What is Psychology
... •Usually carries info towards the cell body from the dendrite •If there is a large enough amount of graded potentials being generated, an action potential is released ...
... •Usually carries info towards the cell body from the dendrite •If there is a large enough amount of graded potentials being generated, an action potential is released ...
Chapter 2 – Biology of the Mind
... fMRI (functional magnetic resonance imaging) brainstem medulla reticular formation thalamus cerebellum limbic system amygdala hypothalamus cerebral glial cells (glia) frontal lobes parietal lobes occipital lobes temporal lobes motor cortex sensory cortex association areas aphasia Broca’s area Wernic ...
... fMRI (functional magnetic resonance imaging) brainstem medulla reticular formation thalamus cerebellum limbic system amygdala hypothalamus cerebral glial cells (glia) frontal lobes parietal lobes occipital lobes temporal lobes motor cortex sensory cortex association areas aphasia Broca’s area Wernic ...
{ How Neurosciences help us to understand some (psycho)therapeutic processes
... Vital to cognitive functions, such as reward anticipation, decision-making, empathy, and emotion. ACC is involved in the processing of the affective dimension of pain responsible for rendering new memories permanent. ...
... Vital to cognitive functions, such as reward anticipation, decision-making, empathy, and emotion. ACC is involved in the processing of the affective dimension of pain responsible for rendering new memories permanent. ...
ALH 1002 Chapter 5 - Biosocial Development
... communicate with other neurons • This is followed by pruning where unused neurons and misconnected dendrites die ...
... communicate with other neurons • This is followed by pruning where unused neurons and misconnected dendrites die ...
Invitation to the Life Span by Kathleen Stassen Berger
... communicate with other neurons • This is followed by pruning where unused neurons and misconnected dendrites die ...
... communicate with other neurons • This is followed by pruning where unused neurons and misconnected dendrites die ...
Ch05LifespanPPT
... communicate with other neurons • This is followed by pruning where unused neurons and misconnected dendrites die ...
... communicate with other neurons • This is followed by pruning where unused neurons and misconnected dendrites die ...
Outline for cognitive neuroscience Chapter 1 Introduction to Method
... The complex cognitive task require the integrative activity of many component operations. Patient with specific brain lesion may lost the ability of one particular operation. Study dysfunctional behavior can help identify the component operations that underlie normal cognitive performance. Kee ...
... The complex cognitive task require the integrative activity of many component operations. Patient with specific brain lesion may lost the ability of one particular operation. Study dysfunctional behavior can help identify the component operations that underlie normal cognitive performance. Kee ...
The Triune Brain: Limbic Mind Mind Plastic, Emotional Mind
... human brain, the fact that he has inherited the structure and organization of three fundamental types of reptiles, ancient or primitive mammals and mammals, or recent evolved. What is very disconcerting is that nature has been able to connect with each other and establish a sort of communication bet ...
... human brain, the fact that he has inherited the structure and organization of three fundamental types of reptiles, ancient or primitive mammals and mammals, or recent evolved. What is very disconcerting is that nature has been able to connect with each other and establish a sort of communication bet ...
ppt - UTK-EECS
... When a neurotransmitter binds to a receptor on the postsynaptic side of the synapse, it results in a change of the postsynaptic cell's excitability: it makes the postsynaptic cell either more or less likely to fire an action potential. If the number of excitatory postsynaptic events are large enough ...
... When a neurotransmitter binds to a receptor on the postsynaptic side of the synapse, it results in a change of the postsynaptic cell's excitability: it makes the postsynaptic cell either more or less likely to fire an action potential. If the number of excitatory postsynaptic events are large enough ...
Document
... The major structures of the basal ganglia (red-shaded areas) include the caudate nucleus, the subthalamic nucleus, the substantia nigra, the globus pallidus, and the putamen. The critical connections (inputs and outputs) of the basal ganglia are illustrated. ...
... The major structures of the basal ganglia (red-shaded areas) include the caudate nucleus, the subthalamic nucleus, the substantia nigra, the globus pallidus, and the putamen. The critical connections (inputs and outputs) of the basal ganglia are illustrated. ...
General PLTW Document - Buncombe County Schools
... and hearing. Senses such as sight and smell are processed by the brain after signals are sent through specialized nerves such as the optic nerve. Alternately, sensory neurons in the skin send signals through the spinal cord in order for the brain to interpret sensations of touch, pain, heat, and col ...
... and hearing. Senses such as sight and smell are processed by the brain after signals are sent through specialized nerves such as the optic nerve. Alternately, sensory neurons in the skin send signals through the spinal cord in order for the brain to interpret sensations of touch, pain, heat, and col ...
The Brain.
... touch, and movement from the rest of the body – such as distance and position of objects. It is also responsible for reading and arithmetic. Injury to this area, or lack of accurate sensory information from the lower levels of the brain, create an inability to discriminate between different stimuli, ...
... touch, and movement from the rest of the body – such as distance and position of objects. It is also responsible for reading and arithmetic. Injury to this area, or lack of accurate sensory information from the lower levels of the brain, create an inability to discriminate between different stimuli, ...
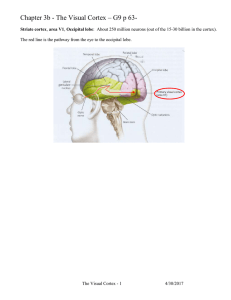
The Eye: III. Central Neurophysiology of Vision
... macula (region for highest visual acuity) ►layered structure like other cortical areas ►columnar organization as well ►receives the primary visual input ...
... macula (region for highest visual acuity) ►layered structure like other cortical areas ►columnar organization as well ►receives the primary visual input ...
Chapter Summary Visual Stimulus Light is part of the
... Neurons in V1 are arranged in columns. Neurons within each column respond best to a line of one particular orientation. Cells in an adjacent column have the highest response rate to a line whose orientation has shifted by only about 10°. A hypercolumn is a series of columns that covers a full cycle ...
... Neurons in V1 are arranged in columns. Neurons within each column respond best to a line of one particular orientation. Cells in an adjacent column have the highest response rate to a line whose orientation has shifted by only about 10°. A hypercolumn is a series of columns that covers a full cycle ...
Why light
... “Hand” neurons: Reseachers discovered neurons that responded to stimuli shaped like a hand “Face” neurons: Other researchers discovered neurons that responded to stimuli shaped like a face, or an actual face. What’s most interesting about these studies is that they were published in the late 1960s a ...
... “Hand” neurons: Reseachers discovered neurons that responded to stimuli shaped like a hand “Face” neurons: Other researchers discovered neurons that responded to stimuli shaped like a face, or an actual face. What’s most interesting about these studies is that they were published in the late 1960s a ...
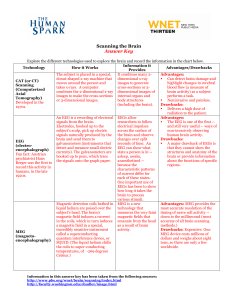
Scanning the Brain AK.rtf
... EEG can show what that they cannot show the encephalograph) currents). The galvanometers are state a person is in -structures and anatomy of the Fun fact: Austrian hooked up to pens, which trace asleep, awake, brain or provide information psychiatrist Hans the signals onto the graph paper. anaesthet ...
... EEG can show what that they cannot show the encephalograph) currents). The galvanometers are state a person is in -structures and anatomy of the Fun fact: Austrian hooked up to pens, which trace asleep, awake, brain or provide information psychiatrist Hans the signals onto the graph paper. anaesthet ...
node of action heroin
... Pete has been admitted to rehab clinics on a regular basis over the past 3 years. He has had drug dependency and addiction issues for around 5-6 years which has seriously jeopardized his health. Pete abuses heroin on a regular basis, mainly injecting the substance. However, he has failed to fully c ...
... Pete has been admitted to rehab clinics on a regular basis over the past 3 years. He has had drug dependency and addiction issues for around 5-6 years which has seriously jeopardized his health. Pete abuses heroin on a regular basis, mainly injecting the substance. However, he has failed to fully c ...
Drugs and Teen Brain_12
... Drugs affect 3 main areas of the brain: › 1. Brain stem (medulla oblongata) in charge of “4 B’s”: breathing, heart beat, body temp and blood pressure › 2. Limbic system (amygdala is in here) Links together brain structures that control emotions like pleasure and pain › 3. Prefrontal cortex Dec ...
... Drugs affect 3 main areas of the brain: › 1. Brain stem (medulla oblongata) in charge of “4 B’s”: breathing, heart beat, body temp and blood pressure › 2. Limbic system (amygdala is in here) Links together brain structures that control emotions like pleasure and pain › 3. Prefrontal cortex Dec ...
Chapter 02
... mental abilities. His theory, though incorrect, nevertheless proposed that different mental abilities were modular. ...
... mental abilities. His theory, though incorrect, nevertheless proposed that different mental abilities were modular. ...
AHISA PASTORAL CARE CONFERENCE, 2006
... • “Use it or lose it” vs “sensitive periods” when the brain is ready to respond to certain stimuli • Supreme importance of first three years of life vs plasticity of brain • Gendered brain vs non-gendered brain • Deak 2003/2004 and Hall 2005/2006 ...
... • “Use it or lose it” vs “sensitive periods” when the brain is ready to respond to certain stimuli • Supreme importance of first three years of life vs plasticity of brain • Gendered brain vs non-gendered brain • Deak 2003/2004 and Hall 2005/2006 ...
Development of the Brain
... Development of the Brain • The fluid-filled cavity becomes the central canal of the spinal cord and the four ventricles of the brain. ...
... Development of the Brain • The fluid-filled cavity becomes the central canal of the spinal cord and the four ventricles of the brain. ...
THE DOGMA OF AN AGING BRAIN
... IMPORTANT WARNING Please note that this PowerPoint Presentation contains animations. In order to view the content properly, an add-in function must be installed into the PowerPoint software. The add-in function is downloadable from the following hyperlink. Swiff Point Player ...
... IMPORTANT WARNING Please note that this PowerPoint Presentation contains animations. In order to view the content properly, an add-in function must be installed into the PowerPoint software. The add-in function is downloadable from the following hyperlink. Swiff Point Player ...
Central Nervous System PPT
... Synapse: The release of a chemical to allow an impulse to travel from one neuron to another neuron. ...
... Synapse: The release of a chemical to allow an impulse to travel from one neuron to another neuron. ...
Neuroesthetics

Neuroesthetics (or neuroaesthetics) is a relatively recent sub-discipline of empirical aesthetics. Empirical aesthetics takes a scientific approach to the study of aesthetic perceptions of art and music. Neuroesthetics received its formal definition in 2002 as the scientific study of the neural bases for the contemplation and creation of a work of art. Neuroesthetics uses neuroscience to explain and understand the aesthetic experiences at the neurological level. The topic attracts scholars from many disciplines including neuroscientists, art historians, artists, and psychologists.