietal Lobe- sensory cortex • Sensory Cortex-registers and processes body sensations • Receives info from skin receptors • More sensitive= bigger area 3.Occipital Lobe- receives visual from opposite sides ...
Neuroesthetics

Neuroesthetics (or neuroaesthetics) is a relatively recent sub-discipline of empirical aesthetics. Empirical aesthetics takes a scientific approach to the study of aesthetic perceptions of art and music. Neuroesthetics received its formal definition in 2002 as the scientific study of the neural bases for the contemplation and creation of a work of art. Neuroesthetics uses neuroscience to explain and understand the aesthetic experiences at the neurological level. The topic attracts scholars from many disciplines including neuroscientists, art historians, artists, and psychologists.