Homework 5
... company and illegally used by competitors. You quickly scrolled through a new illustrated magazine published by your company. (you only viewed each illustration for a short period of time, less than a second). Later you scroll through a competitor’s magazine that have used some of your pictures that ...
... company and illegally used by competitors. You quickly scrolled through a new illustrated magazine published by your company. (you only viewed each illustration for a short period of time, less than a second). Later you scroll through a competitor’s magazine that have used some of your pictures that ...
The Brain - Morales Biology
... pleasure, pain, sex. Regulates water balance, body temperature, and metabolism. Regulates pituitary gland (growth hormones, oxytocin, antidiuretic hormone), thyroid stimulating hormones ...
... pleasure, pain, sex. Regulates water balance, body temperature, and metabolism. Regulates pituitary gland (growth hormones, oxytocin, antidiuretic hormone), thyroid stimulating hormones ...
Psychology Chapter 3
... -If we think of the nervous system as long “chains” of communicating cells, then neurons are the links. -Neurons come in many different shapes and sizes, but the most consist of four basic parts. ...
... -If we think of the nervous system as long “chains” of communicating cells, then neurons are the links. -Neurons come in many different shapes and sizes, but the most consist of four basic parts. ...
Chapter 31.2: Parts of the brain
... processing and relaying information – Most of the neurons that enter and leave the brain do so in a large cluster of neurons and other cells known as the spinal cord. • The spinal cord is the main communication link between the brain and the rest of the body • Certain kinds of information, including ...
... processing and relaying information – Most of the neurons that enter and leave the brain do so in a large cluster of neurons and other cells known as the spinal cord. • The spinal cord is the main communication link between the brain and the rest of the body • Certain kinds of information, including ...
Allison Bynum Neurobiology A.1 – A.3 Allison Bynum A.1 Neural
... A.2 – The anterior part of the neural tube expands to form the brain. Nerve cells migrate to the outer edge of the neural tube and cause the walls to thicken. The neural tube develops into the brain and spinal cord. The anterior end of the tube expands to form the cerebral hemispheres of the br ...
... A.2 – The anterior part of the neural tube expands to form the brain. Nerve cells migrate to the outer edge of the neural tube and cause the walls to thicken. The neural tube develops into the brain and spinal cord. The anterior end of the tube expands to form the cerebral hemispheres of the br ...
Study Guide 1
... 17. What is a neurotransmitter? Which neurotransmitters are excitatory and which are inhibitory? 18. What is depolarization? What is hyperpolarization? 19. Under what conditions does neurotransmitter release cause an action potential? 20. Define spatial summation and temporal summation. 21. Define c ...
... 17. What is a neurotransmitter? Which neurotransmitters are excitatory and which are inhibitory? 18. What is depolarization? What is hyperpolarization? 19. Under what conditions does neurotransmitter release cause an action potential? 20. Define spatial summation and temporal summation. 21. Define c ...
Biology & Behavior
... a lover even…in other words, the relationship of running. “WHAT!?” many of you will be saying. “I thought that I was going to learn how to improve my 10k time.” GO read Runner’s World for that. You see, I don’t view running as what I DO or who I AM, but as this thing, this force, that changes me ove ...
... a lover even…in other words, the relationship of running. “WHAT!?” many of you will be saying. “I thought that I was going to learn how to improve my 10k time.” GO read Runner’s World for that. You see, I don’t view running as what I DO or who I AM, but as this thing, this force, that changes me ove ...
File
... on a wide range of bodily functions and also impact emotions. When they act on the brain, they influence our interest in sex, food, and aggression. A special type of hormone called ...
... on a wide range of bodily functions and also impact emotions. When they act on the brain, they influence our interest in sex, food, and aggression. A special type of hormone called ...
Nervous System
... • Beta-amyloid plaques form between neurons in the brain. • Neurofibrillary tangles form inside neurons, causing their destruction. ...
... • Beta-amyloid plaques form between neurons in the brain. • Neurofibrillary tangles form inside neurons, causing their destruction. ...
Chapter 7: the Nervous System
... • The blood-brain barrier refers to the fact that capillaries in the brain are less permeable than those in other parts of the body; this helps protect your brain from damage due to chemicals in your ...
... • The blood-brain barrier refers to the fact that capillaries in the brain are less permeable than those in other parts of the body; this helps protect your brain from damage due to chemicals in your ...
The Nervous System
... i. _____________: fluid filled structure like a snail’s shell that vibrates from the stirrup’s vibrations causing nerve endings to send impulses to the brain via the ________________________ nerve ii. high-pitch sounds make the nerve endings move differently than lowpitched sounds iii. balance is al ...
... i. _____________: fluid filled structure like a snail’s shell that vibrates from the stirrup’s vibrations causing nerve endings to send impulses to the brain via the ________________________ nerve ii. high-pitch sounds make the nerve endings move differently than lowpitched sounds iii. balance is al ...
Basic Neuroscience Series: Introduction and Series Overview
... From: http://neuroscience.uth.tmc.edu/toc.htm ...
... From: http://neuroscience.uth.tmc.edu/toc.htm ...
Neurons in the Brain
... early preference for faces, symmetry, patterns, vertical orientation; by 3 mos. they prefer FACES over similar complex figures ...
... early preference for faces, symmetry, patterns, vertical orientation; by 3 mos. they prefer FACES over similar complex figures ...
SV3 Neuroscience n Behavior Oct 5 09
... Define cerebral cortex, and explain its importance for the human brain Identify the four lobes of the cerebral cortex Summarize some of the findings on the functions of the motor cortex and the sensory cortex, and discuss the importance of the association areas Describe the five brain areas that wou ...
... Define cerebral cortex, and explain its importance for the human brain Identify the four lobes of the cerebral cortex Summarize some of the findings on the functions of the motor cortex and the sensory cortex, and discuss the importance of the association areas Describe the five brain areas that wou ...
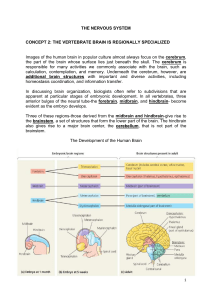
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM CONCEPT 2: THE VERTEBRATE BRAIN
... generating and experiencing emotion. For example, emotions that manifest themselves in behaviors such as laughing and crying involve an interaction of parts of the limbic system with sensory areas of the cerebrum. Structures in the forebrain also attach emotional "feelings" to basic, survivalrelated ...
... generating and experiencing emotion. For example, emotions that manifest themselves in behaviors such as laughing and crying involve an interaction of parts of the limbic system with sensory areas of the cerebrum. Structures in the forebrain also attach emotional "feelings" to basic, survivalrelated ...
Chemical Transmission BETWEEN Neurons
... The brain is both specialized and integrated. The nervous system is “plastic” especially at early ages of development. ...
... The brain is both specialized and integrated. The nervous system is “plastic” especially at early ages of development. ...
Exam - UBC Psychology`s Research Labs
... 3. I will hold additional office hours in preparation for the final exam: Tuesday, December 6: 10:30 - 12:30 Wednesday, December 7: 12:30-2:30 ...
... 3. I will hold additional office hours in preparation for the final exam: Tuesday, December 6: 10:30 - 12:30 Wednesday, December 7: 12:30-2:30 ...
Chapter 48 p. 1040-1053
... long-term depression (LTD): postsynaptic cell’s decreased responsiveness to action potential long-term potentiation(LTP): enhanced responsiveness to action potentials; associated with release of neurotransmitter glutamate (binds with receptors to open gated channels that let in a lot of calcium, ...
... long-term depression (LTD): postsynaptic cell’s decreased responsiveness to action potential long-term potentiation(LTP): enhanced responsiveness to action potentials; associated with release of neurotransmitter glutamate (binds with receptors to open gated channels that let in a lot of calcium, ...
Neuroscience and Behavior
... caused by left hemisphere damage either to Broca’s area (impaired speaking) or to Wernicke’s area (impaired understanding). ...
... caused by left hemisphere damage either to Broca’s area (impaired speaking) or to Wernicke’s area (impaired understanding). ...
Gene Mutation Story
... cells scream in terror. “HAH! We are here to infect this brain of the most common form of dementia, Alzheimer’s” says the Alzheimer’s cells. The Alzheimer’s cells start to infect the brain section, by section slowly taking over the 3 main parts of the brain: The Frontal Lobe, Temporal Lobe, and Pari ...
... cells scream in terror. “HAH! We are here to infect this brain of the most common form of dementia, Alzheimer’s” says the Alzheimer’s cells. The Alzheimer’s cells start to infect the brain section, by section slowly taking over the 3 main parts of the brain: The Frontal Lobe, Temporal Lobe, and Pari ...
4/7
... Is there an evolutionary explanation? Were/are individuals that dream better at passing on genes? ...
... Is there an evolutionary explanation? Were/are individuals that dream better at passing on genes? ...
File
... 1. Which word would the split-brain patient verbalize seeing? Why? 2. Which word, when asked to point with his left hand, would he report seeing? Why? ...
... 1. Which word would the split-brain patient verbalize seeing? Why? 2. Which word, when asked to point with his left hand, would he report seeing? Why? ...
Copy Notes
... that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce computer-generated images of soft tissue; they show brain anatomy fMRI (functional MRI): a technique for revealing ...
... that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce computer-generated images of soft tissue; they show brain anatomy fMRI (functional MRI): a technique for revealing ...