melanin in the body
... There are billions of neuron cells found in the brain that conduct electrical impulses. Neurons are connected to each other making an immense and complex neural network. Each neuron receives thousands of electrical inputs from one another. Impulses arriving at the same time are added together to mak ...
... There are billions of neuron cells found in the brain that conduct electrical impulses. Neurons are connected to each other making an immense and complex neural network. Each neuron receives thousands of electrical inputs from one another. Impulses arriving at the same time are added together to mak ...
BSCI338N, Spring 2013, Dr. Singer
... in medulla for crossing in pyramidal decussation (lateral CT) or in ventral column (anterior CT) LCT: dorsal column & lateral intermediate zone/lateral motor nuclei (LIZ/LMN) (dorsal grey matter) → full cord, movement of contralateral limbs ACT: ventral column & medial intermediate zone/medial motor ...
... in medulla for crossing in pyramidal decussation (lateral CT) or in ventral column (anterior CT) LCT: dorsal column & lateral intermediate zone/lateral motor nuclei (LIZ/LMN) (dorsal grey matter) → full cord, movement of contralateral limbs ACT: ventral column & medial intermediate zone/medial motor ...
The Anterior Cingulate Cortex - John Allman
... of vertebrate brain evolution that he termed “the triune brain.”4 Central to his concept is the idea that the mammalian brain evolved in a series of concentric shells around an ancient reptilean core. The innermost of these shells he termed “paleomammalian,” and it included the cingulate cortex. He ...
... of vertebrate brain evolution that he termed “the triune brain.”4 Central to his concept is the idea that the mammalian brain evolved in a series of concentric shells around an ancient reptilean core. The innermost of these shells he termed “paleomammalian,” and it included the cingulate cortex. He ...
Localization of Cognitive Operations
... performance are strictly localized. This idea fits generally with many network theories in neuroscience and cognition. However, most neuroscience network theories of higher processes (4) provide little information on the specific computations performed at the nodes of the network, and most cognitive ...
... performance are strictly localized. This idea fits generally with many network theories in neuroscience and cognition. However, most neuroscience network theories of higher processes (4) provide little information on the specific computations performed at the nodes of the network, and most cognitive ...
The role of ventral premotor cortex in action execution and action
... and 45, occupying the opercular and triangular parts of the inferior frontal gyrus, form the Broca’s region (Broca, 1864; Amunts et al., 1999). Brodmann’s areas 44 and 6 share a common basic cytoarchitectonic structure, the main characteristics of which are the poverty (BA 44) or lack (BA 6) of gran ...
... and 45, occupying the opercular and triangular parts of the inferior frontal gyrus, form the Broca’s region (Broca, 1864; Amunts et al., 1999). Brodmann’s areas 44 and 6 share a common basic cytoarchitectonic structure, the main characteristics of which are the poverty (BA 44) or lack (BA 6) of gran ...
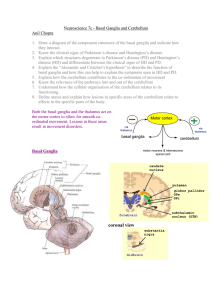
Neuroscience 7c – Basal Ganglia and Cerebellum
... Pars compacta of substantia nigra stimulates striatum Striatum inhibit external globus pallidus, internal globus pallidus and pars reticular of the substantia nigra DIRECTLY. Striatum also inhibit internal globus pallidus INDIRECTLY via the external globus pallidus subthalamic nucleus inte ...
... Pars compacta of substantia nigra stimulates striatum Striatum inhibit external globus pallidus, internal globus pallidus and pars reticular of the substantia nigra DIRECTLY. Striatum also inhibit internal globus pallidus INDIRECTLY via the external globus pallidus subthalamic nucleus inte ...
2-Motor System2009-03-20 18:254.4 MB
... Reticulospinal Tract The reticular formation makes up a central core through much of the brainstem. It contains many different nuclear groups. Pontine and medullary nuclei projects to the anterior horn of the spinal cord. Functions: influence motor functions as for example voluntary & reflex moveme ...
... Reticulospinal Tract The reticular formation makes up a central core through much of the brainstem. It contains many different nuclear groups. Pontine and medullary nuclei projects to the anterior horn of the spinal cord. Functions: influence motor functions as for example voluntary & reflex moveme ...
Yoga Therapy for Neurological disorders
... 1. Physical well being: improve mobility Passive sukshma vyayama Simple asanas in sitting (with props) ...
... 1. Physical well being: improve mobility Passive sukshma vyayama Simple asanas in sitting (with props) ...
PDF only
... Despite the intensive research in this area, the physiological and pathological functions of COX isoforms in the brain are not completely understood, mainly due to the complexity of the system, involving multiple pathways that produce several prostanoids from diverse cell types. In addition, the exi ...
... Despite the intensive research in this area, the physiological and pathological functions of COX isoforms in the brain are not completely understood, mainly due to the complexity of the system, involving multiple pathways that produce several prostanoids from diverse cell types. In addition, the exi ...
A non-invasive method to relate the timing of neural activity to white
... for the resampling. Inter-subject registration of individual FA maps to the Montreal Neurological Institute (MNI305) atlas (Collins et al., 1994) was performed using the average of the two 3D structural images. The resulting transformation was applied to individual FA volumes. The MNI-normalized FA ...
... for the resampling. Inter-subject registration of individual FA maps to the Montreal Neurological Institute (MNI305) atlas (Collins et al., 1994) was performed using the average of the two 3D structural images. The resulting transformation was applied to individual FA volumes. The MNI-normalized FA ...
the manuscript as pdf
... 5. Role of paramedian thalamic nuclei in forebrain integration and arousal Though originally considered to form the core of forebrain arousal systems along with the thalamic reticular nucleus and the tegmental mesencephalon (Moruzzi and Magoun, 1949) the thalamic intralaminar nuclei (ILN) are no lon ...
... 5. Role of paramedian thalamic nuclei in forebrain integration and arousal Though originally considered to form the core of forebrain arousal systems along with the thalamic reticular nucleus and the tegmental mesencephalon (Moruzzi and Magoun, 1949) the thalamic intralaminar nuclei (ILN) are no lon ...
PSYC 2301 Chapter 2
... 1. ________ carry information from the central nervous system to activate various parts of the body, such as muscles and glands. a. Interneurons ...
... 1. ________ carry information from the central nervous system to activate various parts of the body, such as muscles and glands. a. Interneurons ...
Hypothesized neural dynamics of working memory
... scales (e.g., [36]). For example, electroencephalogram (EEG) activity may play causal roles, in some of its manifestations, even if it is epiphenomenal in others. Graded potentials and currents are more ubiquitous aspects of neural physiology than are the action potentials that they sometimes genera ...
... scales (e.g., [36]). For example, electroencephalogram (EEG) activity may play causal roles, in some of its manifestations, even if it is epiphenomenal in others. Graded potentials and currents are more ubiquitous aspects of neural physiology than are the action potentials that they sometimes genera ...
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 5 The Central Nervous
... reveals that the outer cortex is composed of gray matter (cell bodies of neurons), with many folds and sulci (shallow grooves). More centrally located is the white matter (myelinated processes of neurons). (3) Function. The cerebellum is the primary coordinator/integrator of motor actions of the bod ...
... reveals that the outer cortex is composed of gray matter (cell bodies of neurons), with many folds and sulci (shallow grooves). More centrally located is the white matter (myelinated processes of neurons). (3) Function. The cerebellum is the primary coordinator/integrator of motor actions of the bod ...
Kandel and Schwartz, 4th Edition Principles of Neural Science Chap
... one or another kind of stimulus and encode information about the stimulus, such as its location and intensity. The receptors in turn excite sensory neurons that form connections with discrete sets of neurons in the spinal cord. The information from each receptor is then analyzed in the brain stem, ...
... one or another kind of stimulus and encode information about the stimulus, such as its location and intensity. The receptors in turn excite sensory neurons that form connections with discrete sets of neurons in the spinal cord. The information from each receptor is then analyzed in the brain stem, ...
Anatomy Written Exam #2 Cranial Nerves Introduction Embryological
... 1. Transmit general and special sensory information to regions of sensory cortices 2. Receive impulses from cerebellum and basal ganglia and interface with motor regions of frontal lobe 3. Have connections with associative and limbic areas of cortex o Forms dorsal part of third ventricle 2. Hypothal ...
... 1. Transmit general and special sensory information to regions of sensory cortices 2. Receive impulses from cerebellum and basal ganglia and interface with motor regions of frontal lobe 3. Have connections with associative and limbic areas of cortex o Forms dorsal part of third ventricle 2. Hypothal ...
Single nucleotide polymorphism in the neuroplastin locus
... harvard.edu/) and the entire cortex of each individual was inspected for inaccuracies. Individuals with major malformations of the cerebral cortex were excluded from further analysis. Out of 1909 images, 1584 passed these quality control checks. In addition to global mean thickness of the left and r ...
... harvard.edu/) and the entire cortex of each individual was inspected for inaccuracies. Individuals with major malformations of the cerebral cortex were excluded from further analysis. Out of 1909 images, 1584 passed these quality control checks. In addition to global mean thickness of the left and r ...
Cortical Functions Reference
... human brain. It is situated immediately posterior to the primary somatosensory areas (Brodmann areas 3, 1, and 2), and anterior to Brodmann area 7. Clinical significance Lesions in the left superior parietal lobe are associated with ideomotor apraxia (loss of the ability to produce purposeful, skill ...
... human brain. It is situated immediately posterior to the primary somatosensory areas (Brodmann areas 3, 1, and 2), and anterior to Brodmann area 7. Clinical significance Lesions in the left superior parietal lobe are associated with ideomotor apraxia (loss of the ability to produce purposeful, skill ...
DEVELOPMENT OF VESSELS IN THE FOETAL CORTICAL
... consist. of large vessels chaotically dispersed. Frequent large marginal vessels develop on the periphery, surrounding the transplant and giving numerous branchings or linking it with the surrounding tissue. ...
... consist. of large vessels chaotically dispersed. Frequent large marginal vessels develop on the periphery, surrounding the transplant and giving numerous branchings or linking it with the surrounding tissue. ...
view
... Neurolinguistic research has been engaged in evaluating models of language using measures from brain structure and function, and/or in investigating brain structure and function with respect to language representation using proposed models of language. While the aphasiological strategy, which classi ...
... Neurolinguistic research has been engaged in evaluating models of language using measures from brain structure and function, and/or in investigating brain structure and function with respect to language representation using proposed models of language. While the aphasiological strategy, which classi ...
The Motor System of the Cortex and the Brain Stem
... Importantly, after the go signal was given, the discharge remained the same as it was during the delay period. This second observation suggests that the information that whatever the cell was coding during the delay period was the same as after the go signal. It seems likely that this information wa ...
... Importantly, after the go signal was given, the discharge remained the same as it was during the delay period. This second observation suggests that the information that whatever the cell was coding during the delay period was the same as after the go signal. It seems likely that this information wa ...
Human brain
The human brain is the main organ of the human nervous system. It is located in the head, protected by the skull. It has the same general structure as the brains of other mammals, but with a more developed cerebral cortex. Large animals such as whales and elephants have larger brains in absolute terms, but when measured using a measure of relative brain size, which compensates for body size, the quotient for the human brain is almost twice as large as that of a bottlenose dolphin, and three times as large as that of a chimpanzee. Much of the size of the human brain comes from the cerebral cortex, especially the frontal lobes, which are associated with executive functions such as self-control, planning, reasoning, and abstract thought. The area of the cerebral cortex devoted to vision, the visual cortex, is also greatly enlarged in humans compared to other animals.The human cerebral cortex is a thick layer of neural tissue that covers most of the brain. This layer is folded in a way that increases the amount of surface that can fit into the volume available. The pattern of folds is similar across individuals, although there are many small variations. The cortex is divided into four lobes – the frontal lobe, parietal lobe, temporal lobe, and occipital lobe. (Some classification systems also include a limbic lobe and treat the insular cortex as a lobe.) Within each lobe are numerous cortical areas, each associated with a particular function, including vision, motor control, and language. The left and right sides of the cortex are broadly similar in shape, and most cortical areas are replicated on both sides. Some areas, though, show strong lateralization, particularly areas that are involved in language. In most people, the left hemisphere is dominant for language, with the right hemisphere playing only a minor role. There are other functions, such as visual-spatial ability, for which the right hemisphere is usually dominant.Despite being protected by the thick bones of the skull, suspended in cerebrospinal fluid, and isolated from the bloodstream by the blood–brain barrier, the human brain is susceptible to damage and disease. The most common forms of physical damage are closed head injuries such as a blow to the head, a stroke, or poisoning by a variety of chemicals which can act as neurotoxins, such as ethanol alcohol. Infection of the brain, though serious, is rare because of the biological barriers which protect it. The human brain is also susceptible to degenerative disorders, such as Parkinson's disease, and Alzheimer's disease, (mostly as the result of aging) and multiple sclerosis. A number of psychiatric conditions, such as schizophrenia and clinical depression, are thought to be associated with brain dysfunctions, although the nature of these is not well understood. The brain can also be the site of brain tumors and these can be benign or malignant.There are some techniques for studying the brain that are used in other animals that are just not suitable for use in humans and vice versa. It is easier to obtain individual brain cells taken from other animals, for study. It is also possible to use invasive techniques in other animals such as inserting electrodes into the brain or disabling certains parts of the brain in order to examine the effects on behaviour – techniques that are not possible to be used in humans. However, only humans can respond to complex verbal instructions or be of use in the study of important brain functions such as language and other complex cognitive tasks, but studies from humans and from other animals, can be of mutual help. Medical imaging technologies such as functional neuroimaging and EEG recordings are important techniques in studying the brain. The complete functional understanding of the human brain is an ongoing challenge for neuroscience.